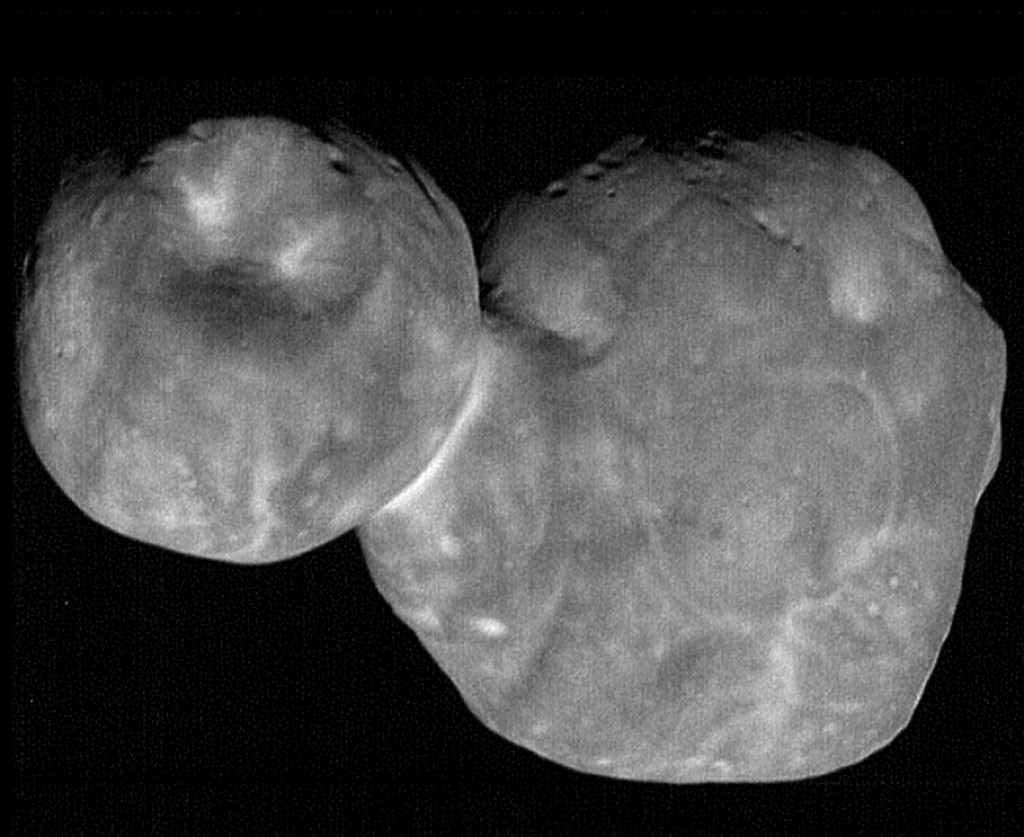
Calcédoine aux mille couleurs
On qualifie d'agates les calcédoines présentant plusieurs couleurs. Ces colorations peuvent se présenter en zones parallèles, concentriques ou se répartir dans la masse de façon irrégulière. À noter ici la finesse des lignes colorées et les tubes d'échappement de gaz dans cette agate du Brésil.
Bruno Cupillard