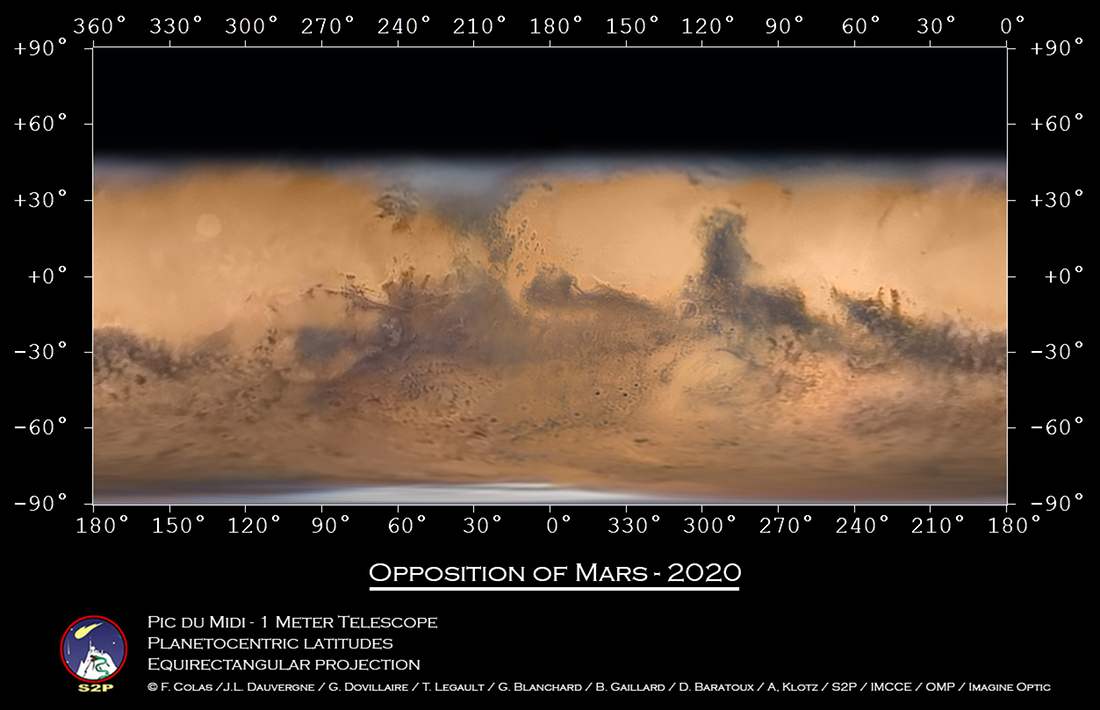
2020 November 30
Image Credit & Copyright: Bowen James Cameron
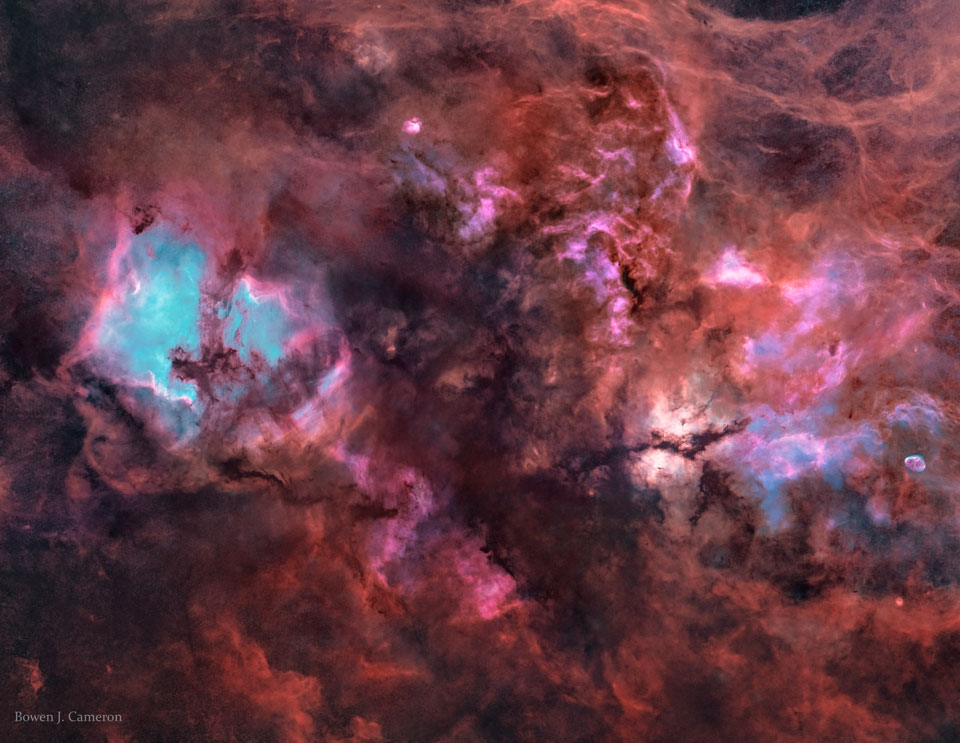
Explanation: The sky is filled with faintly glowing gas, though it can take a sensitive camera and telescope to see it. For example, this twelve-degree-wide view of the northern part of the constellation Cygnus reveals a complex array of cosmic clouds of gas along the plane of our Milky Way galaxy. The featured mosaic of telescopic images was recorded through two filters: an H-alpha filter that transmits only visible red light from glowing hydrogen atoms, and a blue filter that transmits primarily light emitted by the slight amount of energized oxygen. Therefore, in this 18-hour exposure image, blue areas are hotter than red. Further digital processing has removed the myriad of point-like Milky Way stars from the scene. Recognizable bright nebulas include NGC 7000 (North America Nebula), and IC 5070 (Pelican Nebula) on the left with IC 1318 (Butterfly Nebula) and NGC 6888 (Crescent Nebula) on the right -- but others can be found throughout the wide field.