2021 September 30
Image Credit & Copyright: Luca Fornaciari
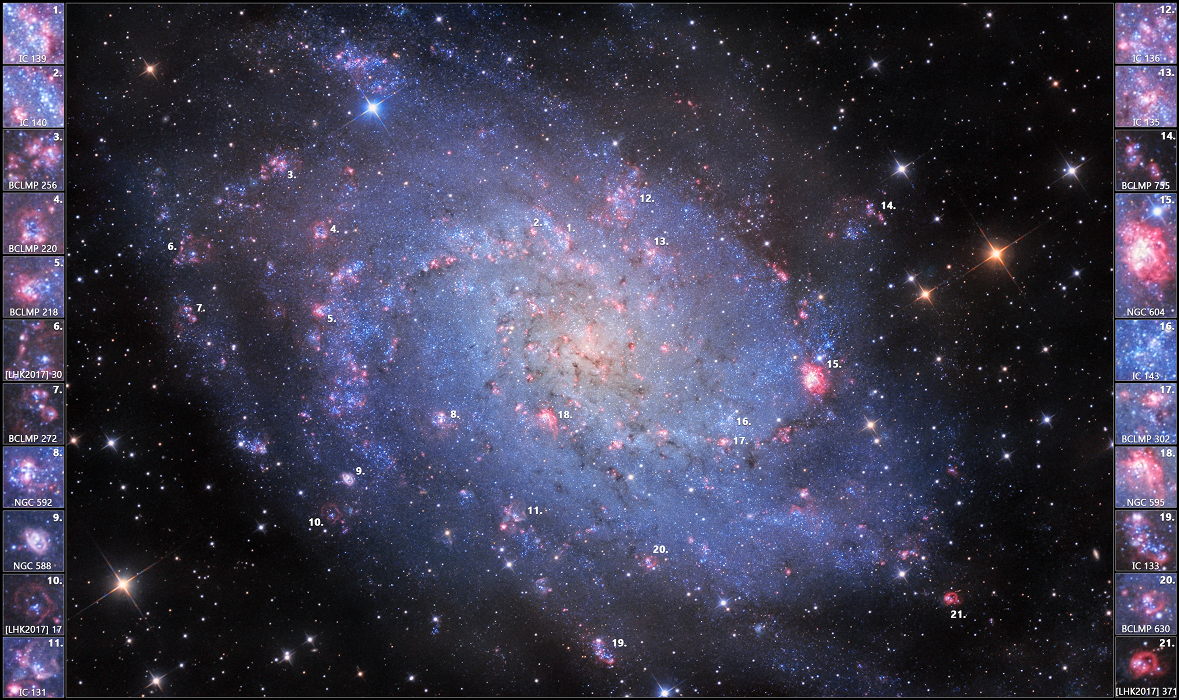
Explanation: Gorgeous spiral galaxy M33 seems to have more than its fair share of glowing hydrogen gas. A prominent member of the local group of galaxies, M33 is also known as the Triangulum Galaxy and lies a mere 3 million light-years away. Sprawling along loose spiral arms that wind toward the core, M33's giant HII regions are some of the largest known stellar nurseries, sites of the formation of short-lived but very massive stars. Intense ultraviolet radiation from the luminous massive stars ionizes the surrounding hydrogen gas and ultimately produces the characteristic red glow. To highlight the HII regions in this telescopic image, broadband data used to produce a color view of the galaxy were combined with narrowband data recorded through a hydrogen-alpha filter, transmitting the light of the strongest hydrogen emission line. Close-ups of cataloged HII regions appear in the sidebar insets. Use the individual reference number to find their location within the Triangulum Galaxy. For example, giant HII region NGC604 is identified in an inset on the right and appears at position number 15. That's about 4 o'clock from galaxy center in this portrait of M33.