Nombre total de pages vues
30/06/2022
MERVEILLEUX MONDE SOUS-MARIN - La flabelline blanche
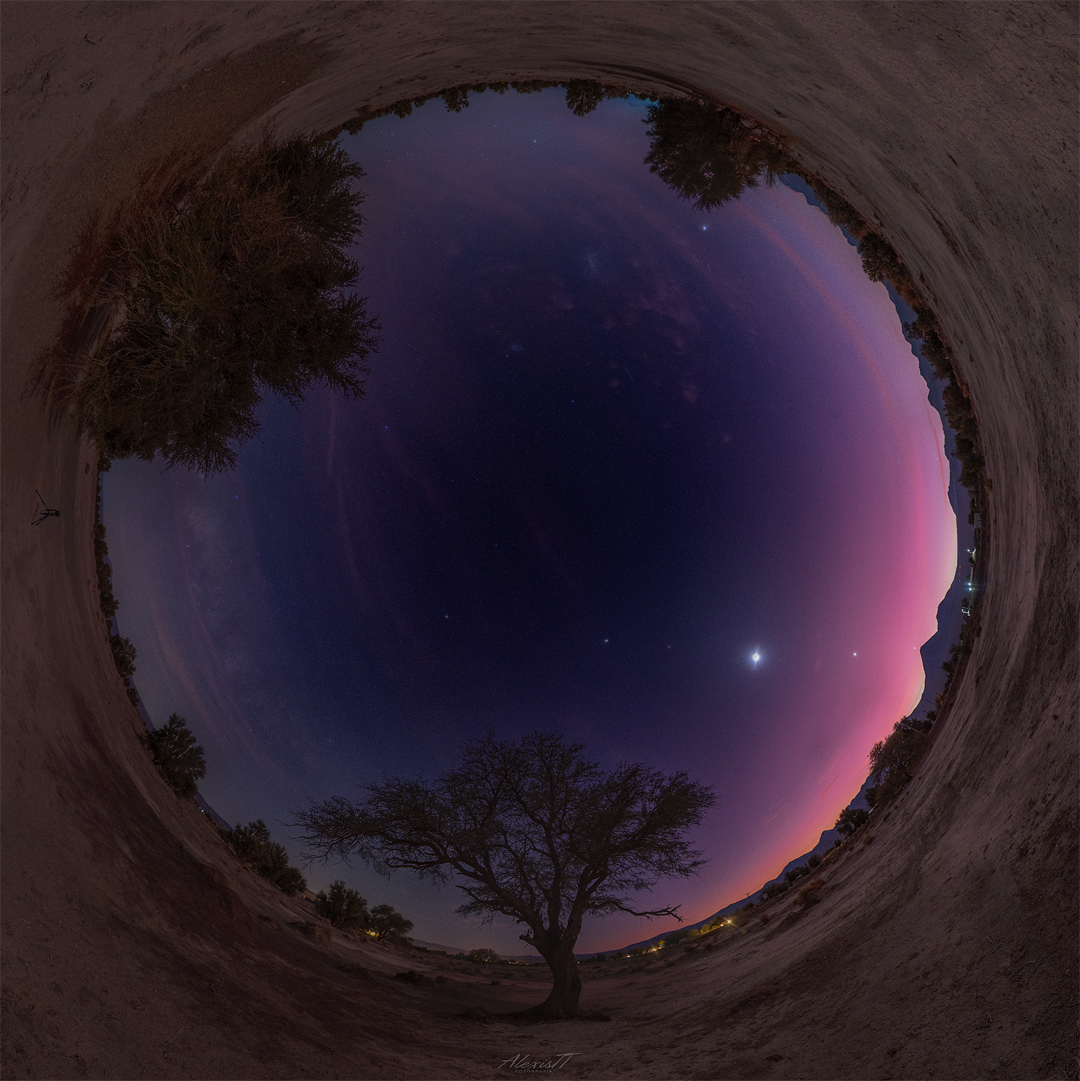
ASTRONOMY - Solar System Family Portrait
2022 June 30
Image Credit & Copyright: Alexis Trigo
Explanation: Yes, but have you ever seen all of the planets at once? A rare roll-call of planets has been occurring in the morning sky for much of June. The featured fisheye all-sky image, taken a few mornings ago near the town of San Pedro de Atacama in Chile, caught not only the entire planet parade, but the Moon between Mars and Venus. In order, left to right along the ecliptic plane, members of this Solar System family portrait are Earth, Saturn, Neptune, Jupiter, Mars, Uranus, Venus, Mercury, and Earth. To emphasize their locations, Neptune and Uranus have been artificially enhanced. The volcano just below Mercury is Licancabur. In July, Mercury will move into the Sun's glare but reappear a few days later on the evening side. Then, in August, Saturn will drift past the direction opposite the Sun and so become visible at dusk instead of dawn. The next time that all eight planets will be simultaneously visible in the evening sky will be in 2122.
28/06/2022
ASTRONOMY - Mercury from Passing BepiColombo
2022 June 28
Image Credit & License: ESA, JAXA, BepiColombo, MTM
Explanation: Which part of the Moon is this? No part -- because this is the planet Mercury. Mercury's old surface is heavily cratered like that of Earth's Moon. Mercury, while only slightly larger than Luna, is much denser and more massive than any Solar System moon because it is made mostly of iron. In fact, our Earth is the only planet more dense. Because Mercury rotates exactly three times for every two orbits around the Sun, and because Mercury's orbit is so elliptical, visitors on Mercury could see the Sun rise, stop in the sky, go back toward the rising horizon, stop again, and then set quickly over the other horizon. From Earth, Mercury's proximity to the Sun causes it to be visible only for a short time just after sunset or just before sunrise. The featured image was captured last week by ESA and JAXA's passing BepiColombo spacecraft as it sheds energy and prepares to orbit the innermost planet starting in 2025.
26/06/2022
SAUDE/MEDECINA - Estamos muito perto de encontrar uma vacina contra o cancro
Na área do cancro, a chamada medicina de precisão tem sido fundamental na identificação de mutações tumorais que podem ser usadas como alvo de vacinas de mRNA personalizadas. “Durante muitos anos ficámos todos deslumbrados com a possibilidade de identificarmos alterações genéticas nos genes do cancro, mas agora já estamos a perceber que existem também muitas alterações no RNA [ácido ribonucleico, molécula essencial na síntese de proteínas] e no metabolismo de pequenas moléculas”, comenta Maria do Carmo Fonseca, cientista galardoada com o Prémio Pessoa em 2010, atualmente presidente da RNA Society.
“Da mesma maneira que, na Covid-19, injetamos o mRNA que codifica a proteína Spike, numa vacina contra o cancro temos de incluir a informação genética que codifica as proteínas próprias das células cancerosas e que são especificas daquele cancro”, explica a investigadora. No entanto, ao contrário do SARS-CoV-2, em que a proteína Spike é igual para todos os doentes, no cancro cada caso é um caso e a vacina tem de ser muito personalizada.
Testadas sobretudo em pacientes com melanoma, na Alemanha e nos Estados Unidos da América, as vacinas já foram administradas a “centenas de doentes” no âmbito de ensaios clinicos, “com resultados muito promissores”, assegura Carmo Fonseca.
Em Portugal, a cientista conduz uma investigação revolucionária que, no futuro, poderá criar uma vacina de mRNA capaz de “ensinar o nosso sistema imune a reconhecer as células cancerosas, assim que elas aparecem no corpo, e a destruí-las imediatamente”. Esta vacina vai ser específica para cancros hereditários resultantes de mutação BRCA e, neste momento, os investigadores estão focados na mutação fundadora portuguesa, que é a mais frequente em Portugal.
Os mais importantes avanços da Ciência na área do cancro – seja na prevenção, como no caso das vacinas, seja no diagnóstico (em que a Inteligência Artificial começa a dar cartas) e, principalmente, no tratamento (com as novas terapias celulares a ensinarem o nosso corpo a adquirir uma “superimunidade”) – são longamente esmiuçados num artigo da VISÃO Saúde .
Nada disto é ficção científica – a tecnologia está aí e, em muitos casos, consegue mesmo salvar-nos.
Visão
ASTRONOMY - Light Echoes from V838 Mon
2022 June 26
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, H. E. Bond (STScI)
Explanation: What caused this outburst of V838 Mon? For reasons unknown, star V838 Mon's outer surface suddenly greatly expanded with the result that it became one of the brighter stars in the Milky Way Galaxy in early 2002. Then, just as suddenly, it shrunk and faded. A stellar flash like this had never been seen before -- supernovas and novas expel matter out into space. Although the V838 Mon flash appears to expel material into space, what is seen in the featured image from the Hubble Space Telescope is actually an outwardly expanding light echo of the original flash. In a light echo, light from the flash is reflected by successively more distant surfaces in the complex array of ambient interstellar dust that already surrounded the star. V838 Mon lies about 20,000 light years away toward the constellation of the unicorn (Monoceros), while the light echo above spans about six light years in diameter.
OVNI - Espirais de luz azul no céu da Nova Zelândia
Eram 19h25 de domingo quando Alasdair Burns, guia de observação de estrelas na Ilha Stewart, Nova Zelândia, recebeu uma mensagem de um amigo a pedir que fosse olhar para o céu. Burns saiu de casa e testemunhou uma enorme espiral azul de luz no meio da escuridão do céu. “Parecia uma enorme galáxia em espiral, ali a pairar no céu e a atravessá-lo lentamente. Foi uma sensação muito estranha”, confessa, citado pelo The Guardian.
Depois de ter observado o fenómeno durante uns segundos, rapidamente se lembrou de eternizar o momento e capturou algumas imagens.
Richard Easther, físico na Universidade de Auckland, explicou ao jornal que são formadas nuvens desta natureza quando um foguetão leva um satélite para a órbita da terra. “Quando o combustível propulsor é ejetado, o que temos essencialmente é água e dióxido de carbono, que formam uma nuvem iluminada pelo sol”, começa por explicar.
“A combinação da geometria da trajetória da órbita do satélite e da forma como nós estamos posicionados em relação ao Sol foi o que foi capaz de produzir estas nuvens esquisitas que eram visíveis da Ilha Sul”, acrescenta o físico.
O “espetáculo” observado terá sido provocado pelo lançamento do satélite da Globalstar a cargo da SpaceX, que foi enviado para uma órbita mais baixa a partir do Cabo Canaveral, na Flórida.
Visão
25/06/2022
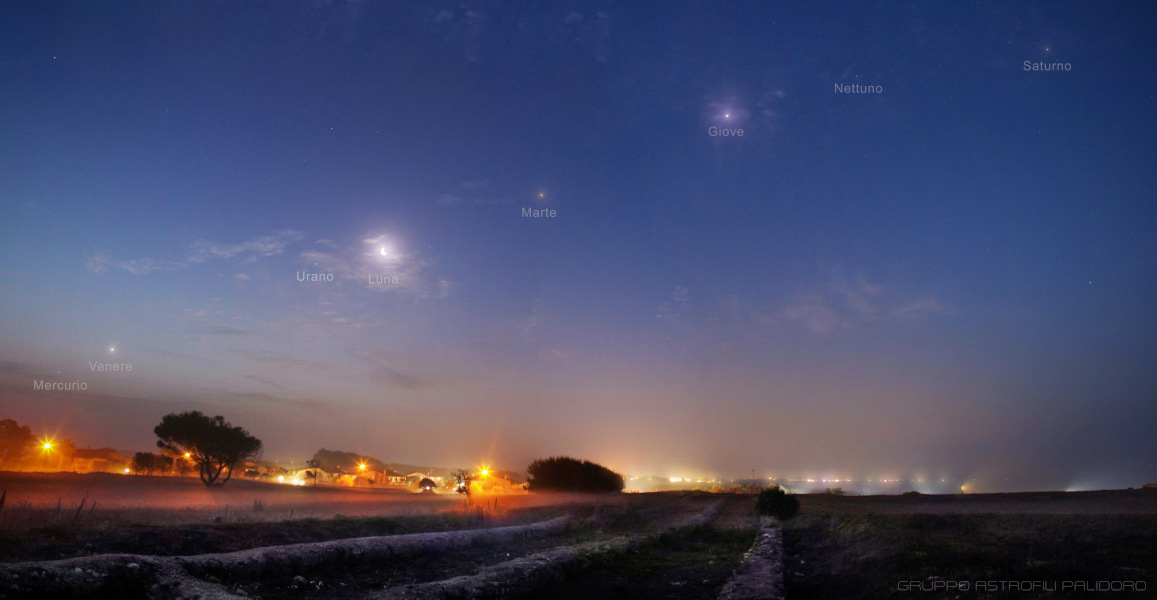
ASTRONOMY - Planets of the Solar System
2022 June 25
Image Credit & Copyright: Antonio Canaveras, Chiara Tronci, Giovanni Esposito, Giuseppe Conzo, Luciana Guariglia, (Gruppo Astrofili Palidoro)
Explanation: Simultaneous images from four cameras were combined to construct this atmospheric predawn skyscape. The cooperative astro-panorama captures all the planets of the Solar System, just before sunrise on June 24. That foggy morning found innermost planet Mercury close to the horizon but just visible against the twilight, below and left of brilliant Venus. Along with the waning crescent Moon, the other bright naked-eye planets, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn lie near the ecliptic, arcing up and to the right across the wide field of view. Binoculars would have been required to spot the much fainter planets Uranus and Neptune, though they also were along the ecliptic in the sky. In the foreground are excavations at an ancient Roman villa near Marina di San Nicola, Italy, planet Earth.
24/06/2022
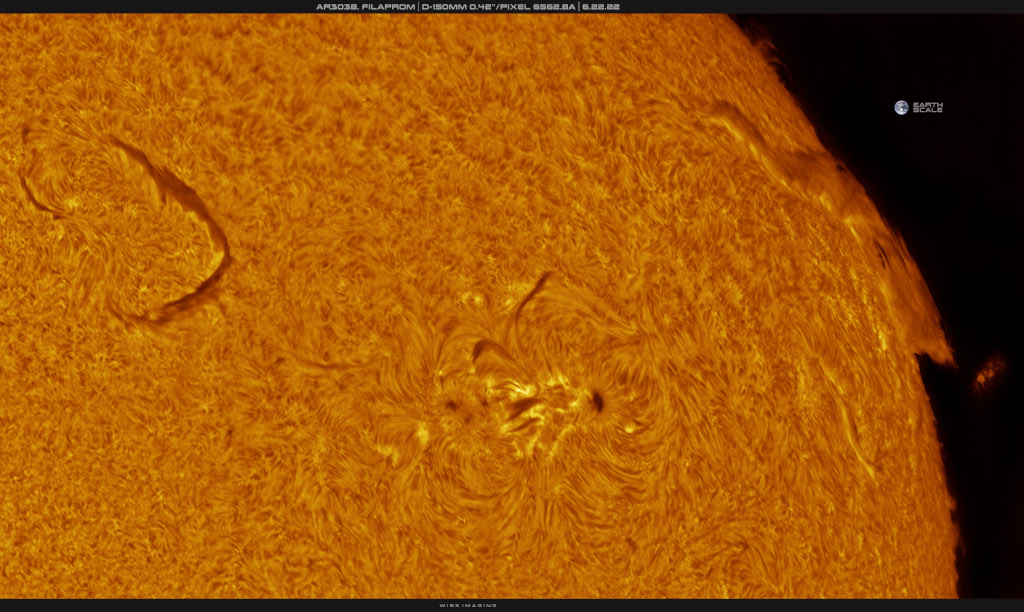
ASTRONOMY - Filaprom on the Western Limb
2022 June 24
Image Credit & Copyright: Martin Wise
Explanation: A solar filament is an enormous stream of incandescent plasma suspended above the active surface of the Sun by looping magnetic fields. Seen against the solar disk it looks dark only because it's a little cooler, and so slightly dimmer, than the solar photosphere. Suspended above the solar limb the same structure looks bright when viewed against the blackness of space and is called a solar prominence. A filaprom would be both of course, a stream of magnetized plasma that crosses in front of the solar disk and extends beyond the Sun's edge. In this hydrogen-alpha close-up of the Sun captured on June 22, active region AR3038 is near the center of the frame. Active region AR3032 is seen at the far right, close to the Sun's western limb. As AR3032 is carried by rotation toward the Sun's visible edge, what was once a giant filament above it is now partly seen as a prominence, How big is AR3032's filaprom? For scale planet Earth is shown near the top right corner.
23/06/2022
MERVEILLEUX MONDE SOUS-MARIN - Le dugon
METEO EXTREME - L’éclair le plus long
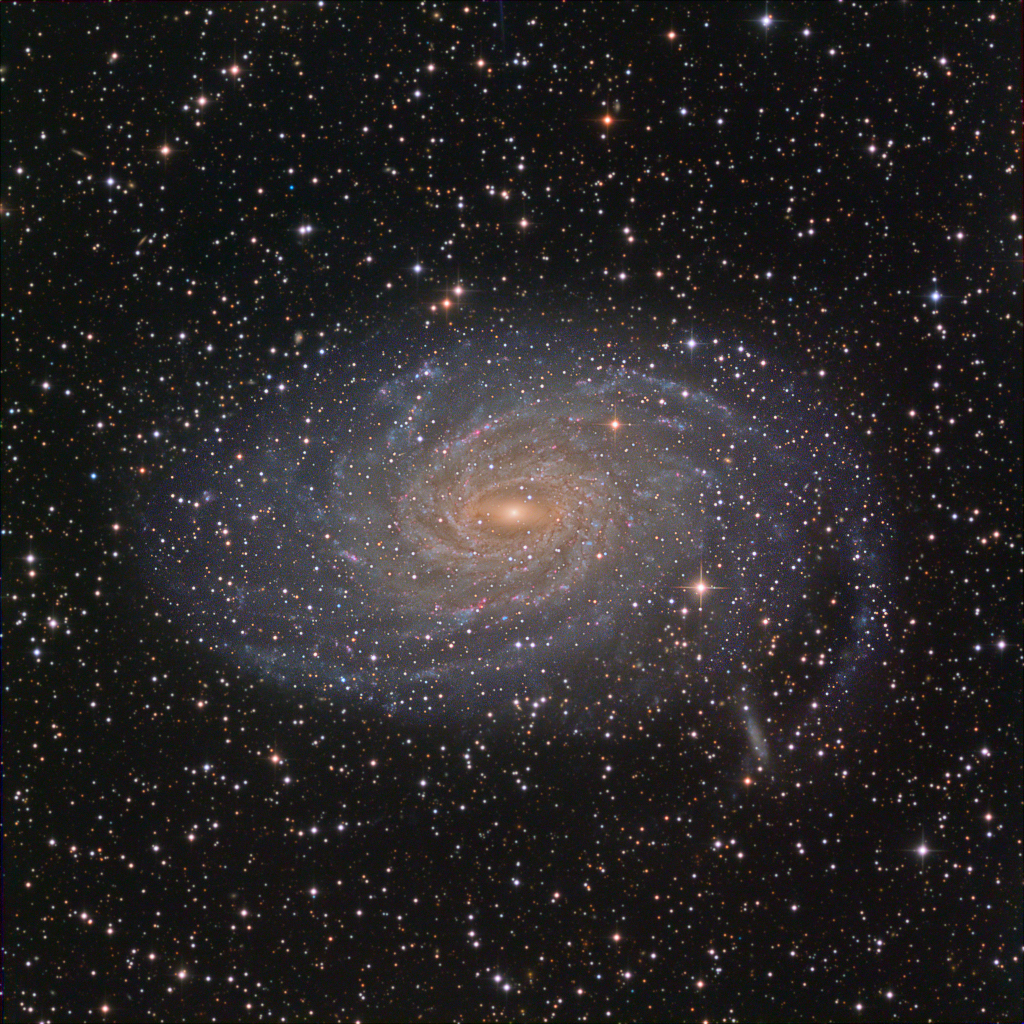
ASTRONOMY - Spiral Galaxy NGC 6744
2022 June 23
Image Credit & Copyright: Basudeb Chakrabarti
Explanation: Beautiful spiral galaxy NGC 6744 is nearly 175,000 light-years across, larger than our own Milky Way. It lies some 30 million light-years distant in the southern constellation Pavo but appears as only a faint, extended object in small telescopes. We see the disk of the nearby island universe tilted towards our line of sight in this remarkably detailed galaxy portrait, a telescopic view that spans an area about the angular size of a full moon. In it, the giant galaxy's elongated yellowish core is dominated by the light from old, cool stars. Beyond the core, grand spiral arms are filled with young blue star clusters and speckled with pinkish star forming regions. An extended arm sweeps past smaller satellite galaxy NGC 6744A at the lower right. NGC 6744's galactic companion is reminiscent of the Milky Way's satellite galaxy the Large Magellanic Cloud.
22/06/2022
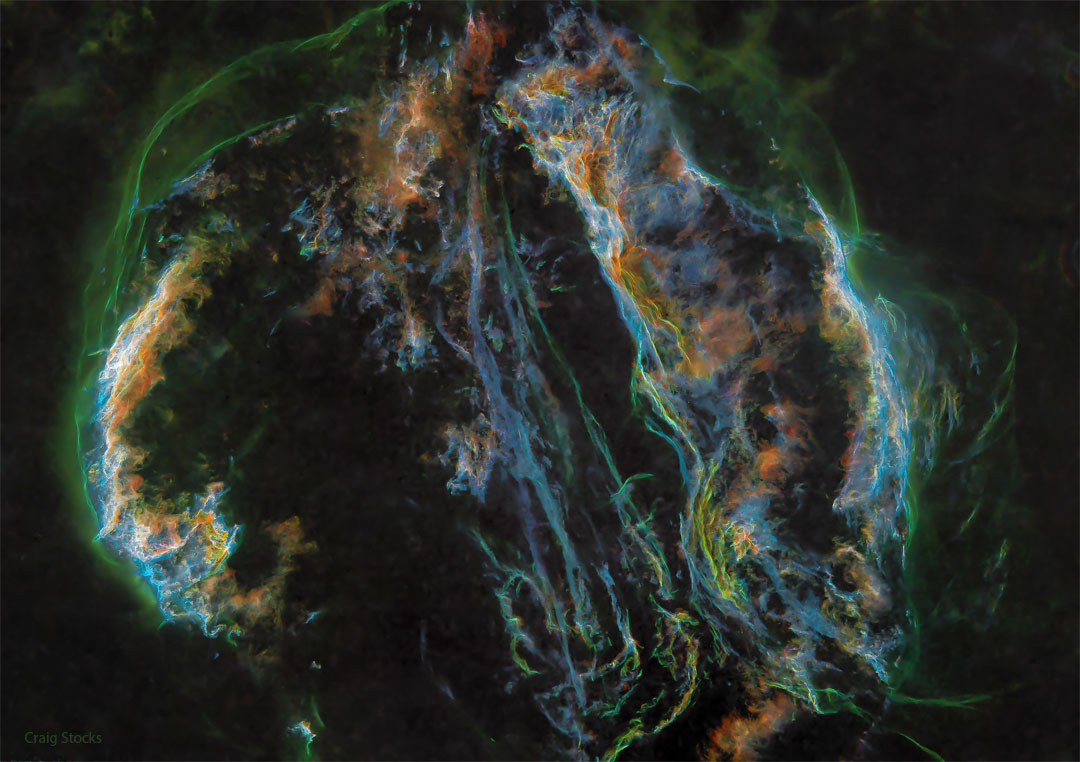
ASTRONOMY - Supernova Remnant: The Veil Nebula
2022 June 22
Image Credit & Copyright: Craig Stocks (Utah Desert Remote Observatories)
Explanation: Ten thousand years ago, before the dawn of recorded human history, a new light would have suddenly have appeared in the night sky and faded after a few weeks. Today we know this light was from a supernova, or exploding star, and record the expanding debris cloud as the Veil Nebula, a supernova remnant. Imaged with color filters featuring light emitted by sulfur (red), hydrogen (green), and oxygen (blue), this deep wide-angle view was processed to remove the stars and so better capture the impressive glowing filaments of the Veil. Also known as the Cygnus Loop, the Veil Nebula is roughly circular in shape and covers nearly 3 degrees on the sky toward the constellation of the Swan (Cygnus). Famous nebular sections include the Bat Nebula, the Witch's Broom Nebula, and Fleming's Triangular Wisp. The complete supernova remnant lies about 1,400 light-years away.
ASTROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Éclipse hybride du Soleil
© Eugen Kamenew, Flickr
21/06/2022
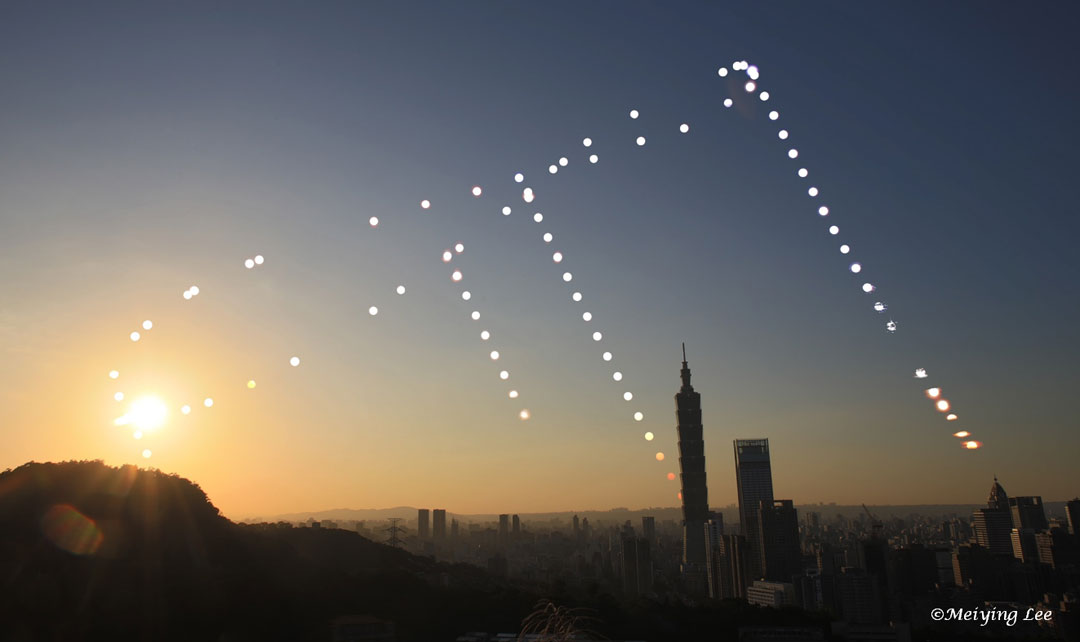
ASTRONOMY - Analemma over Taipei
2022 June 21
Image Credit & Copyright: Meiying Lee
Explanation: Does the Sun return to the same spot on the sky every day? No. A better and more visual answer to that question is an analemma, a composite of images taken at the same time and from the same place over the course of a year. The featured analemma was compiled at 4:30 pm many afternoons from Taiwan during 2021, with the city skyline of Taipei in the foreground, including tall Taipei 101. The Sun's location in December -- at the December solstice -- is shown on the far left, while its location at the June solstice is captured on the far right. Also shown are the positions of the Sun throughout the rest of the day on the solstices and equinoxes. Today is the June solstice of 2022, the day in Earth's northern hemisphere when the Sun spends the longest time in the sky. In many countries, today marks the official beginning of a new season, for example winter in Earth's southern hemisphere.
20/06/2022
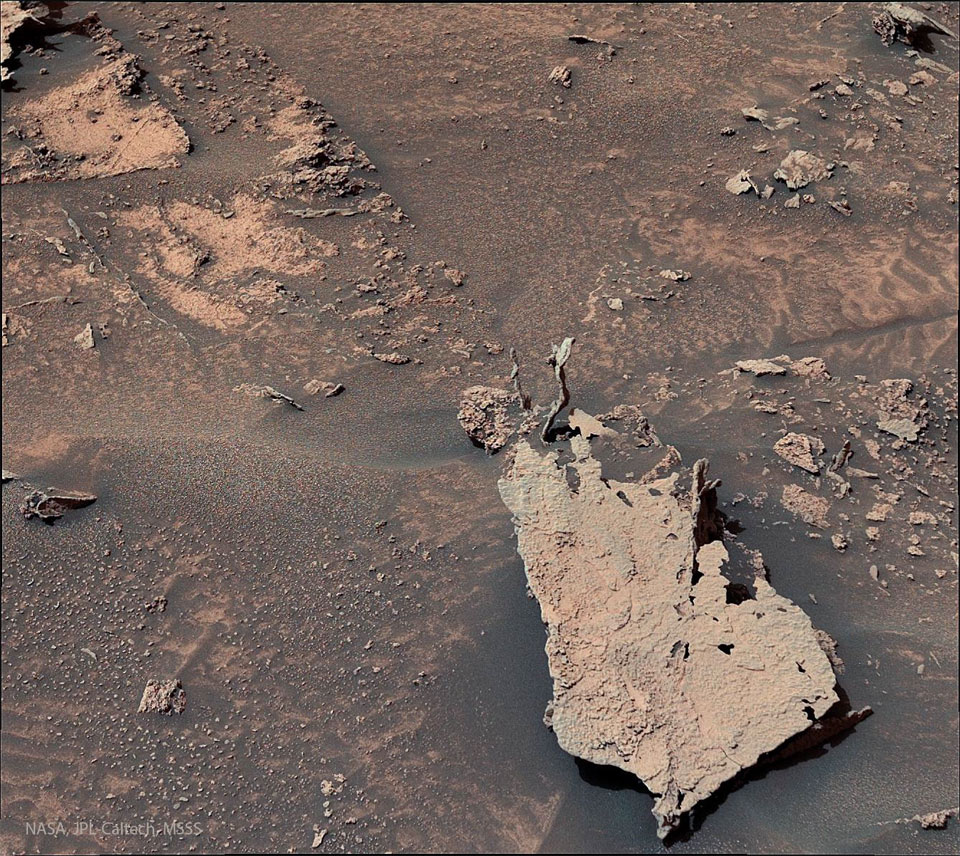
ASTRONOMY - Rock Fingers on Mars
2022 June 20
Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, MSSS
Explanation: There, just right of center, what is that? The surface of Mars keeps revealing new surprises with the recent discovery of finger-like rock spires. The small nearly-vertical rock outcrops were imaged last month by the robotic Curiosity rover on Mars. Although similar in size and shape to small snakes, the leading explanation for their origin is as conglomerations of small minerals left by water flowing through rock crevices. After these relatively dense minerals filled the crevices, they were left behind when the surrounding rock eroded away. Famous rock outcrops on Earth with a similar origin are called hoodoos. NASA's Curiosity Rover continues to search for new signs of ancient water in Gale Crater on Mars, while also providing a geologic background important for future human exploration.
18/06/2022
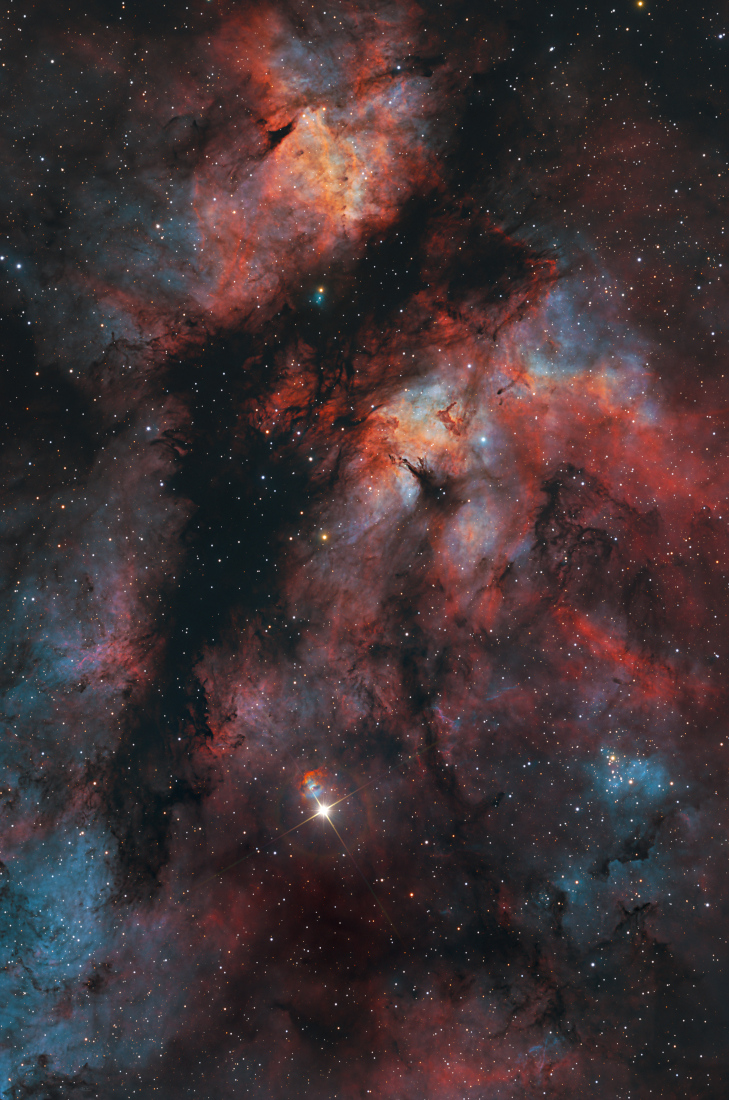
ASTRONOMY - The Gamma Cygni Nebula
2022 June 18
Image Credit & Copyright: Min Xie, Chen Wu, Yizhou Zhang, and Benchu Tang
Explanation: Supergiant star Gamma Cygni is at the center of the Northern Cross. Near the plane of our Milky Way galaxy, that famous asterism flies high in northern summer night skies in the constellation Cygnus the Swan. Known by the proper name Sadr, Gamma Cygni also lies just below center in this telescopic skyscape, with colors mapped from both broadband and narrowband image data. The field of view spans about 3 degrees (six Full Moons) on the sky and includes emission nebula IC 1318 and open star cluster NGC 6910. Filling the upper part of the frame and shaped like two glowing cosmic wings divided by a long dark dust lane, IC 1318's popular name is understandably the Butterfly Nebula. Right of Gamma Cygni, are the young, still tightly grouped stars of NGC 6910. The distance to Gamma Cygni is around 560 parsecs or 1,800 light-years. Estimates for IC 1318 and NGC 6910 range from 2,000 to 5,000 light-years.
17/06/2022
ASTRONOMY - Good Morning Planets from Chile
2022 June 17
Image Credit & Copyright: Elke Schulz (Daniel Verschatse Observatory)
Explanation: On June 15, innermost planet Mercury had wandered about as far from the Sun as it ever gets in planet Earth's sky. Near the eastern horizon just before sunrise it stands over distant Andes mountain peaks in this predawn snapshot from the valley of Rio Hurtado in Chile. June's other morning planets are arrayed above it, as all the naked-eye planets of the Solar System stretch in a line along the ecliptic in the single wide-field view. Tilted toward the north, the Solar System's ecliptic plane arcs steeply through southern hemisphere skies. Northern hemisphere early morning risers will see the lineup of planets along the ecliptic at a shallower angle tilting toward the south. From both hemispheres June's beautiful morning planetary display finds the visible planets in order of their increasing distance from the Sun.
16/06/2022
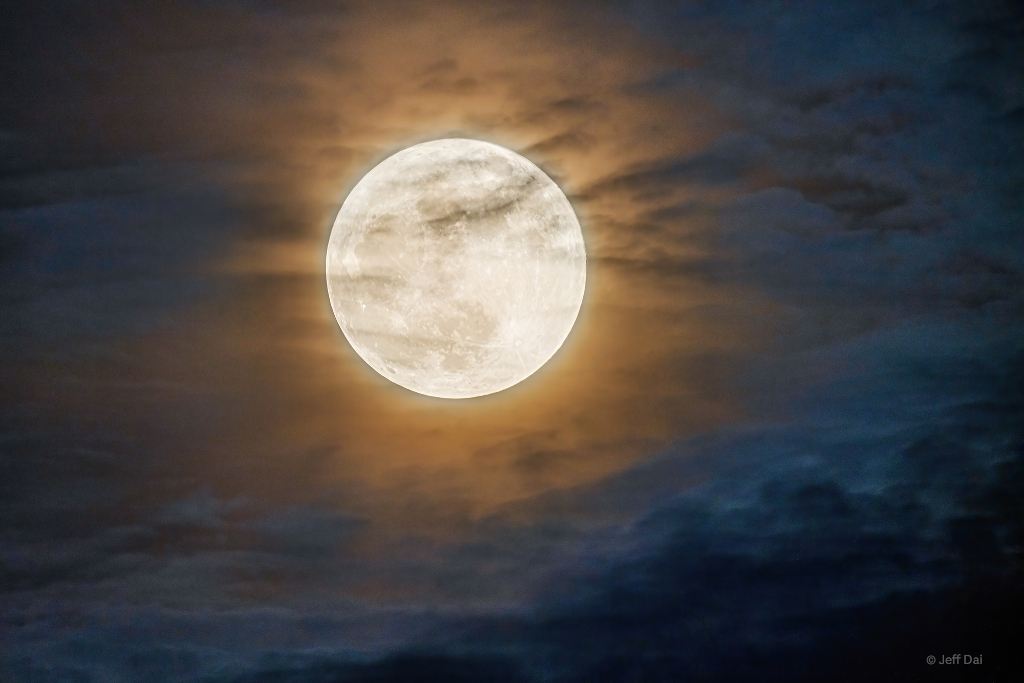
ASTRONOMY - Strawberry Supermoon from China
2022 June 16
Image Credit & Copyright: Jeff Dai (TWAN)
Explanation: There are four Full Supermoons in 2022. Using the definition of a supermoon as a Full Moon near perigee, that is within at least 90% of its closest approach to Earth in a given orbit, the year's Full Supermoon dates are May 16, June 14, July 13, and August 12. Full Moons near perigee really are the brightest and largest in planet Earth's sky. But size and brightness differences between Full Moons are relatively small and an actual comparison with other Full Moons is difficult to make by eye alone. Two exposures are blended in this supermoon and sky view from June 14. That Full Moon was also known to northern hemisphere skygazers as the Strawberry moon. The consecutive short and long exposures allow familiar features on the fully sunlit lunar nearside to be seen in the same image as a faint lunar corona and an atmospheric cloudscape. They were captured in skies over Chongqing, China.
15/06/2022
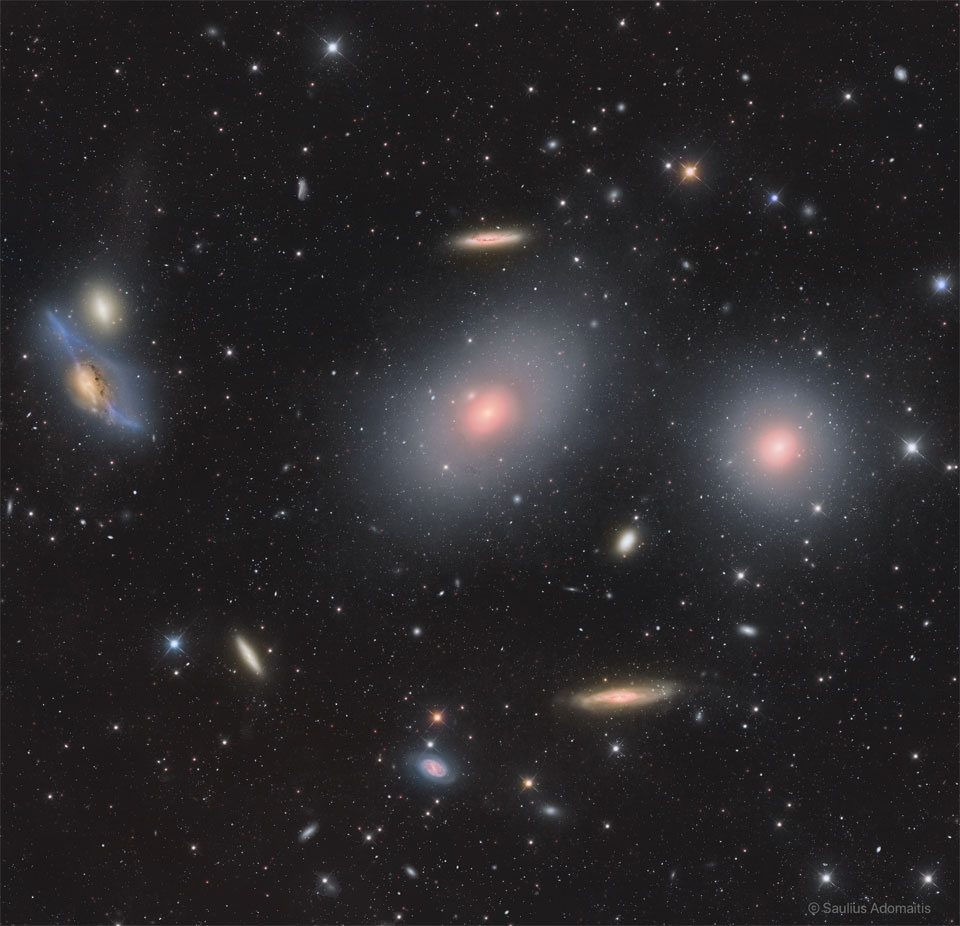
ASTRONOMY - In the Heart of the Virgo Cluster
2022 June 15
Image Credit & Copyright: Saulius Adomaitis
Explanation: The Virgo Cluster of Galaxies is the closest cluster of galaxies to our Milky Way Galaxy. The Virgo Cluster is so close that it spans more than 5 degrees on the sky - about 10 times the angle made by a full Moon. With its heart lying about 70 million light years distant, the Virgo Cluster is the nearest cluster of galaxies, contains over 2,000 galaxies, and has a noticeable gravitational pull on the galaxies of the Local Group of Galaxies surrounding our Milky Way Galaxy. The cluster contains not only galaxies filled with stars but also gas so hot it glows in X-rays. Motions of galaxies in and around clusters indicate that they contain more dark matter than any visible matter we can see. Pictured here, the heart of the Virgo Cluster includes bright Messier galaxies such as Markarian's Eyes on the upper left, M86 just to the upper right of center, M84 on the far right, as well as spiral galaxy NGC 4388 at the bottom right.
14/06/2022
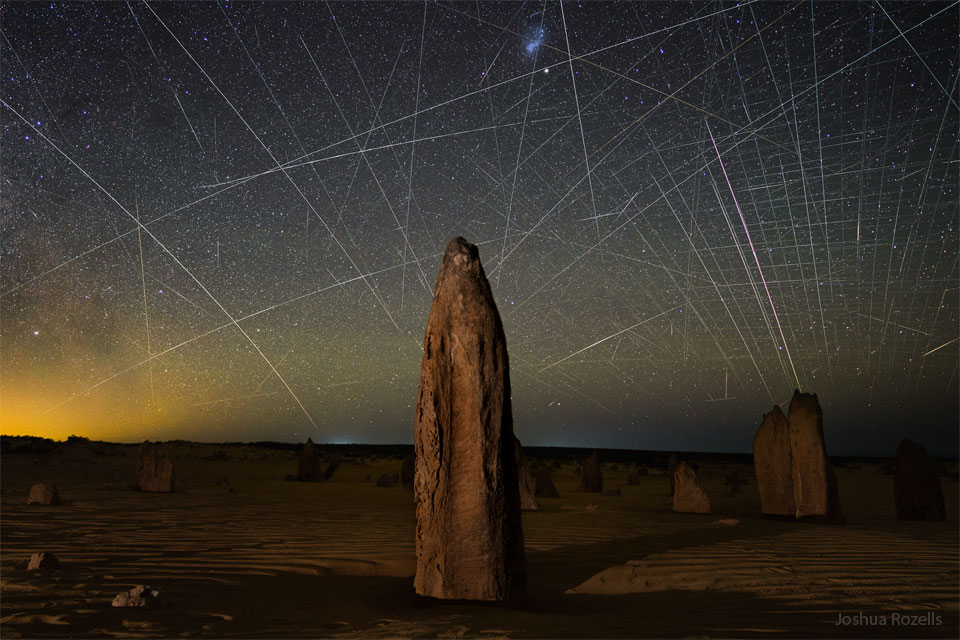
ASTRONOMY - Satellites Behind Pinnacles
2022 June 14
Image Credit & Copyright: Joshua Rozells
Explanation: What are all those streaks across the background? Satellite trails. First, the foreground features picturesque rock mounds known as Pinnacles. Found in the Nambung National Park in Western Australia, these human-sized spires are made by unknown processes from ancient sea shells (limestone). Perhaps more eye-catching, though, is the sky behind. Created by low-Earth orbit satellites reflecting sunlight, all of these streaks were captured in less than two hours and digitally combined onto the single featured image, with the foreground taken consecutively by the same camera and from the same location. Most of the streaks were made by the developing Starlink constellation of communication satellites, but some are not. In general, the streaks are indicative of an increasing number of satellites nearly continuously visible above the Earth after dusk and before dawn. Understanding and removing the effects of satellite trails on images from Earth's ground-based cameras and telescopes is now important not only for elegant astrophotography, but for humanity's scientific understanding of the distant universe.
13/06/2022
SANTé/MEDECINE - Où doit-on jeter les emballages de médicaments?
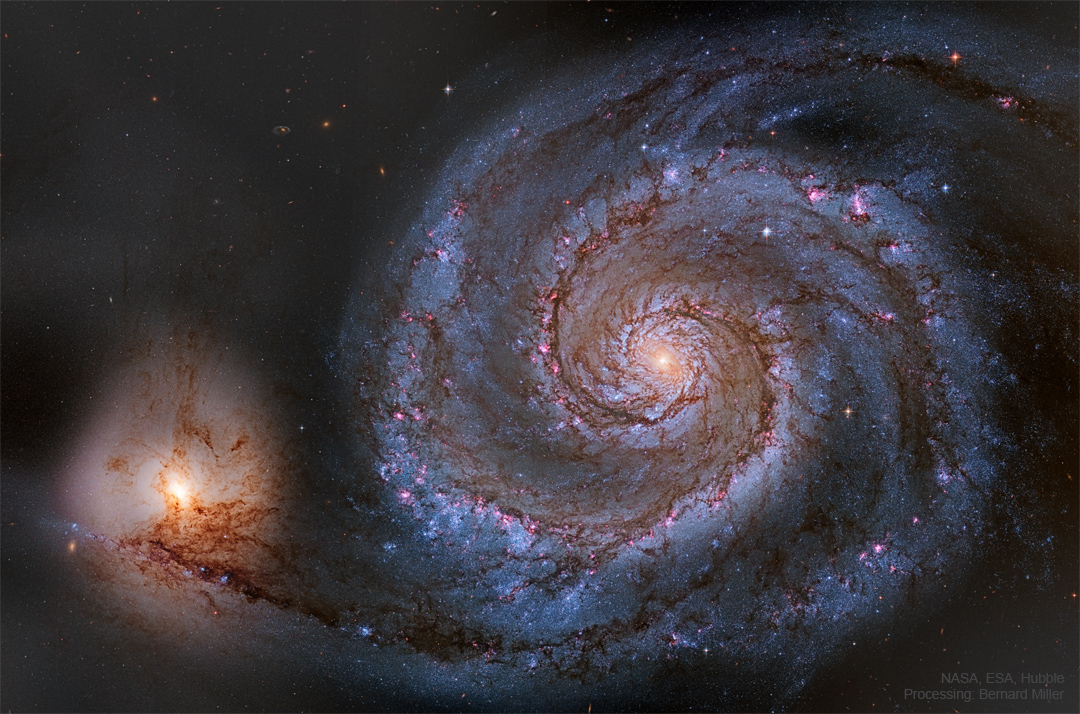
ASTRONOMY - M51: The Whirlpool Galaxy from Hubble
2022 June 13
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, HLA; Processing & Copyright: Bernard Miller
Explanation: The Whirlpool Galaxy is a classic spiral galaxy. At only 30 million light years distant and fully 60 thousand light years across, M51, also known as NGC 5194, is one of the brightest and most picturesque galaxies on the sky. The featured image is a digital combination of images taken in different colors by the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope, highlighting many sharp features. Anyone with a good pair of binoculars, however, can see this Whirlpool toward the constellation of the Hunting Dogs (Canes Venatici). M51 is a spiral galaxy of type Sc and is the dominant member of a whole group of galaxies. Astronomers speculate that M51's spiral structure is primarily due to its gravitational interaction with the smaller galaxy on the image left.
12/06/2022
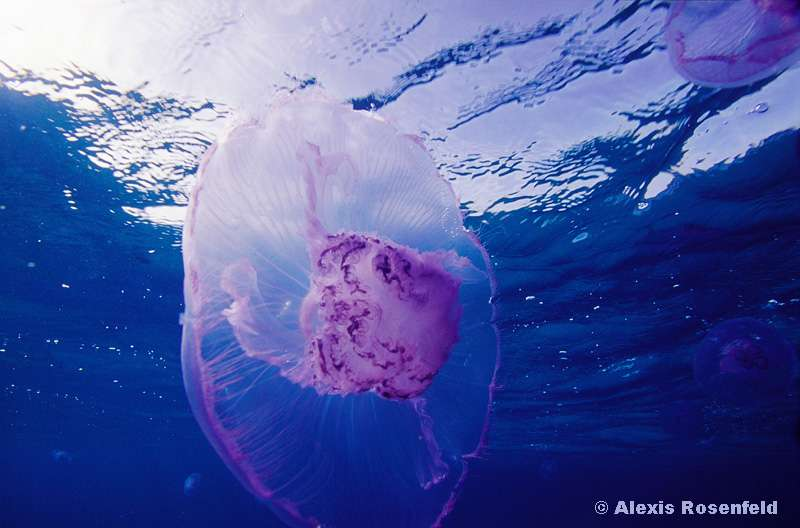
MERVEILLEUX MONDE SOUS-MARIN - L'aurélie, la méduse commune
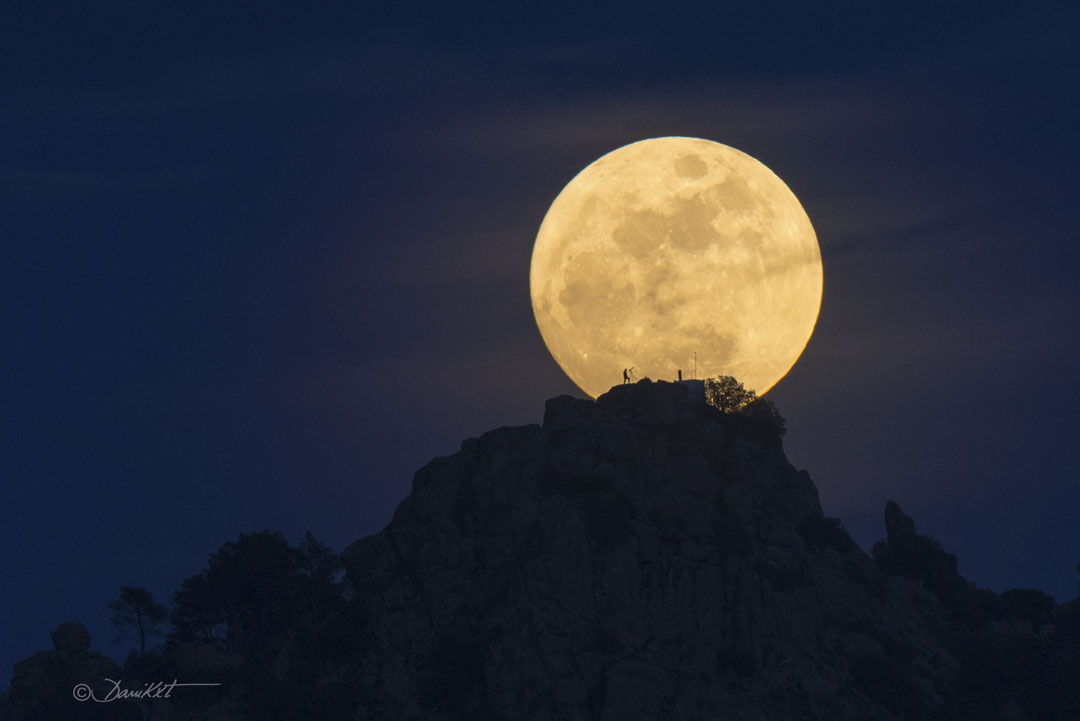
ASTRONOMY - Find the Man in the Moon
2022 June 12
Image Credit & Copyright: Dani Caxete
Explanation: Have you ever seen the Man in the Moon? This common question plays on the ability of humans to see pareidolia -- imagining familiar icons where they don't actually exist. The textured surface of Earth's full Moon is home to numerous identifications of iconic objects, not only in modern western culture but in world folklore throughout history. Examples, typically dependent on the Moon's perceived orientation, include the Woman in the Moon and the Rabbit in the Moon. One facial outline commonly identified as the Man in the Moon starts by imagining the two dark circular areas -- lunar maria -- here just above the Moon's center, to be the eyes. Surprisingly, there actually is a man in this Moon image -- a close look will reveal a real person -- with a telescope -- silhouetted against the Moon. This featured well-planned image was taken in 2016 in Cadalso de los Vidrios in Madrid, Spain. Do you have a favorite object that you see in the Moon?
11/06/2022
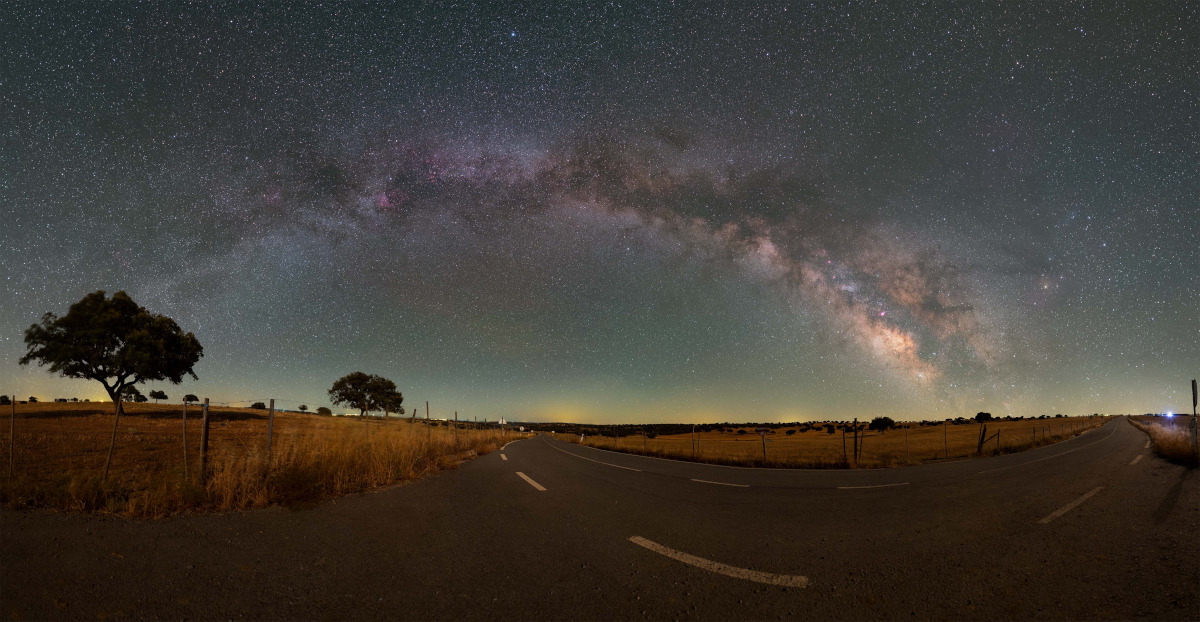
ASTRONOMY - The Road and the Milky Way
2022 June 11
Image Credit & Copyright: David Cruz
Explanation: At night you can follow this road as it passes through the Dark Sky Alqueva reserve not too far from Alentejo, Portugal. Or you could stop, look up, and follow the Milky Way through the sky. Both stretch from horizon to horizon in this 180 degree panorama recorded on June 3. Our galaxy's name, the Milky Way, does refer to its appearance as a milky path in the sky. The word galaxy itself derives from the Greek for milk. From our fair planet the arc of the Milky Way is most easily visible on moonless nights from dark sky areas, though not quite so bright or colorful as in this image. The glowing celestial band is due to the collective light of myriad stars along the galactic plane too faint to be distinguished individually. The diffuse starlight is cut by dark swaths of the galaxy's obscuring interstellar dust clouds. Standing above the Milky Way arc near the top of this panoramic nightscape is bright star Vega, with the galaxy's central bulge near the horizon at the right.
10/06/2022
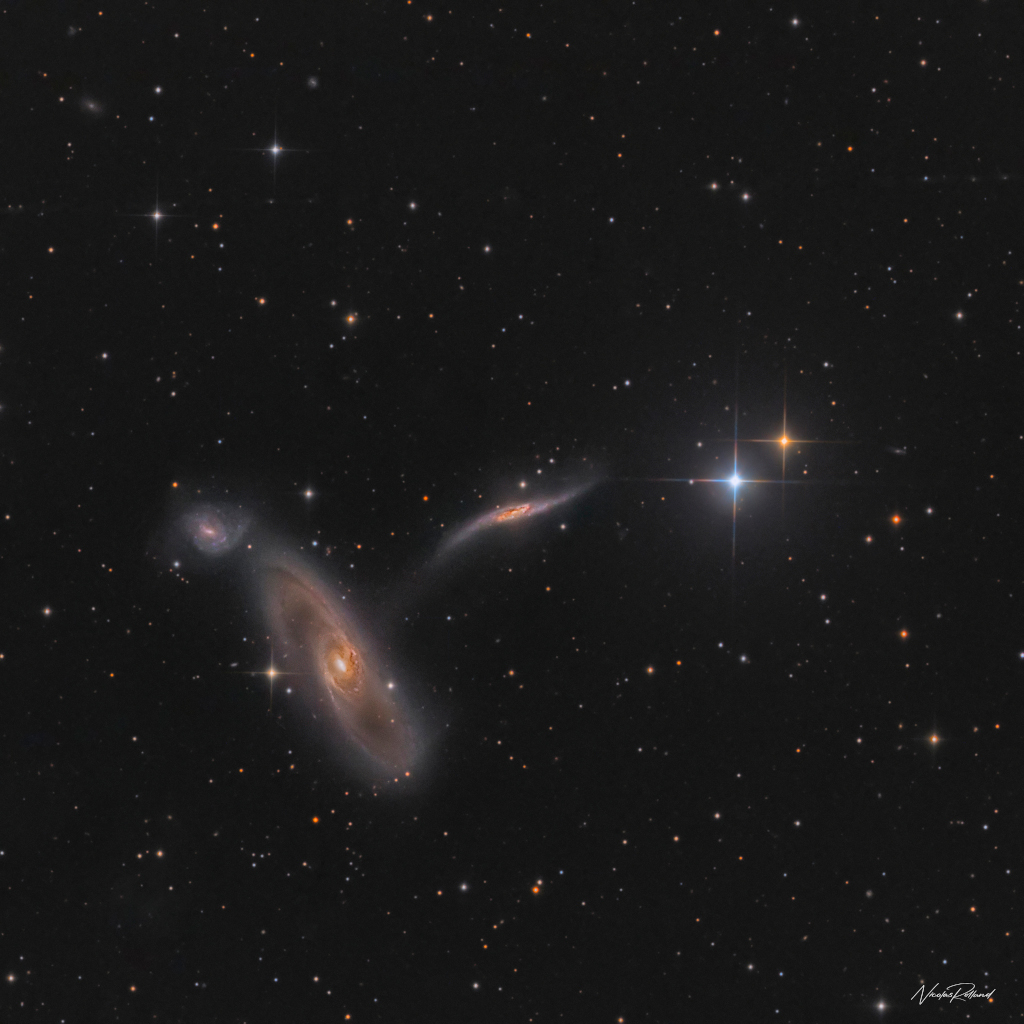
ASTRONOMY - Arp 286: Trio in Virgo
2022 June 10
Image Credit & Copyright: Nicolas Rolland, Telescope.Live
Explanation: This colorful telescopic field of view features a trio of interacting galaxies almost 90 million light-years away, toward the constellation Virgo. On the right two spiky, foreground Milky Way stars echo the extragalactic hues, a reminder that stars in our own galaxy are like those in distant island universes. With sweeping spiral arms and obscuring dust lanes, the dominant member of the trio, NGC 5566, is enormous, about 150,000 light-years across. Just above it lies smaller, bluish NGC 5569. Near center a third galaxy, NGC 5560, is apparently stretched and distorted by its interaction with massive NGC 5566. The trio is also included in Halton Arp's 1966 Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies as Arp 286. Of course, such cosmic interactions are now appreciated as part of the evolution of galaxies.
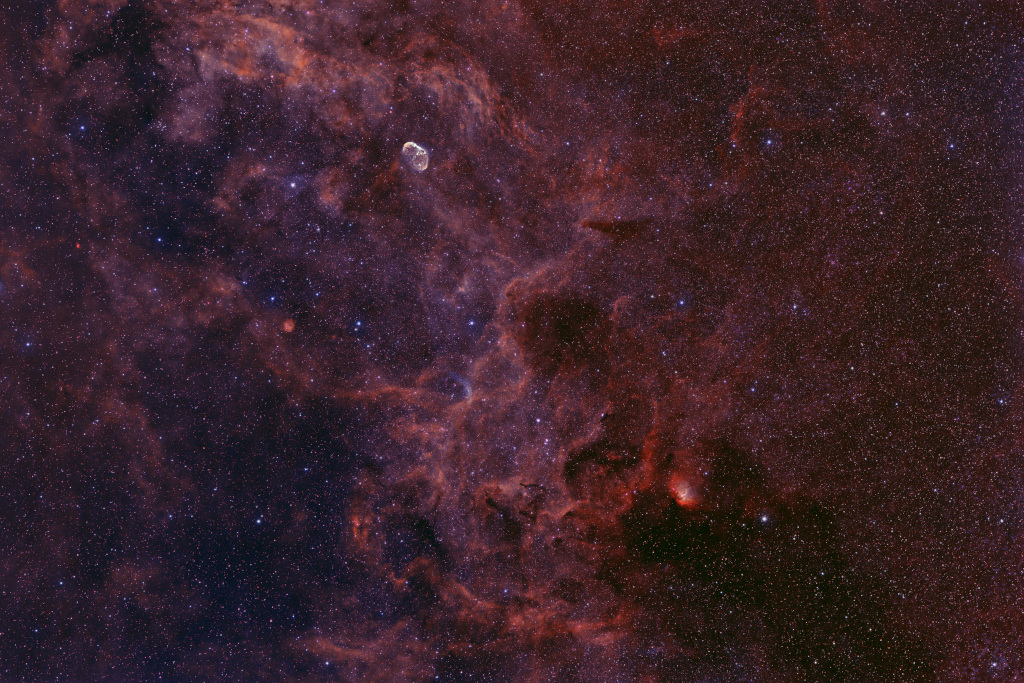
09/06/2022
ASTRONOMY - Cosmic Clouds in Cygnus
2022 June 9
Image Credit & Copyright: Wolfgang Zimmermann
Explanation: These cosmic clouds of gas and dust drift through rich star fields along the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy toward the high flying constellation Cygnus. They're too faint to be seen with the unaided eye though, even on a clear, dark night. Image data from a camera and telephoto lens using narrowband filters was used to construct this 10 degree wide field of view. The deep mosaic reveals a region that includes star forming dust clouds seen in silhouette against the characteristic glow of atomic hydrogen and oxygen gas. NGC 6888 is the standout emission nebula near the top. Blown by winds from an massive Wolf-Rayet star it's about 25 light-years across and known as the Crescent Nebula. A faint bluish curl just below center in the frame is also the signature of a Wolf-Rayet star. Burning fuel at a prodigious rate and near the end of their stellar lives, both stars will ultimately go out with a bang in a spectacular supernova explosion. Toward the right, a massive, young O type star powers the glow of Sh2-101, the Tulip Nebula.
08/06/2022
SANTé/MEDECINE - Espoir : Des bio-implants immunologiques contre le cancer
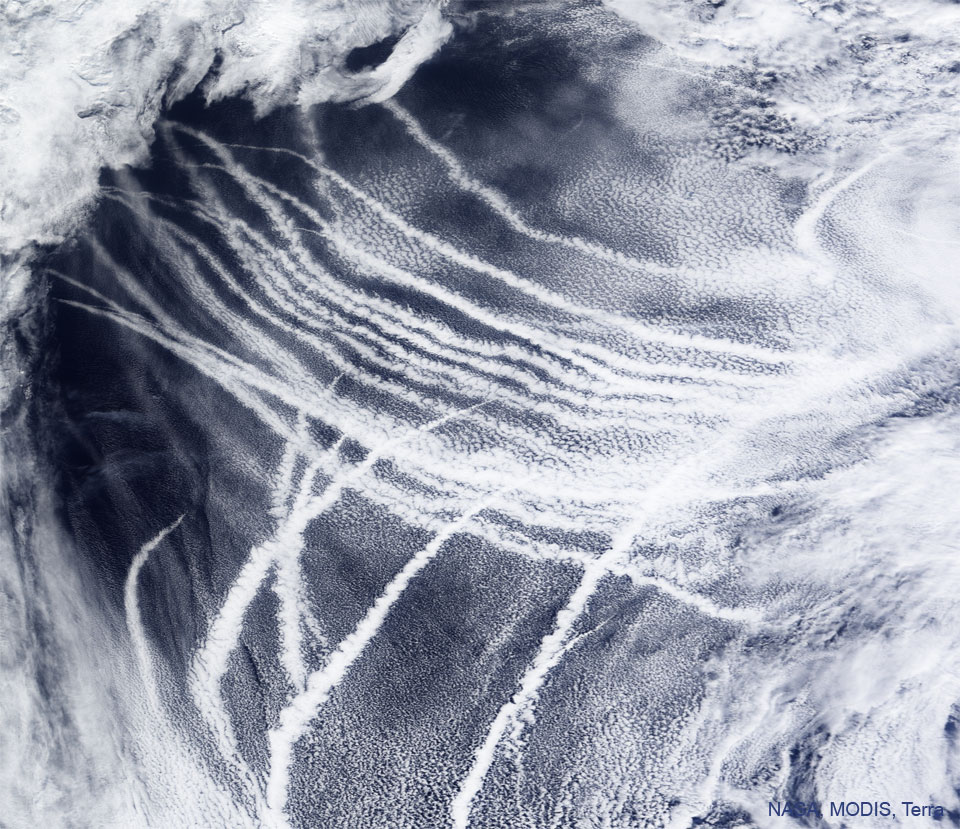
ASTRONOMY - Ship Tracks over the Pacific Ocean
2022 June 8
Image Credit: NASA, Terra, MODIS; Text: Raymond Shaw (MTU)
Explanation: What are those unusual streaks? Some images of planet Earth show clear bright streaks that follow the paths of ships. Known as ship tracks, these low and narrow bands are caused by the ship's engine exhaust. Water vapor condenses around small bits of exhaust known as aerosols, which soon grow into floating water drops that efficiently reflect sunlight. Ship tracks were first discovered in 1965 in Earth images taken by NASA's TIROS satellites. Multiple ship tracks are visible across the featured image that was captured in 2009 over the Pacific Ocean by the MODIS instrument on NASA's Terra satellite. Inspired by ship-tracks, some scientists have suggested deploying a network of floating buoys in the worlds' oceans that spray salt-aerosol containing sea-water into the air so that, with the help of the wind, streams of sunlight-reflecting clouds would also form. Why do this? These human-made clouds could reflect so much sunlight they might help fight global warming.
07/06/2022
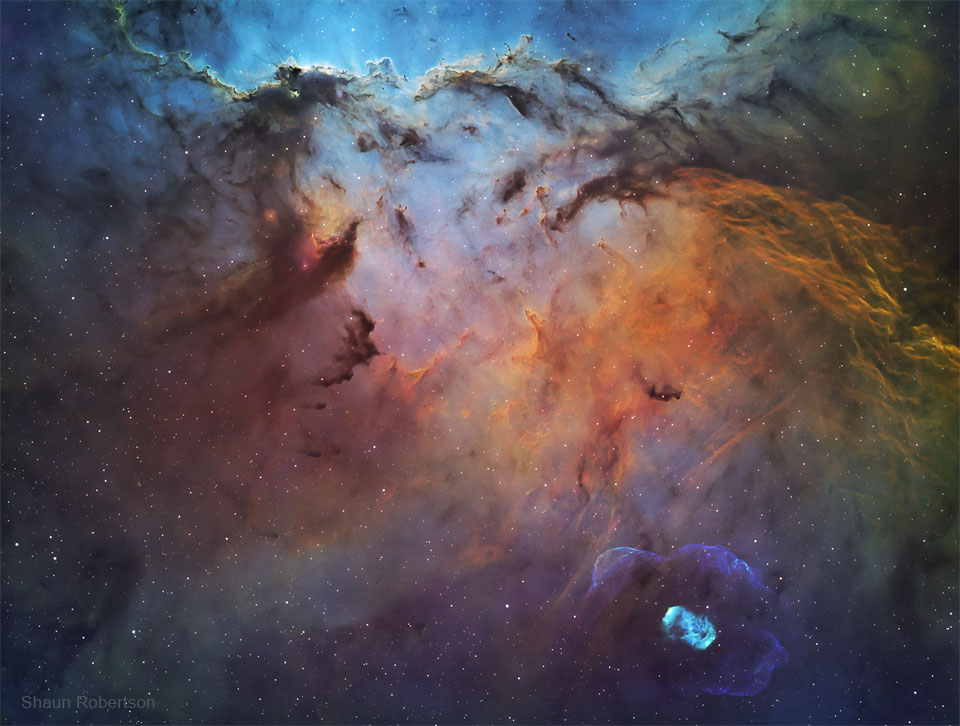
ASTRONOMY - NGC 6188: Dragons of Ara
2022 June 7
Image Credit & Copyright: Shaun Robertson
Explanation: Do dragons fight on the altar of the sky? Although it might appear that way, these dragons are illusions made of thin gas and dust. The emission nebula NGC 6188, home to the glowing clouds, is found about 4,000 light years away near the edge of a large molecular cloud unseen at visible wavelengths, in the southern constellation Ara (the Altar). Massive, young stars of the embedded Ara OB1 association were formed in that region only a few million years ago, sculpting the dark shapes and powering the nebular glow with stellar winds and intense ultraviolet radiation. The recent star formation itself was likely triggered by winds and supernova explosions, from previous generations of massive stars, that swept up and compressed the molecular gas. Joining NGC 6188 on this cosmic canvas, visible toward the lower right, is rare emission nebula NGC 6164, also created by one of the region's massive O-type stars. Similar in appearance to many planetary nebulae, NGC 6164's striking, symmetric gaseous shroud and faint halo surround its bright central star near the bottom edge. This impressively wide field of view spans over 2 degrees (four full Moons), corresponding to over 150 light years at the estimated distance of NGC 6188.
06/06/2022
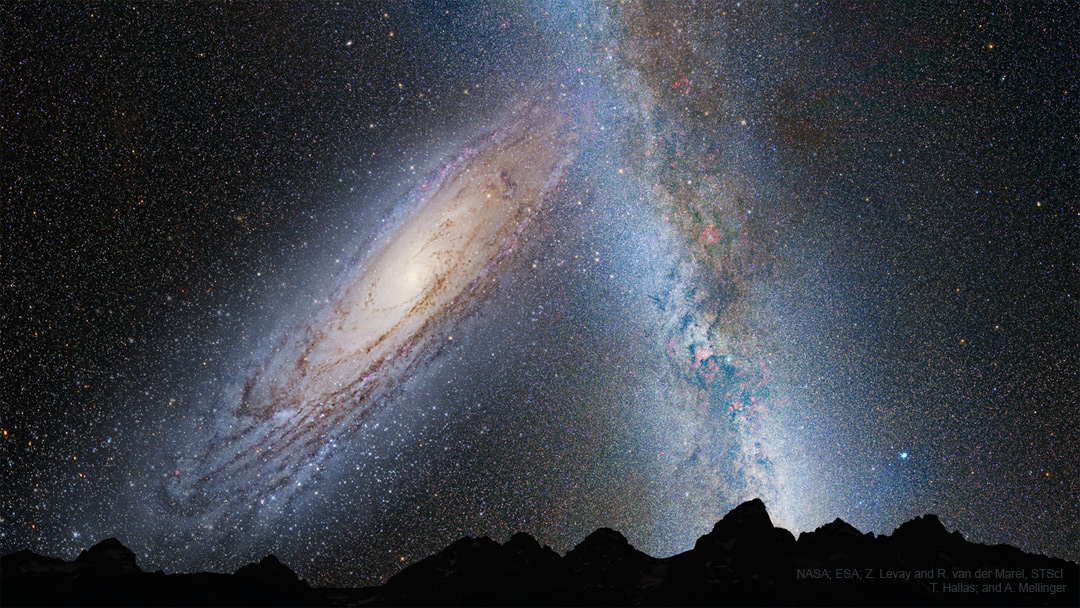
ASTRONOMY - Milky Way Galaxy Doomed: Collision with Andromeda Pending
2022 June 6
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Z. Levay and R. van der Marel (STScI); T. Hallas; and A. Mellinger
Explanation: Will our Milky Way Galaxy collide one day with its larger neighbor, the Andromeda Galaxy? Most likely, yes. Careful plotting of slight displacements of M31's stars relative to background galaxies on recent Hubble Space Telescope images indicate that the center of M31 could be on a direct collision course with the center of our home galaxy. Still, the errors in sideways velocity appear sufficiently large to admit a good chance that the central parts of the two galaxies will miss, slightly, but will become close enough for their outer halos to become gravitationally entangled. Once that happens, the two galaxies will become bound, dance around, and eventually merge to become one large elliptical galaxy -- over the next few billion years. Pictured here is a combination of images depicting the sky of a world (Earth?) in the distant future when the outer parts of each galaxy begin to collide. The exact future of our Milky Way and the entire surrounding Local Group of Galaxies is likely to remain an active topic of research for years to come.
05/06/2022
PHOTOGRAPHIE - Milky Way fascination
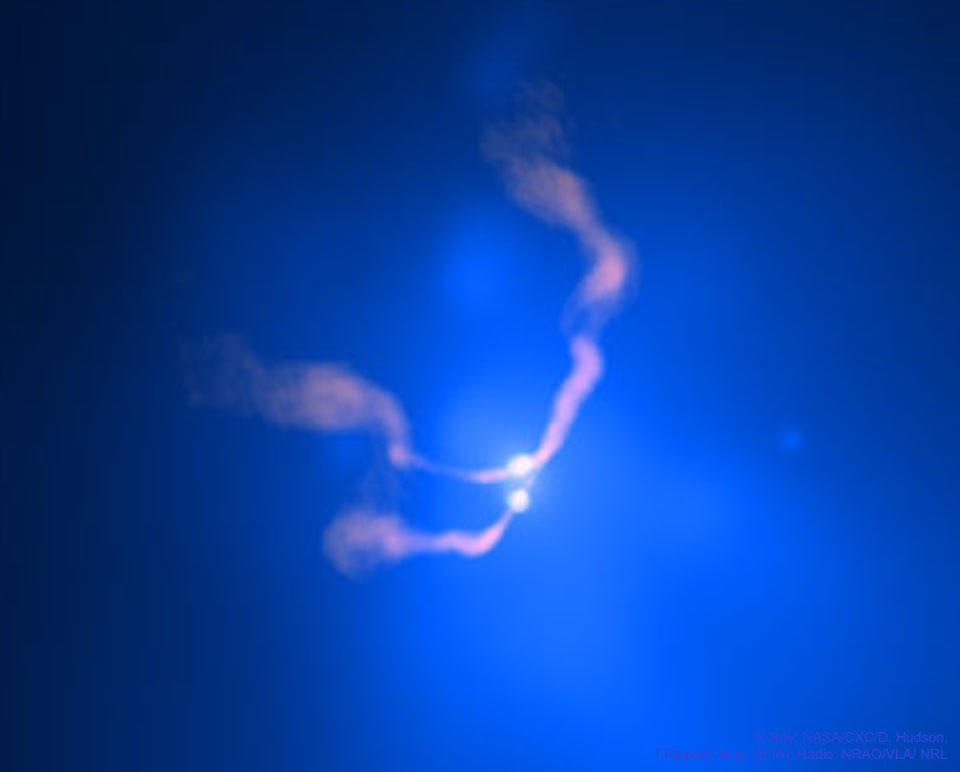
ASTRONOMY - Two Black Holes Dancing in 3C 75
2022 June 5
Image Credit: X-Ray: NASA/CXC/D. Hudson, T. Reiprich et al. (AIfA); Radio: NRAO/VLA/ NRL
Explanation: What's happening at the center of active galaxy 3C 75? The two bright sources at the center of this composite x-ray (blue)/ radio (pink) image are co-orbiting supermassive black holes powering the giant radio source 3C 75. Surrounded by multimillion degree x-ray emitting gas, and blasting out jets of relativistic particles the supermassive black holes are separated by 25,000 light-years. At the cores of two merging galaxies in the Abell 400 galaxy cluster they are some 300 million light-years away. Astronomers conclude that these two supermassive black holes are bound together by gravity in a binary system in part because the jets' consistent swept back appearance is most likely due to their common motion as they speed through the hot cluster gas at about 1200 kilometers per second. Such spectacular cosmic mergers are thought to be common in crowded galaxy cluster environments in the distant universe. In their final stages, the mergers are expected to be intense sources of gravitational waves.
04/06/2022
ASTRONOMY - Tau Herculids from Space
2022 June 4
Image Credit & Copyright: Zhuoxiao Wang, Yangwang-1 Space Telescope, Origin.Space
Explanation: On May 31 tens of parallel meteor streaks were recorded in this 8 degree wide field of view of planet Earth's limb from space. The image is one of a series of 5 minute long observations by the orbiting Yangwang-1 space telescope. It was captured at 03:43 UT, near the peak of the Tau Herculid meteor shower. As predicted, the meteor shower was an active one this year, caused as Earth swept through a relatively dense stream of debris from disintegrating Comet 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 3, but was lacking bright meteors. Nearly all of the Tau Herculid meteors in the Yangwang-1 image are too faint to be detected by groundbased instruments. But on that date patient earthbound skywatchers under clear skies still enjoyed a memorable showing of the Tau Herculids.
03/06/2022
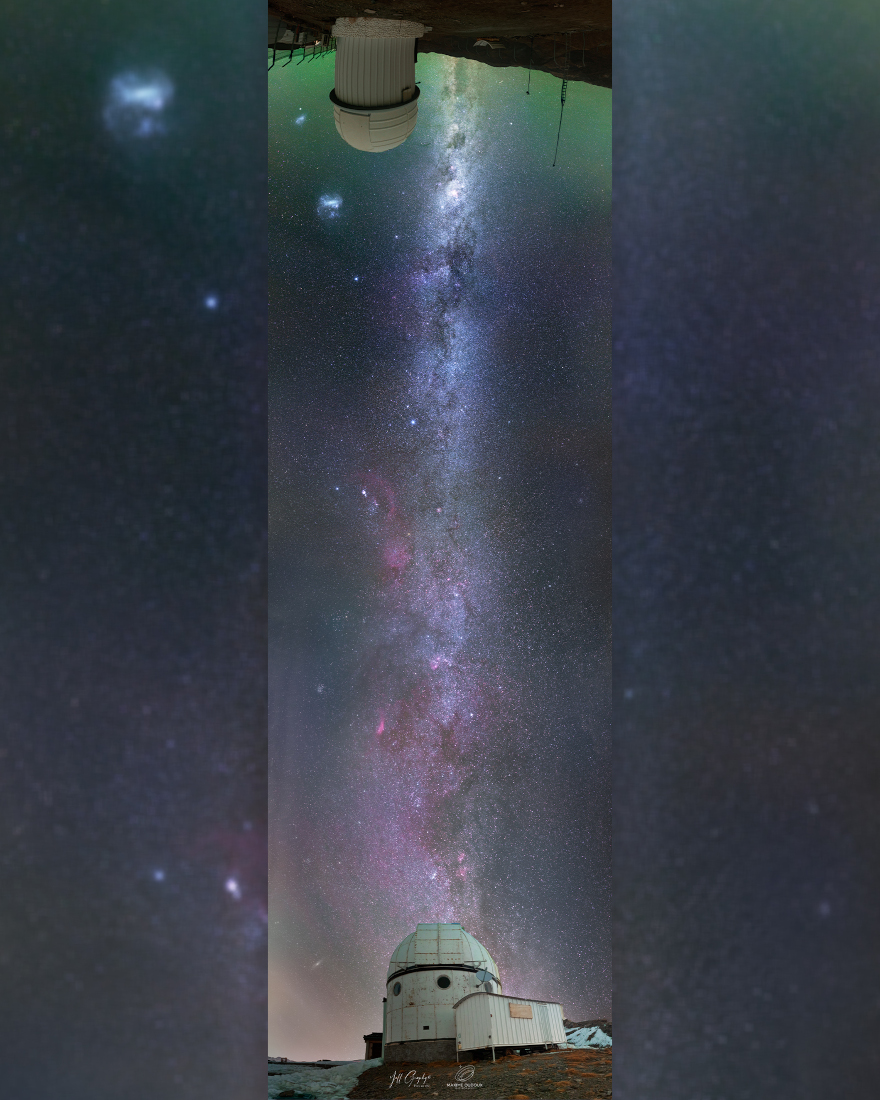
ASTRONOMY - A 10,000 Kilometer Galactic Bridge
2022 June 3
Image Credit & Copyright: Maxime Oudoux, Jean-Francois GELY
Explanation: With this creative astro-collaboration you can follow the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy as it bridges northern and southern hemisphere skies. To construct the expansive composite nightscape, skies over Observatorio El Sauce in Chile (top) were imaged on the same date but 6 hours later than the skies over the Saint-Veran observatory in the French Alps. The 6 hour time-lag allowed Earth's rotation to align the Milky Way above domes at the two sites. All exposures were made with similar cameras and lenses mounted on simple tripods. A faint greenish airglow is visible in the dark Chilean sky that also features the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds near the observatory dome. In the French Alps light pollution is apparent, but the distant Andromeda Galaxy can still be spotted near the horizon in the northern night. On planet Earth the two observatories are separated by about 10,000 kilometers.
02/06/2022
ASTRONOMY - Lunar Occultation of Venus
2022 June 2
Image Credit & Copyright: Quentin Gineys
Explanation: On May 27 Venus rose as the morning star, near the waning crescent Moon in a predawn sky already full of planets. It was close on the sky to the Moon's crescent and a conjunction of the second an third brightest celestial beacons were enjoyed by skygazers around the world. But seen from locations along a track through southeast Asia and the Indian Ocean the Moon actually passed in front of Venus in a lunar occultation. In this animated gif the 75 percent illuminated disk of Venus approaches and just begins to disappear behind the sunlit southwestern lunar limb. The telescopic frames used to construct it were captured from Reunion Island in the Indian Ocean around 4:50am local time, with the Moon and Venus very close to the eastern horizon. At the time Venus was over 180 million kilometers from Reunion Island, compared to a lunar distance of a mere 400 thousand kilometers or so. About 50 minutes later Venus emerged from behind the Moon.
01/06/2022
ASTROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Voie lactée dans un ciel limpide
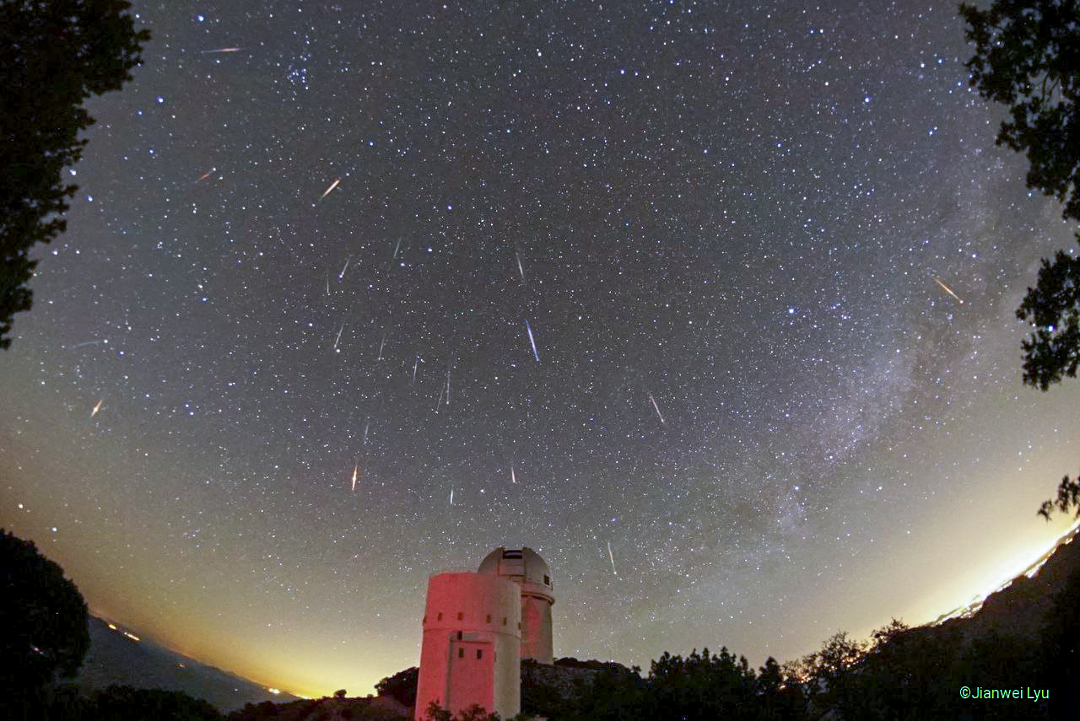
ASTRONOMY - Tau Herculids Meteors over Kitt Peak Telescopes
2022 June 1
Image Credit & Copyright: Jianwei Lyu (Steward Obs., U. Arizona)
Explanation: It wasn't the storm of the century -- but it was a night to remember. Last night was the peak of the Tau Herculids meteor shower, a usually modest dribble of occasional meteors originating from the disintegrating Comet 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 3. This year, calculations showed that the Earth might be passing through a particularly dense stream of comet debris -- at best creating a storm of bright meteors streaking out from the constellation of Hercules. What actually happened fell short of a meteor storm, but could be called a decent meteor shower. Featured here is a composite image taken at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, USA accumulated over 2.5 hours very late on May 30. Over that time, 19 Tau Herculids meteors were captured, along with 4 unrelated meteors. (Can you find them?) In the near foreground is the Bok 2.3-meter Telescope with the 4.0-meter Mayall Telescope just behind it. Next year, the annual Tau Herculids are expected to return to its normal low rate, with the next active night forecast for 2049.
SANTé/MEDECINE - Tout savoir sur le coeur humain - 2 - Anatomie du cœur humain
Le cœur comprend quatre cavités : deux oreillettes , situées dans la partie supérieure, et deux ventricules , dans la partie inférieure du c...

-
2022 September 26 All the Water on Planet Earth Illustration Credit: Jack Cook, Adam Nieman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ; Data ...
-
2025 May 11 The Surface of Venus from Venera 14 Image Credit: Soviet Planetary Exploration Program , Venera 14 ; Processing & Copyri...