Nombre total de pages vues
27/06/2019
Science & Technology - Space : Phoenix prominence eruption
25/06/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : Anticrepuscular Rays Converge Opposite the Sun
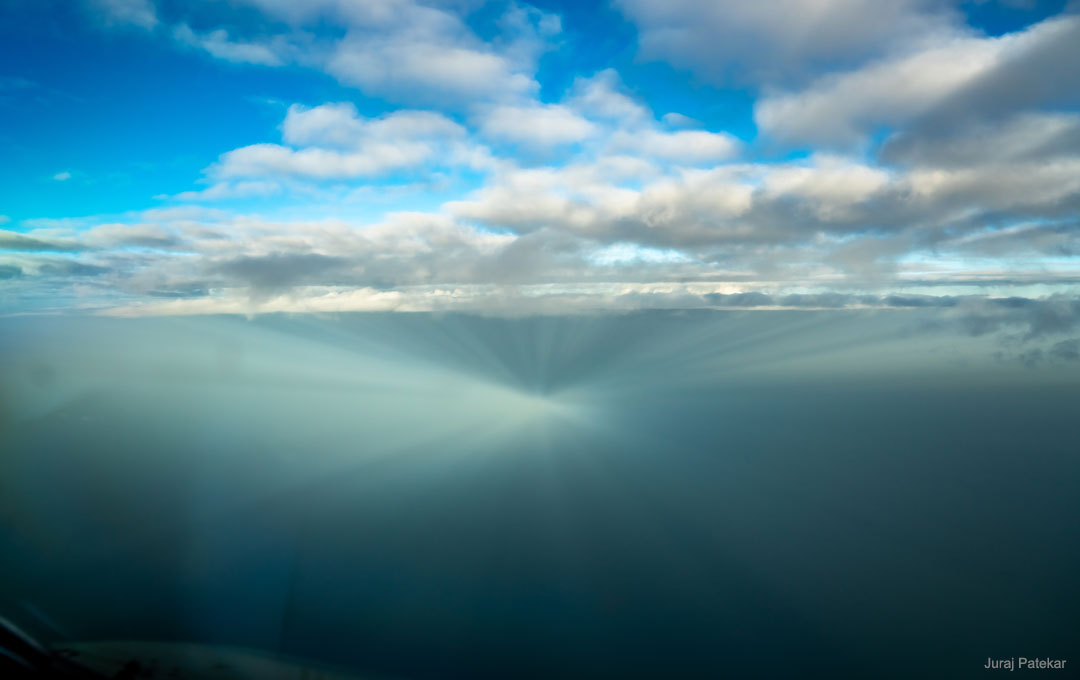

Image Credit & Copyright: Juraj Patekar
Explanation: Is there ever anything interesting to see in the direction opposite the Sun? Sometimes there is. Notable items include your own shadow, a shadow of the Moon during a total solar eclipse, a full moon -- in eclipse if the alignment's good enough, a full earth, planets at opposition, glints from planets, the gegenschein from interplanetary dust, the center of a rainbow, hall-of-mountain fogbows, an airplane glory, and something yet again different if your timing, clouds and Sun position are just right. This different effect starts with clouds near the Sun that are causing common crepuscular rays to stream through. In the featured rare image taken from an airplane in mid-April, these beamswere caught converging 180 degrees around, on the opposite side of the sky from the Sun, where they are called anticrepuscular rays. Therefore, it may look like something bright is shining at the antisolar point near the image center, but actually it is reverse-shining because, from your direction, light is streaming in, not out.
22/06/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : Ares 3 Landing Site: The Martian Revisited
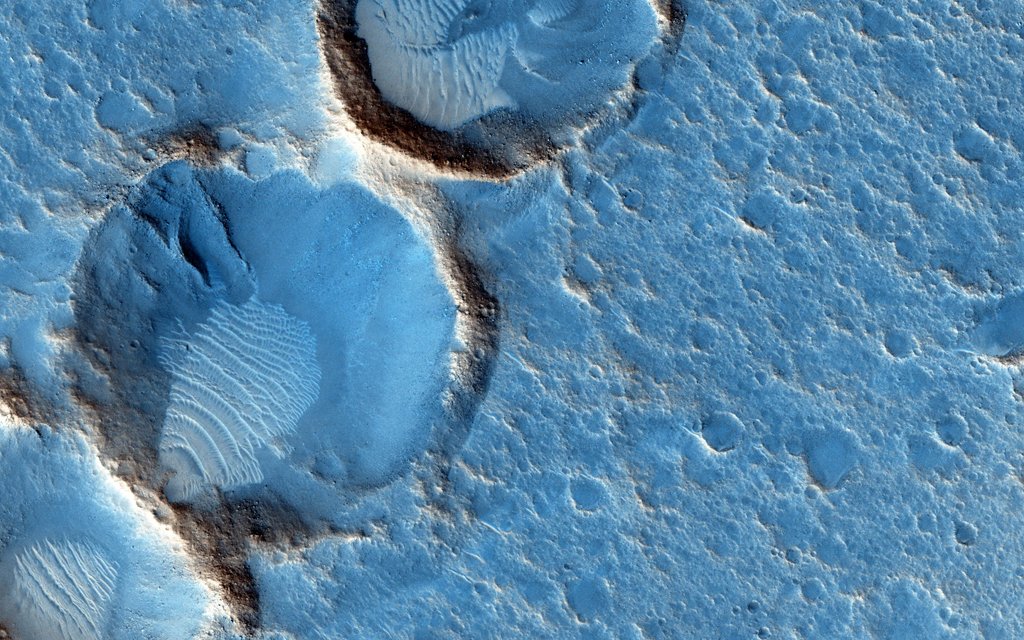

Explanation: This close-up from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's HiRISE camera shows weathered craters and windblown deposits in southern Acidalia Planitia. A striking shade of blue in standard HiRISE image colors, to the human eye the area would probably look grey or a little reddish. But human eyes have not gazed across this terrain, unless you count the eyes of NASA astronauts in the scifi novel The Martian by Andy Weir. The novel chronicles the adventures of Mark Watney, an astronaut stranded at the fictional Mars mission Ares 3 landing site corresponding to the coordinates of this cropped HiRISE frame. For scale Watney's 6-meter-diameter habitat at the site would be about 1/10th the diameter of the large crater. Of course, the Ares 3 landing coordinates are only about 800 kilometers north of the (real life) Carl Sagan Memorial Station, the 1997 Pathfinder landing site.
21/06/2019
Science & Technologie - Avions du futur : Le Select de Northrop Grumman, un avion économe

Cet avion a l'air très ordinaire mais il ne l'est pas du tout. Pour ce Select (pour Silent Efficient Low Emissions Commercial Transport, en anglais), Northrop Grumman a étudié un appareil de petite capacité - 120 passagers - à très faibles émissions de carbone, réunissant alliages à mémoire de forme, nanotechnologies et matériaux composites en céramique. Le Select pourrait se poser sur des pistes courtes (1.500 mètres) pour utiliser des petits aéroports, ce qui permettrait de déconcentrer le trafic aérien.
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : Sunset Analemma
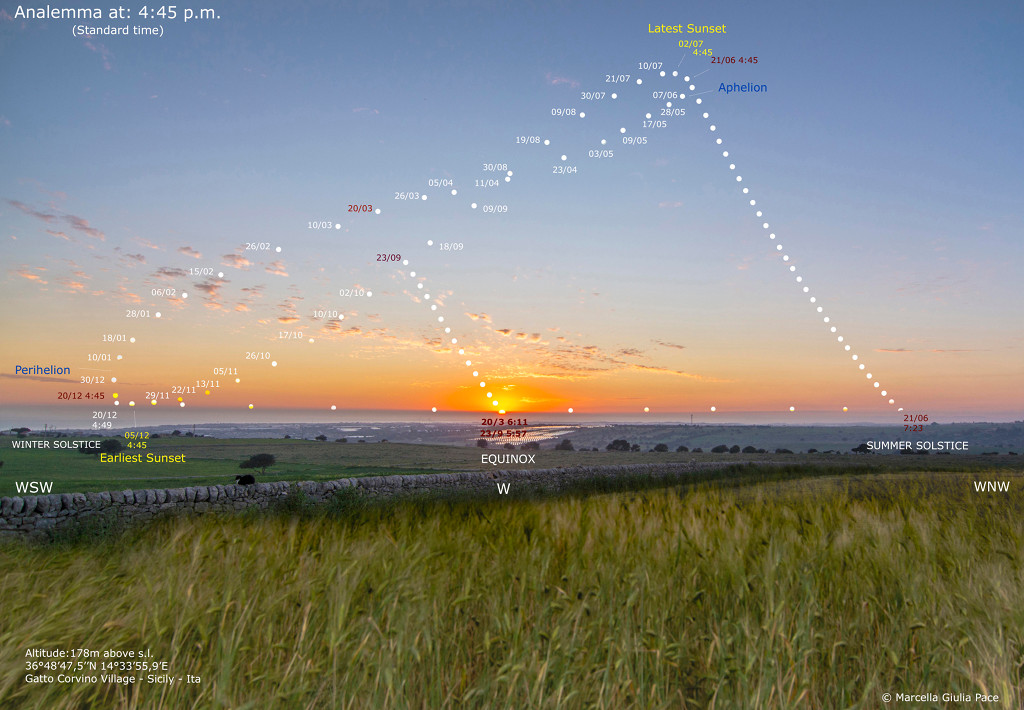
Explanation: Today, the solstice is at 15:54 Universal Time, the Sun reaching the northernmost declination in its yearly journey through planet Earth's sky. A June solstice marks the astronomical beginning of summer in the northern hemisphere and winter in the south. It also brings the north's longest day, the longest period between sunrise and sunset. In fact the June solstice sun is near the top, at the most northern point in the analemma or figure 8 curve traced by the position of the Sun in this composite photo. The analemma was created (video) from images taken every 10 days at the same time from June 21, 2018 and June 7, 2019. The time was chosen to be the year's earliest sunset near the December solstice, so the analemma's lowest point just kisses the unobstructed sea horizon at the left. Sunsets arranged along the horizon toward the right (north) are centered on the sunset at the September equinox and end with sunset at the June solstice.
20/06/2019
Science & Technologie - Avions du futur : La double bulle D8 du MIT

Le D8 « double bulle » du Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) propose une cabine large, pour 180 passagers sur ce projet. Les matériaux composites allègent la cellule et les réacteurs, disposés au-dessus de la cellule (ce qui réduit le bruit), sont à double flux mais avec un flux central (chaud, car sortant de la turbine) très étroit, tandis que le flux périphérique (issu du grand ventilateur frontal) est plus large.
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : Spiral Galaxy M96 from Hubble
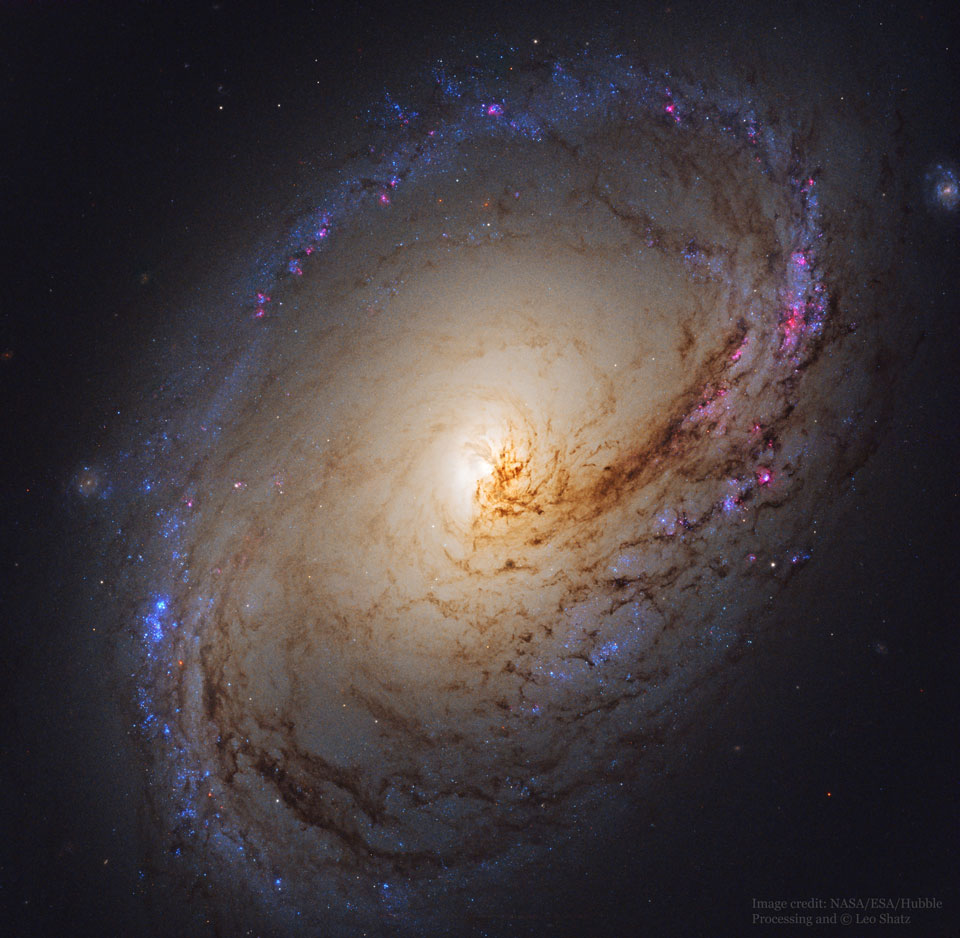

Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble; Processing & Copyright: Leo Shatz
Explanation: Dust lanes seem to swirl around the core of Messier 96 in this colorful, detailed portrait of the center of a beautiful island universe. Of course M96 is a spiral galaxy, and counting the faint arms extending beyond the brighter central region, it spans 100 thousand light-years or so, making it about the size of our own Milky Way. M96, also known as NGC 3368, is known to be about 35 million light-years distant and a dominant member of the Leo I galaxy group. The featured image was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. The reason for M96's asymmetry is unclear -- it could have arisen from gravitational interactions with other Leo I group galaxies, but the lack of an intra-group diffuse glow seems to indicate few recent interactions. Galaxies far in the background can be found by examining the edges of the picture.
19/06/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : Our Galaxy's Magnetic Center
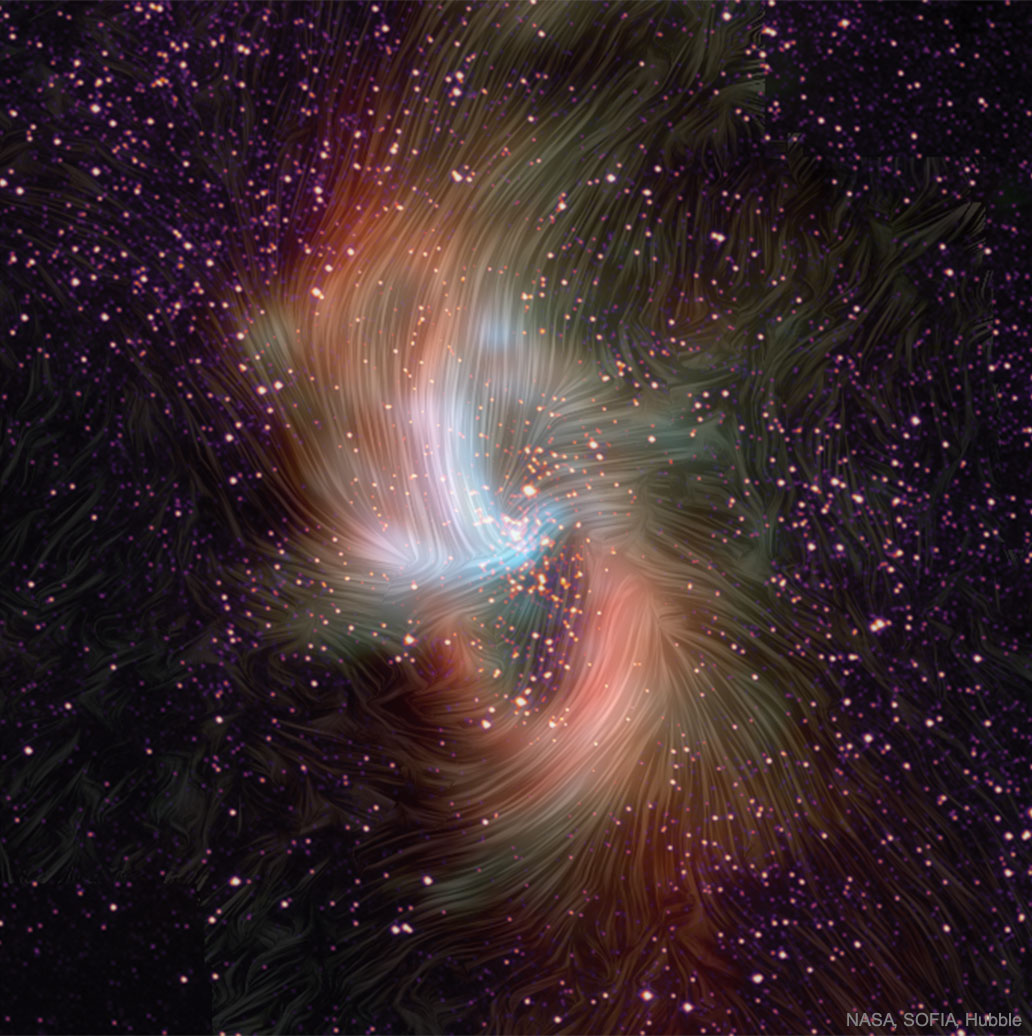

Image Credit: NASA, SOFIA, Hubble
Explanation: What's the magnetic field like in the center of our Milky Way Galaxy? To help find out, NASA's SOFIA -- an observatory flying in a modified 747 -- imaged the central region with an instrument known as HAWC+.HAWC+ maps magnetism by observing polarized infrared light emitted by elongated dust grains rotating in alignment with the local magnetic field. Now at our Milky Way's center is a supermassive black hole with a hobby of absorbing gas from stars it has recently destroyed. Our galaxy's black hole, though, is relatively quiet compared to the absorption rate of the central black holes in active galaxies. The featured image gives a clue as to why -- a surrounding magnetic field may either channel gas into the black hole -- which lights up its exterior, or forces gas into an accretion-disk holding pattern, causing it to be less active -- at least temporarily. Inspection of the featured image -- appearing perhaps like a surreal mashup of impasto art and gravitational astrophysics -- brings out this telling clue by detailing the magnetic field in and around a dusty ring surrounding Sagittarius A*, the black hole in our Milky Way's center.
Inscription à :
Articles (Atom)
ASTRONOMY - Comet C/2025 R2 (SWAN)
2025 September 18 Comet C/2025 R2 (SWAN) Image Credit & Copyright : Team Ciel Austral Explanation: A new visitor from the outer So...

-
2022 September 26 All the Water on Planet Earth Illustration Credit: Jack Cook, Adam Nieman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ; Data ...
-
2024 December 3 Ice Clouds over a Red Planet Image Credit: NASA , JPL-Caltech , Kevin M. Gill ; Processing: Rogelio Bernal Andreo Expla...
