Image Credit & Copyright: Bray Falls
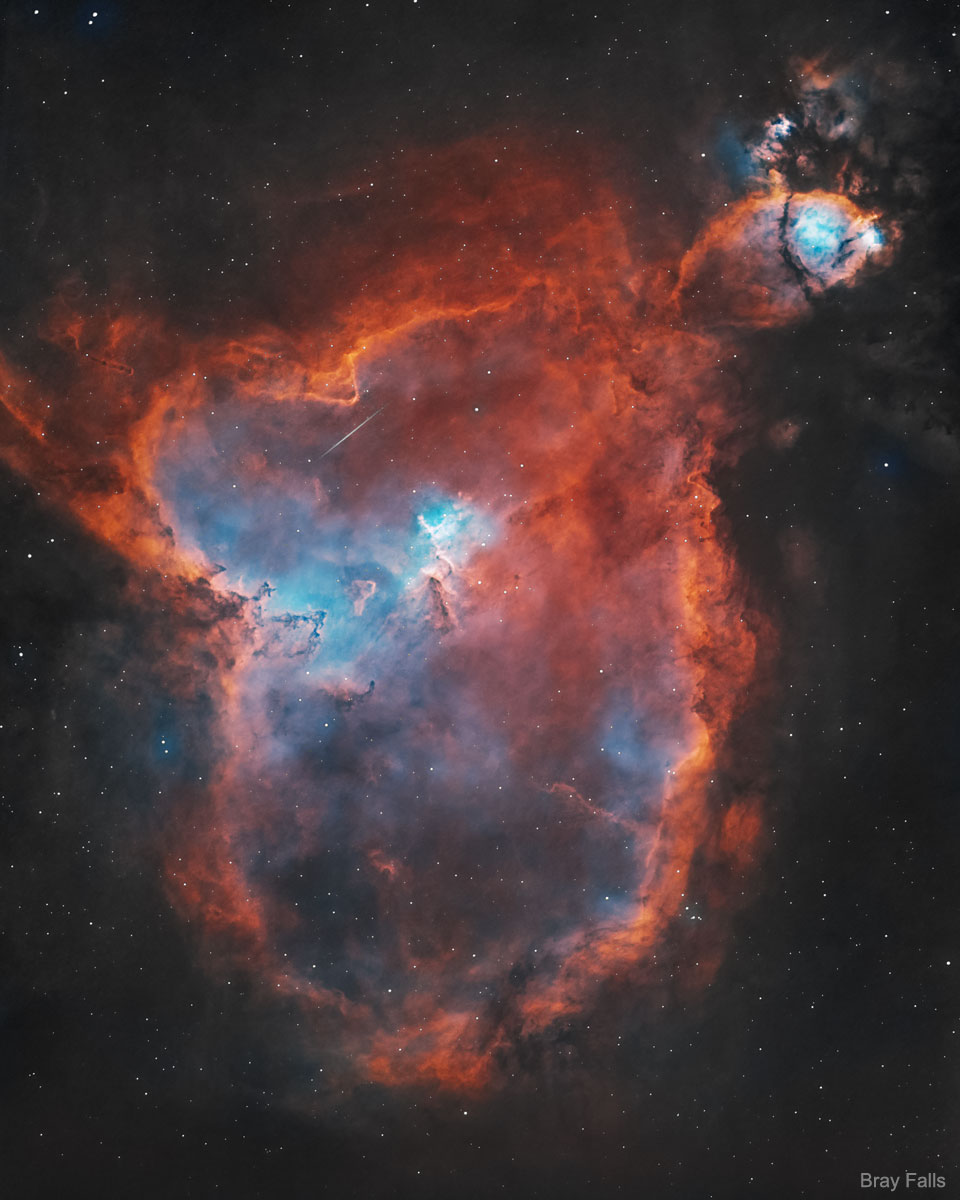
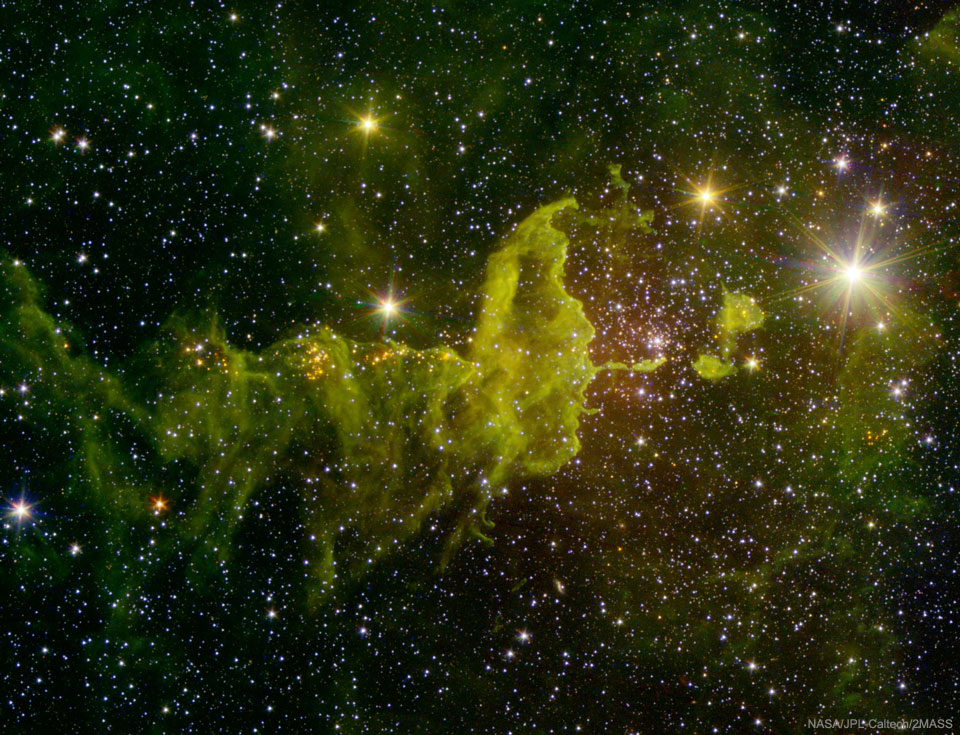
Explanation: What energizes the Heart Nebula? First, the large emission nebula dubbed IC 1805 looks, in whole, like a human heart. The nebula glows brightly in red light emitted by its most prominent element: hydrogen. The red glow and the larger shape are all powered by a small group of stars near the nebula's center. In the center of the Heart Nebula are young stars from the open star cluster Melotte 15 that are eroding away several picturesque dust pillarswith their energetic light and winds. The open cluster of stars contains a few bright stars nearly 50 times the mass of our Sun, many dim stars only a fraction of the mass of our Sun, and an absent microquasar that was expelled millions of years ago. The Heart Nebula is located about 7,500 light years away toward the constellation of Cassiopeia. Coincidentally, a small meteor was captured in the foreground during imaging and is visible above the dust pillars. At the top right is the companion Fishhead Nebula.