"Piano Concerto No. 21 - Andante"
Nombre total de pages vues
14/09/2019
13/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : A Harvest Moon
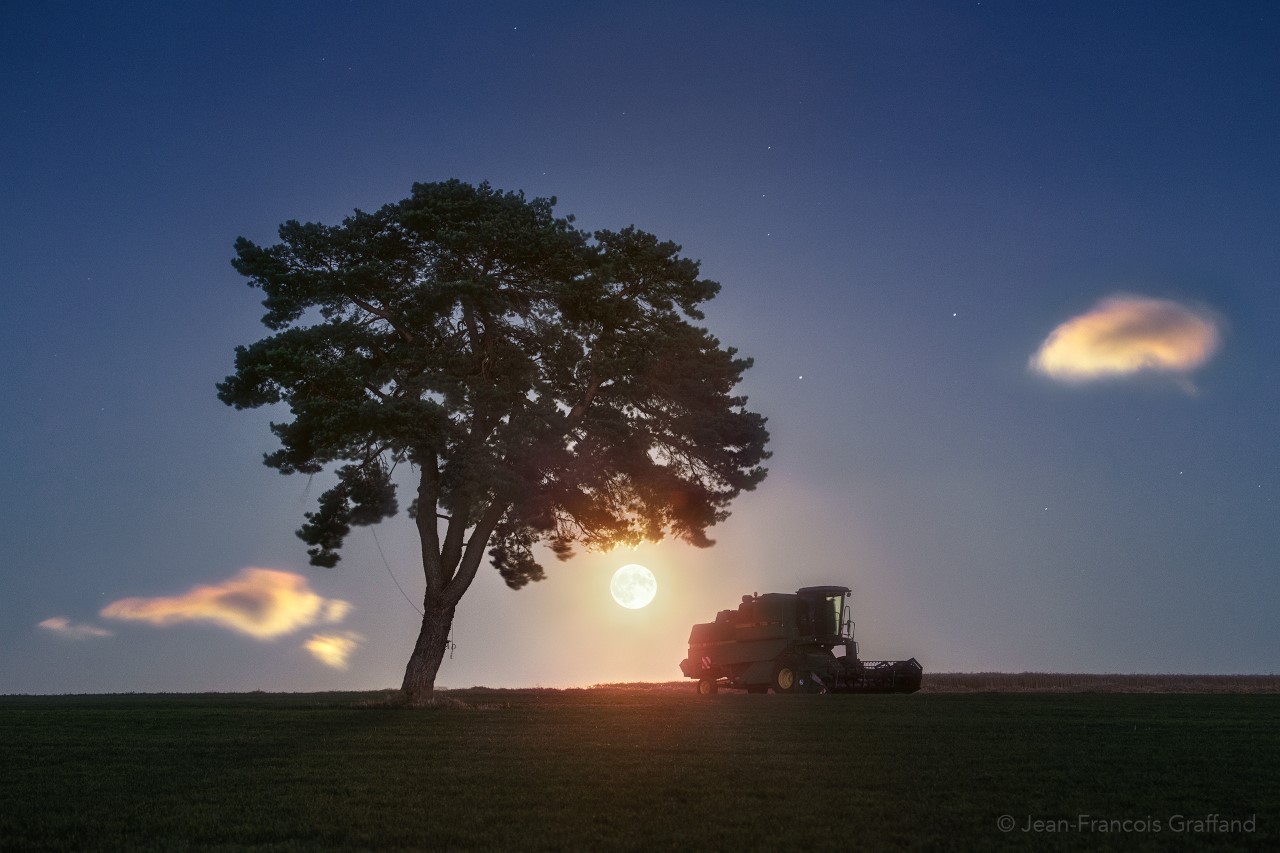

Image Credit & Copyright: Jean-Francois Graffand
Explanation: Famed in festival, story, and song the best known full moon is the Harvest Moon. For northern hemisphere dwellers that's a traditional name of the closest full moon to the September equinox. In most North America time zones this year's Harvest Moon will officially rise on Friday, September 13. In fact the same Harvest Moon will rise on September 14 for much of the planet though. Of course the Moon will look almost full in the surrounding days. Regardless of your time zone the Harvest Moon, like any other full moon, will rise just opposite the setting Sun. Near the horizon, the Moon Illusion might make it appear bigger and brighter to you but this Harvest Moon will be nearlunar apogee. That's the closest point in its orbit, making it the most distant, and so the smallest, full moon of the year. On August 15 a wheat field harvested in south central France made this a harvest moon scene too, the full moon shining on with beautiful iridescent clouds at sunset.
11/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : IC 1805: The Heart Nebula
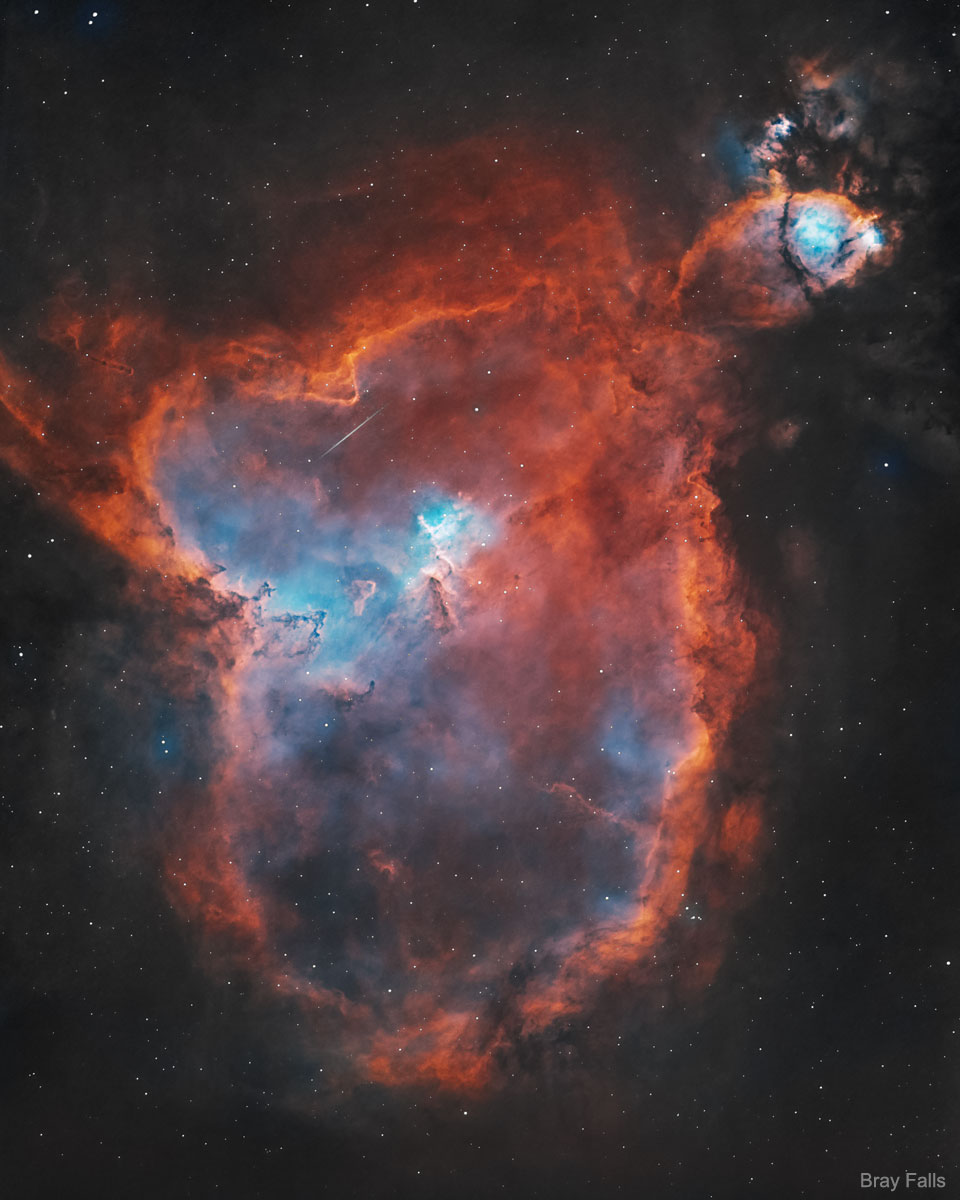

Image Credit & Copyright: Bray Falls
Explanation: What energizes the Heart Nebula? First, the large emission nebula dubbed IC 1805 looks, in whole, like a human heart. The nebula glows brightly in red light emitted by its most prominent element: hydrogen. The red glow and the larger shape are all powered by a small group of stars near the nebula's center. In the center of the Heart Nebula are young stars from the open star cluster Melotte 15 that are eroding away several picturesque dust pillarswith their energetic light and winds. The open cluster of stars contains a few bright stars nearly 50 times the mass of our Sun, many dim stars only a fraction of the mass of our Sun, and an absent microquasar that was expelled millions of years ago. The Heart Nebula is located about 7,500 light years away toward the constellation of Cassiopeia. Coincidentally, a small meteor was captured in the foreground during imaging and is visible above the dust pillars. At the top right is the companion Fishhead Nebula.
10/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : "Pluto in True Color"
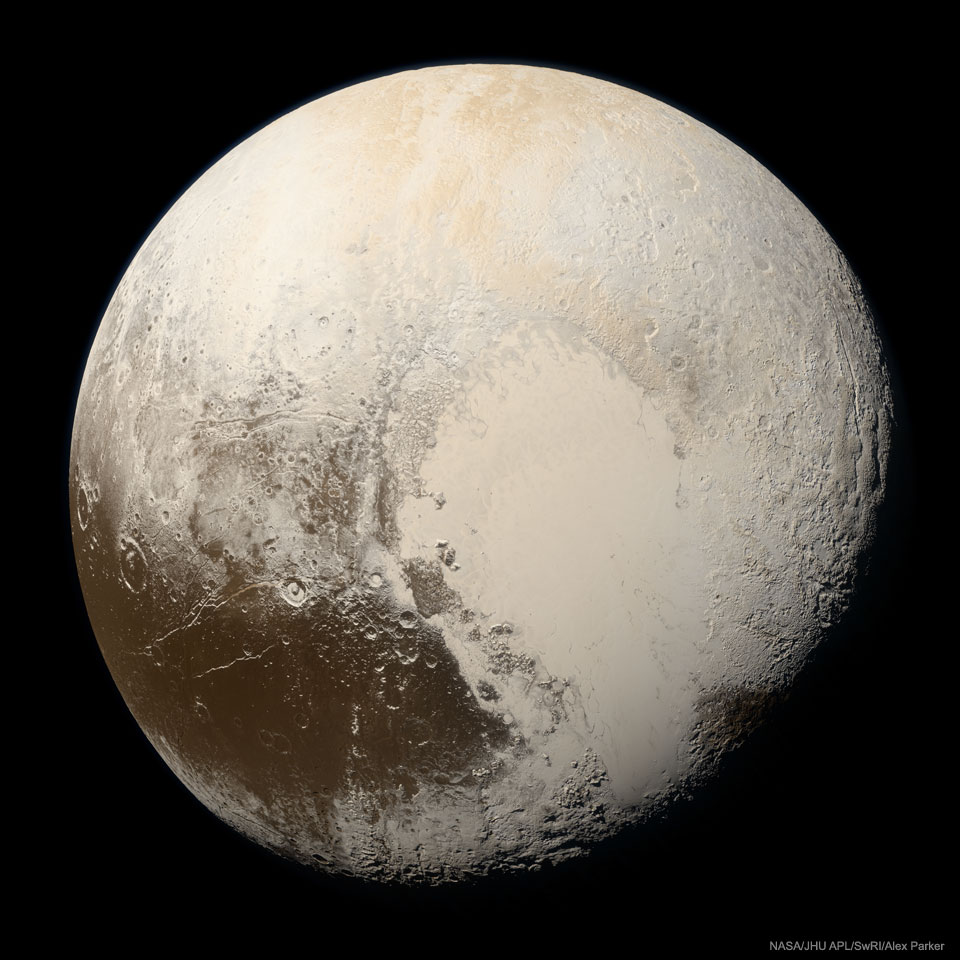

Image Credit: NASA, JHU APL, SwRI, Alex Parker
Explanation: What color is Pluto, really? It took some effort to figure out. Even given all of the images sent back to Earth when the robotic New Horizons spacecraft sped past Pluto in 2015, processing these multi-spectral frames to approximate what the human eye would see was challenging. The result featured here, released three years after the raw data was acquired by New Horizons, is the highest resolution true color image of Pluto ever taken. Visible in the image is the light-colored, heart-shaped, Tombaugh Regio, with the unexpectedly smooth Sputnik Planitia, made of frozen nitrogen, filling its western lobe. New Horizons found the dwarf-planet to have a surprisingly complex surfacecomposed of many regions having perceptibly different hues. In total, though, Pluto is mostly brown, with much of its muted color originating from small amounts of surface methane energized by ultraviolet light from the Sun.
09/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : M31: The Andromeda Galaxy
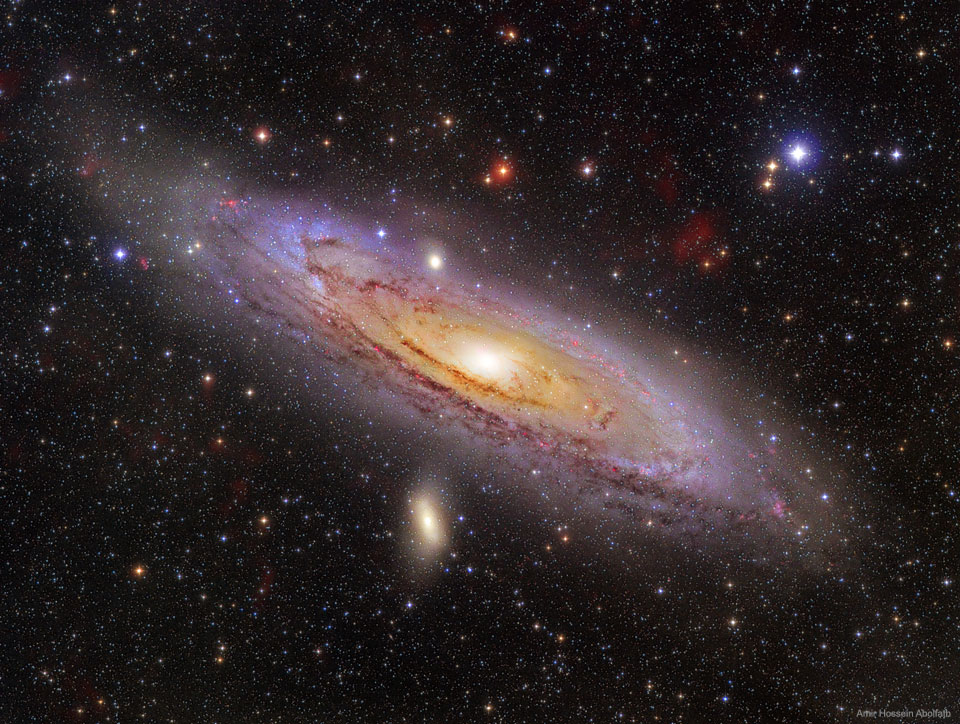

Image Credit & Copyright: Amir H. Abolfath (TWAN)
Explanation: How far can you see? The most distant object easily visible to the unaided eye is M31, the great Andromeda Galaxy, over two million light-years away. Without a telescope, even this immense spiral galaxy appears as an unremarkable, faint, nebulous cloud in the constellation Andromeda. But a bright yellow nucleus, dark winding dust lanes, luminous blue spiral arms, and bright red emission nebulas are recorded in this stunning six-hour telescopic digital mosaic of our closest major galactic neighbor. While even casual skygazers are now inspired by the knowledge that there are many distant galaxies like M31, astronomers seriously debated this fundamental concept only 100 years ago. Were these "spiral nebulae" simply outlying gas clouds in our own Milky Way Galaxy or were they "island universes" -- distant galaxies of stars comparable to the Milky Way itself? This question was central to the famous Shapley-Curtis debate of 1920, which was later resolved by observations favoring Andromeda being just like our Milky Way Galaxy -- a conclusion making the rest of the universe much more vast than many had ever imagined.
07/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : In Wolf's Cave
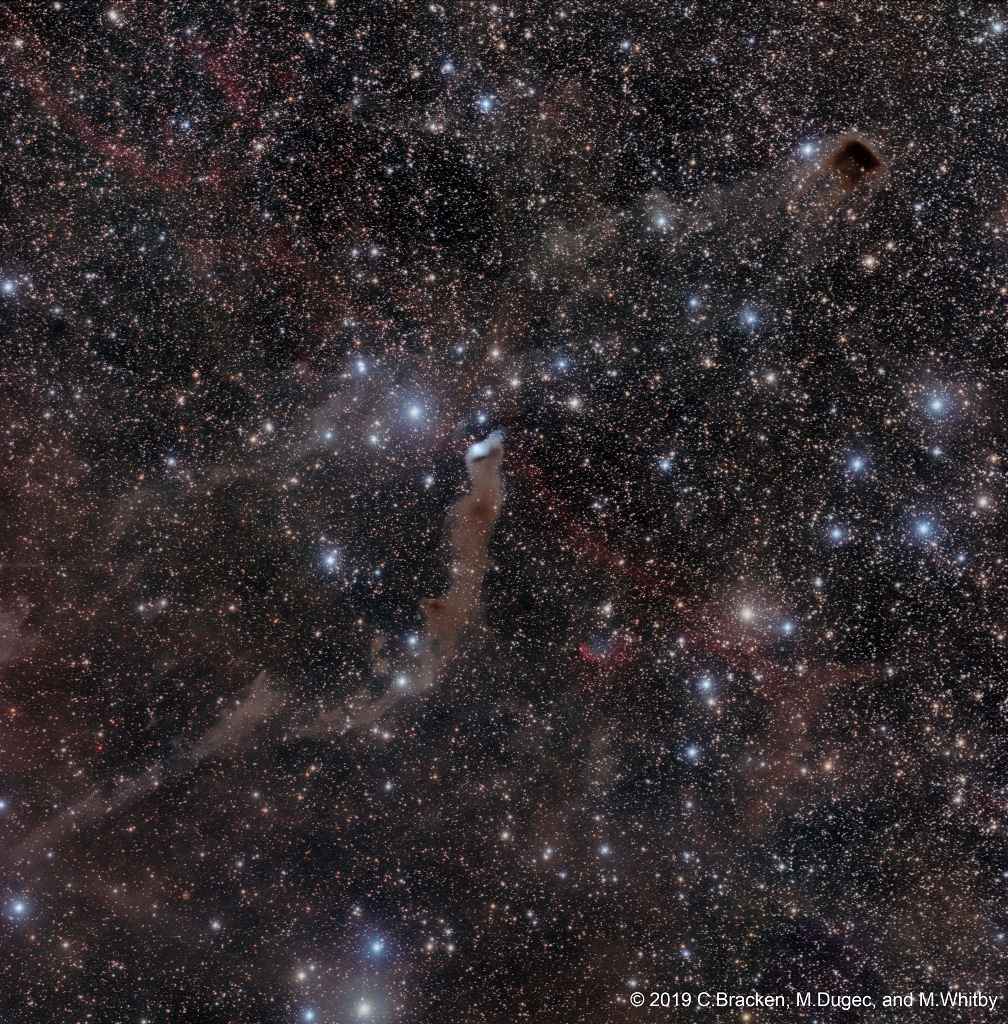

Explanation: The mysterious blue reflection nebula found in catalogs as VdB 152 or Ced 201 really is very faint. It lies at the tip of the long dark nebula Barnard 175 in a dusty complex that has also been called Wolf's Cave. At the center of this deep and widefield telescopic view, the cosmic apparitions are nearly 1,400 light-years away along the northern Milky Way in the royal constellation Cepheus. Near the edge of a large molecular cloud, pockets of interstellar dust in the region block light from background stars or scatter light from the embedded bright star giving the the nebula its characteristic blue color. Ultraviolet light from the star is also thought to cause a dim reddish luminescence in the nebular dust. Though stars do form in molecular clouds, this star seems to have only accidentally wandered into the area, as its measured velocity through space is very different from the cloud's velocity. Another dense, obscuring dark nebula, LDN 1221, is easy to spot at the upper right in the frame, while the more colorful planetary nebula Dengel-Hartl 5 is just below center. Faint reddish emission from an ancient supernova remnant can also be traced (lower right to upper left) against the dust-rich complex in Cepheus.
06/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : Recycling Cassiopeia A
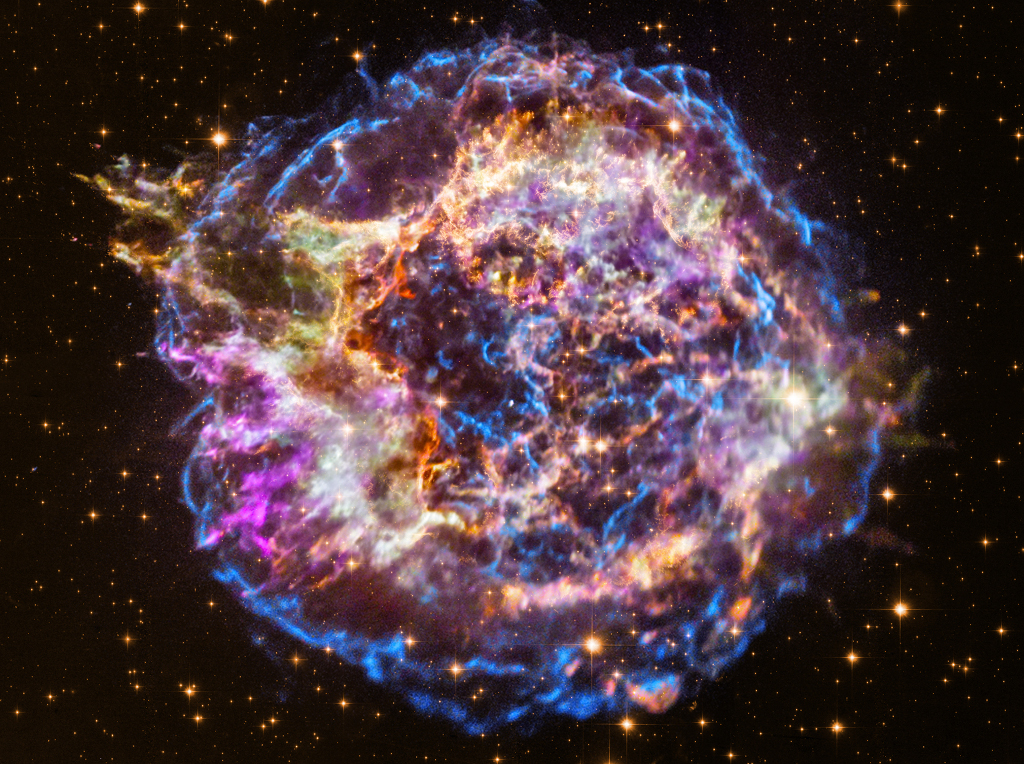

Image Credit: X-ray - NASA, CXC, SAO; Optical - NASA,STScI
Explanation: Massive stars in our Milky Way Galaxy live spectacular lives. Collapsing from vast cosmic clouds, their nuclear furnaces ignite and create heavy elements in their cores. After a few million years, the enriched material is blasted back into interstellar space where star formation can begin anew. The expanding debris cloud known as Cassiopeia A is an example of this final phase of the stellar life cycle. Light from the explosion which created this supernova remnant would have been first seen in planet Earth's sky about 350 years ago, although it took that light about 11,000 years to reach us. This false-color image, composed of X-ray and optical image data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope, shows the still hot filaments and knots in the remnant. It spans about 30 light-years at the estimated distance of Cassiopeia A. High-energy X-ray emission from specific elements has been color coded, silicon in red, sulfur in yellow, calcium in green and iron in purple, to help astronomers explore the recycling of our galaxy's star stuff. Still expanding, the outer blast wave is seen in blue hues. The bright speck near the center is a neutron star, the incredibly dense, collapsed remains of the massive stellar core.
05/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : The Large Cloud of Magellan
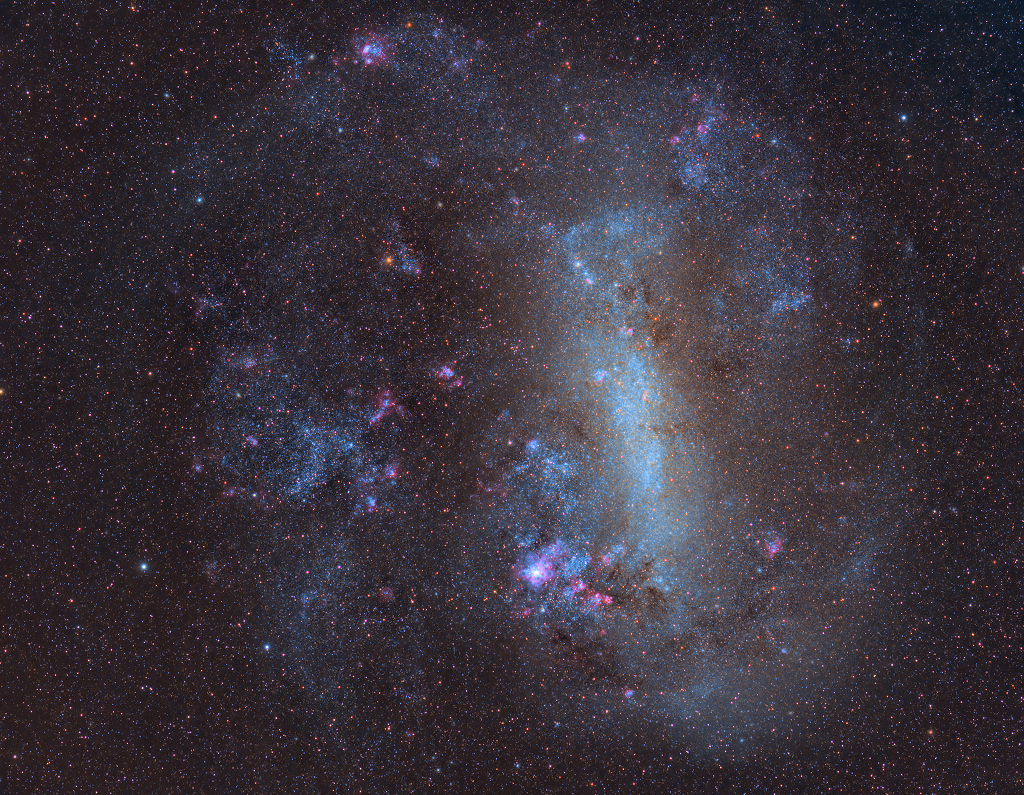

Image Credit & Copyright: Alessandro Cipolat Bares
Explanation: The 16th century Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the southern sky during the first circumnavigation of planet Earth. As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like objects easily visible to southern hemisphere skygazers are known as the Clouds of Magellan, now understood to be satellite galaxies of our much larger, spiral Milky Way galaxy. About 160,000 light-years distant in the constellation Dorado, the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is seen here in a remarkably deep, colorful, image. Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is the most massive of the Milky Way's satellite galaxies and is the home of the closest supernova in modern times,SN 1987A. The prominent patch below center is 30 Doradus, also known as the magnificent Tarantula Nebula, a giant star-forming region about 1,000 light-years across.
Science & Technologie - Astronomie - HOJE, AUJOURD'HUI, TODAY : Triangle Lune Jupiter Antarès
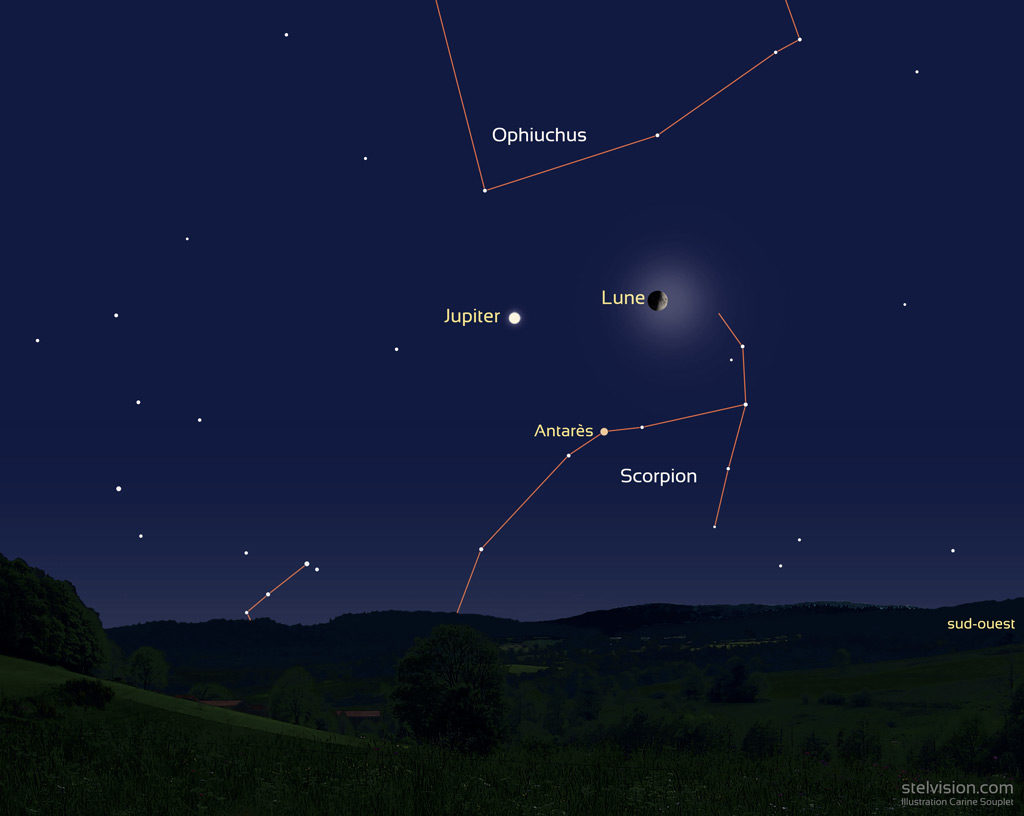
Jeudi 5 septembre à la nuit tombante, la Lune, Jupiter et Antarès forment un triangle visible à l’œil nu.
Alors que la journée se termine en ce jeudi 5 septembre, recherchez sur l’horizon sud sud-ouest la Lune au premier quartier. A peu près à la même hauteur mais plus à l’est, la brillante planète Jupiter se repère facilement même avant la nuit. Ces deux astres matérialisent deux des trois sommets d’un triangle céleste remarquable et presque équilatéral.
Pour voir le troisième sommet du triangle, il faut attendre que la nuit s’installe un peu, vers 21h (heure de Paris). Vous distinguerez alors sans peine la brillante étoile orangée Antarès située dans la constellation du Scorpion, plus près de l’horizon. L’ensemble s’observe jusqu’aux environs de 22h30, heure à laquelle Antarès se couche.Notre satellite, une planète géante gazeuse et une étoile supergéante joliment colorée, voilà un joli trio à observer pour faire sa rentrée astronomique !
Stelvision
04/09/2019
Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day : The Spider Nebula in Infrared
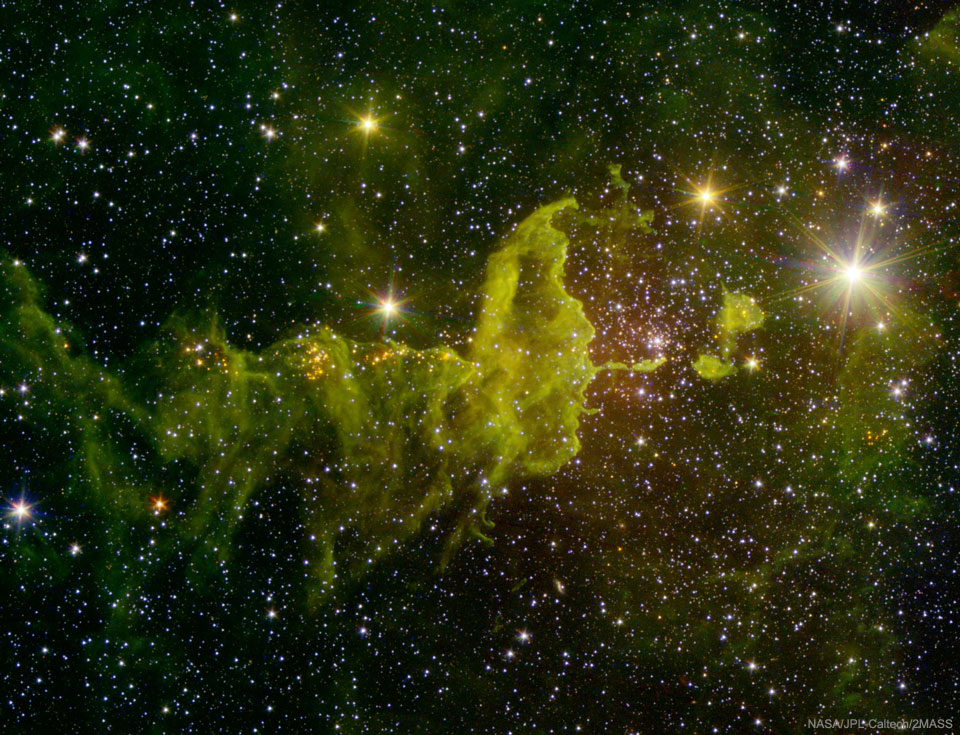

Explanation: Will the spider ever catch the fly? Not if both are large emission nebulas toward the constellation of the Charioteer (Auriga). The spider-shaped gas cloud on the left is actually an emission nebula labelled IC 417, while the smaller fly-shaped cloud on the right is dubbed NGC 1931 and is both an emission nebula and a reflection nebula. About 10,000 light-years distant, both nebulas harbor young, open star clusters. For scale, the more compact NGC 1931 (Fly) is about 10 light-years across. The featured picture in scientifically-assigned, infrared colors combines images from the Spitzer Space Telescope and the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS). Spitzer is celebrating its 16th year orbiting the Sun near the Earth.
Inscription à :
Commentaires (Atom)
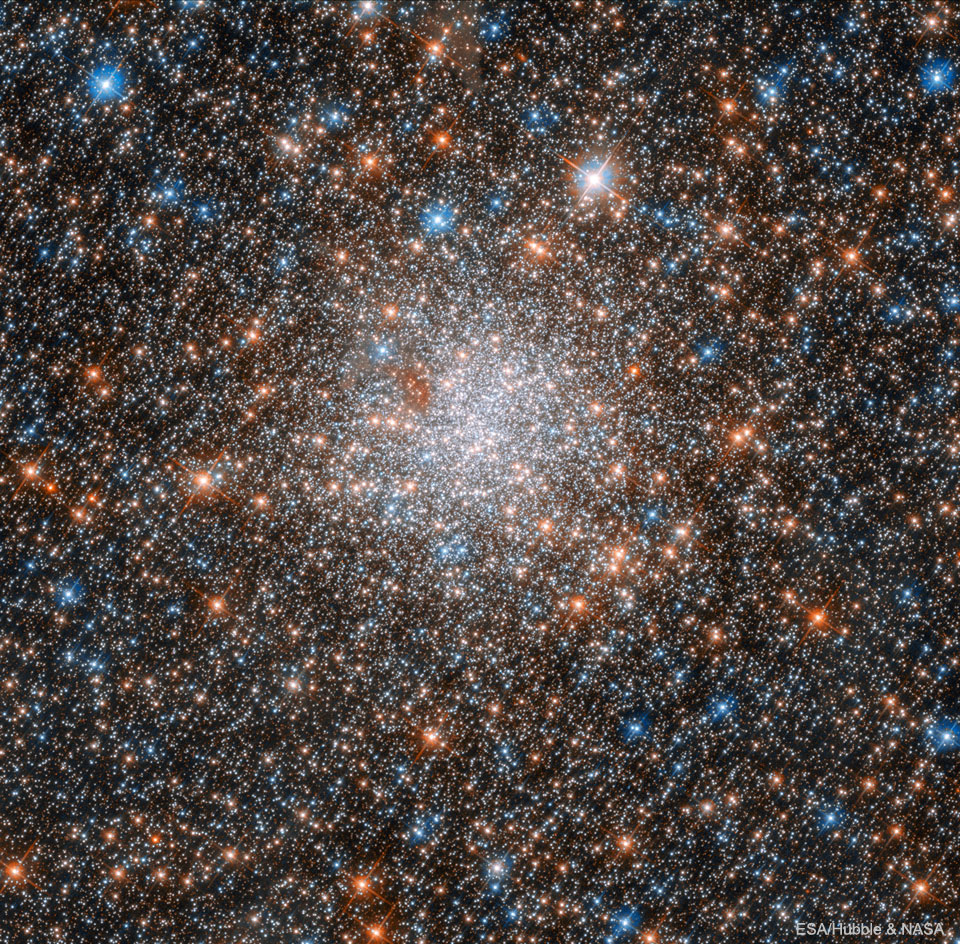
ASTRONOMY - NGC 1898: Globular Cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud
025 December 28 NGC 1898: Globular Cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud Image Credit: ESA / Hubble & NASA Explanation: Jewels don...

-
2022 September 26 All the Water on Planet Earth Illustration Credit: Jack Cook, Adam Nieman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ; Data ...
-
2025 May 11 The Surface of Venus from Venera 14 Image Credit: Soviet Planetary Exploration Program , Venera 14 ; Processing & Copyri...