2020 November 27
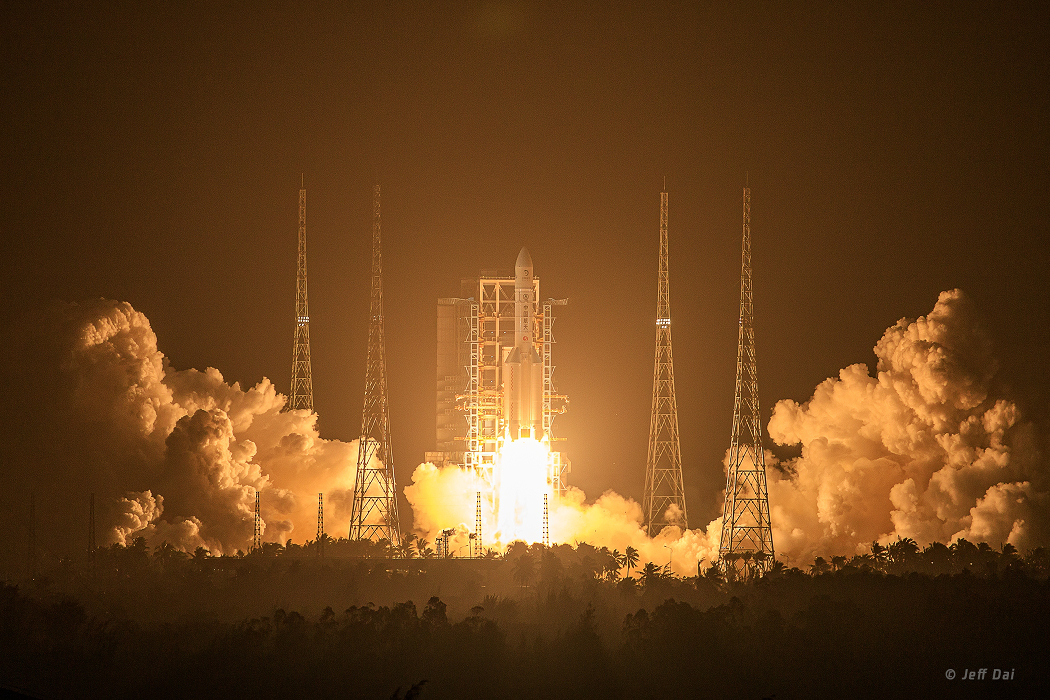
Image Credit & Copyright: Jeff Dai (TWAN)
Explanation: This Long March-5 rocket blasted off from the Wenchang launch site in southernmost Hainan province on Tuesday November 24, at 4:30 am Beijing Time, carrying China's Chang'e-5 mission to the Moon. The lunar landing mission is named for the ancient Chinese goddess of the moon. Its goal is to collect about 2 kilograms (4.4 pounds) of lunar material from the surface and return it to planet Earth, the first robotic sample return mission to the Moon since the Soviet Union's Luna 24 mission in 1976. The complex Chang'e-5 mission landing target is in the Oceanus Procellarum (Ocean of Storms). The smooth volcanic plain was also visited by the Apollo 12 mission in 1969. Chang'e-5's lander is solar-powered and scheduled to operate on the lunar surface during its location's lunar daylight, which will last about two Earth weeks, beginning around November 27. A capsule with the lunar sample on board would return to Earth in mid-December.