2021 March 29
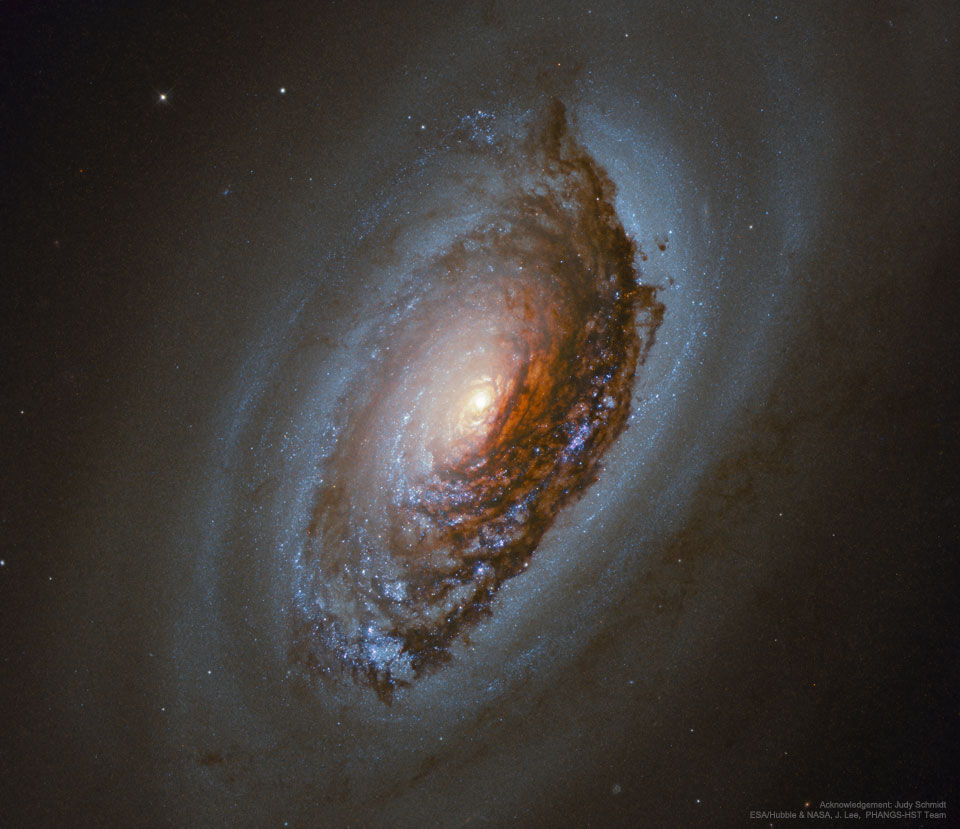
Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA & the PHANGS-HST Team; Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt
Explanation: Who knows what evil lurks in the eyes of galaxies? The Hubble knows -- or in the case of spiral galaxy M64 -- is helping to find out. Messier 64, also known as the Evil Eye or Sleeping Beauty Galaxy, may seem to have evil in its eye because all of its stars rotate in the same direction as the interstellar gas in the galaxy's central region, but in the opposite direction in the outer regions. Captured here in great detail by the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope, enormous dust clouds obscure the near-side of M64's central region, which are laced with the telltale reddish glow of hydrogen associated with star formation. M64 lies about 17 million light years away, meaning that the light we see from it today left when the last common ancestor between humans and chimpanzees roamed the Earth. The dusty eye and bizarre rotation are likely the result of a billion-year-old merger of two different galaxies.