2021 July 18
Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, GALEX
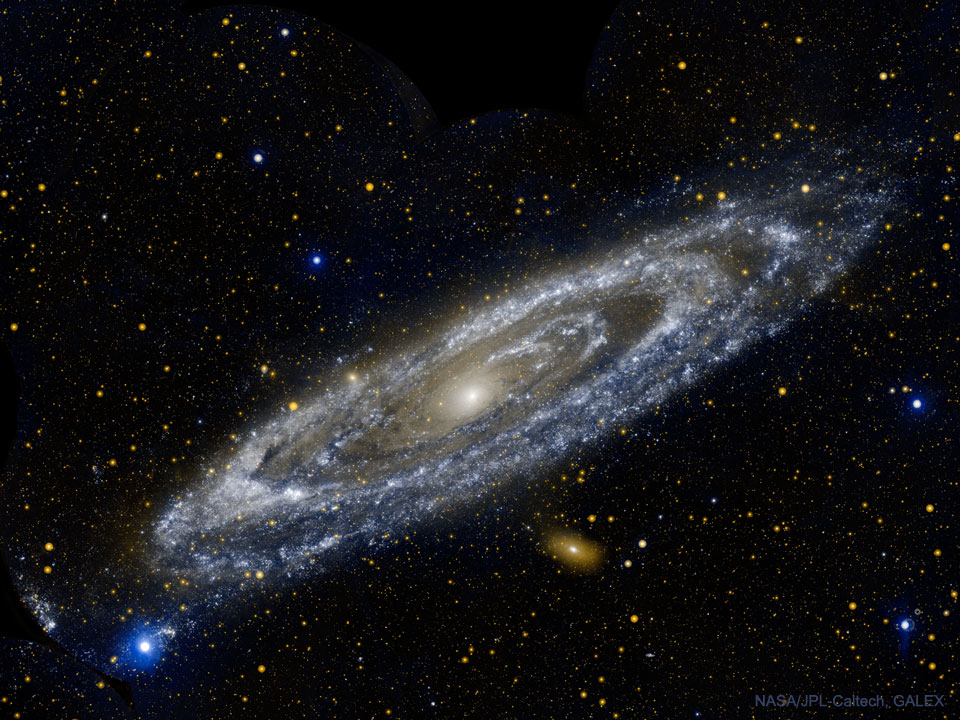
Explanation: What does the Andromeda galaxy look like in ultraviolet light? Young blue stars circling the galactic center dominate. A mere 2.5 million light-years away, the Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31, really is just next door as large galaxies go. Spanning about 230,000 light-years, it took 11 different image fields from NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) satellite telescope to produce this gorgeous portrait of the spiral galaxy in ultraviolet light in 2003. While its spiral arms stand out in visible light images, Andromeda's arms look more like rings in ultraviolet. The rings are sites of intense star formation and have been interpreted as evidence that Andromeda collided with its smaller neighboring elliptical galaxy M32 more than 200 million years ago. The Andromeda galaxy and our own comparable Milky Way galaxy are the most massive members of the Local Group of galaxies and are projected to collide in several billion years -- perhaps around the time that our Sun's atmosphere will expand to engulf the Earth.