Nombre total de pages vues
04/09/2021
POURQUOI - Pourquoi rêve-t-on ?
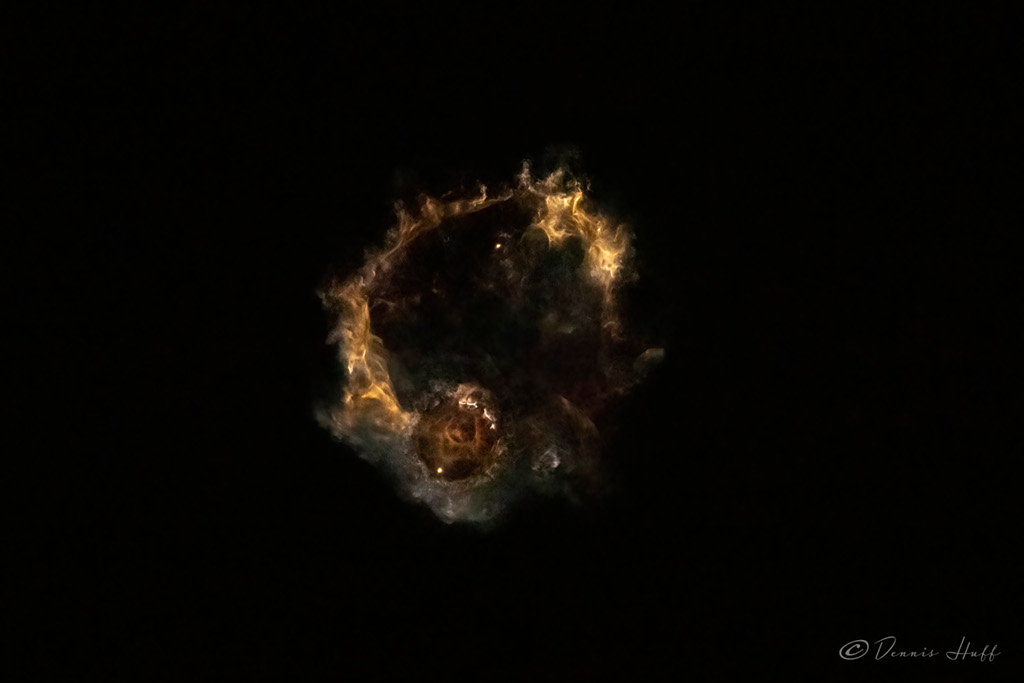
ASTRONOMY - A Falcon 9 Nebula
2021 September 4
Image Credit & Copyright: Dennis Huff
Explanation: Not the Hubble Space Telescope's latest view of a distant galactic nebula, this illuminated cloud of gas and dust dazzled early morning spacecoast skygazers on August 29. The snapshot was taken at 3:17am from Space View Park in Titusville, Florida. That's about 3 minutes after the launch of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the CRS-23 mission to resupply the International Space Station. It captures drifting plumes and exhaust from the separated first and second stage of the rocket rising through still dark skies. The lower bright dot is the second stage continuing on to low Earth orbit. The upper one is the rocket's first stage performing a boostback burn. Of course the first stage booster returned to make the first landing on the latest autonomous drone ship to arrive in the Atlantic, A Short Fall of Gravitas.
03/09/2021
02/09/2021
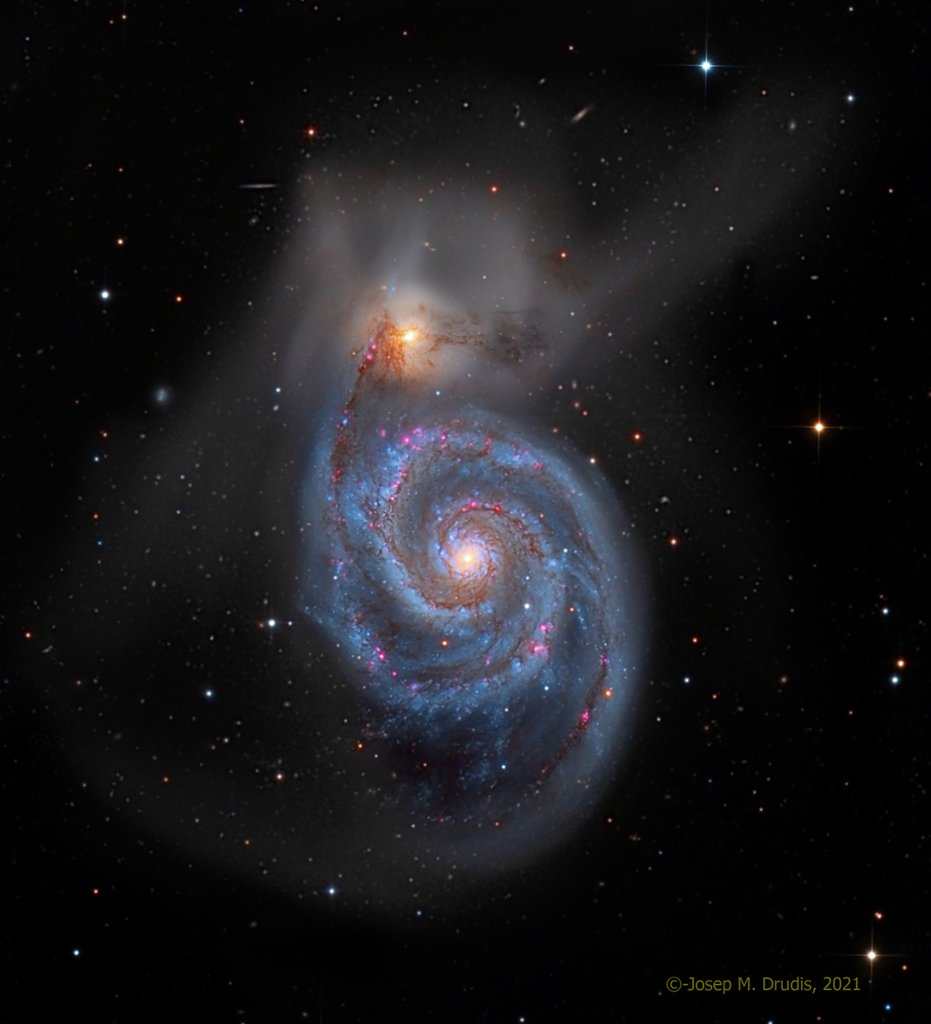
ASTRONOMY - M51: The Whirlpool Galaxy
2021 September 2
Image Credit & Copyright: Josep Drudis
Explanation: Find the Big Dipper and follow the handle away from the dipper's bowl until you get to the last bright star. Then, just slide your telescope a little south and west and you'll come upon this stunning pair of interacting galaxies, the 51st entry in Charles Messier's famous catalog. Perhaps the original spiral nebula, the large galaxy with well defined spiral structure is also cataloged as NGC 5194. Its spiral arms and dust lanes clearly sweep in front of its companion galaxy (top), NGC 5195. The pair are about 31 million light-years distant and officially lie within the angular boundaries of the small constellation Canes Venatici. Though M51 looks faint and fuzzy to the eye, deep images like this one reveal its striking colors and galactic tidal debris.
01/09/2021
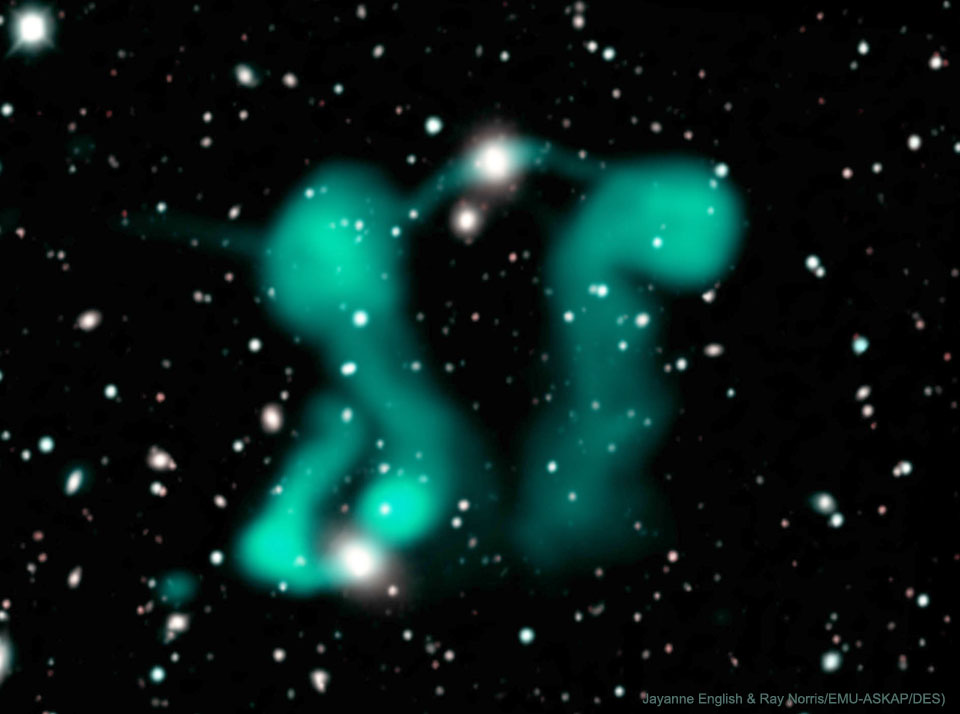
ASTRONOMY - Dancing Ghosts: Curved Jets from Active Galaxies
Image Credit: Jayanne English & Ray Norris, EMU-ASKAP, DES; Text: Jayanne English (U. Manitoba)
Explanation: Why would galaxies emit jets that look like ghosts? And furthermore, why do they appear to be dancing? The curled and fluffy jets from the supermassive black holes at the centers of two host galaxies (top center and lower left) are unlike anything seen before. They were found by astronomers using the Australian Square Kilometer Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) radio telescope when creating maps tracing the evolution of galaxies. Images preceding this Evolutionary Map of the Universe survey only showed amorphous blobs. Eventually, comparisons of relative amounts of energy emitted revealed the glowing elongated structures were created by electrons streaming around magnetic field lines. Overlaying the radio data on an optical view of the sky (Dark Energy Survey) confirmed that the electron streams originated from the centers of active galaxies. Usually such Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) produce straight jets. A leading hypothesis for the geometric origin of these unusually graceful shapes involves the flow of large-scale intergalactic winds.
29/08/2021
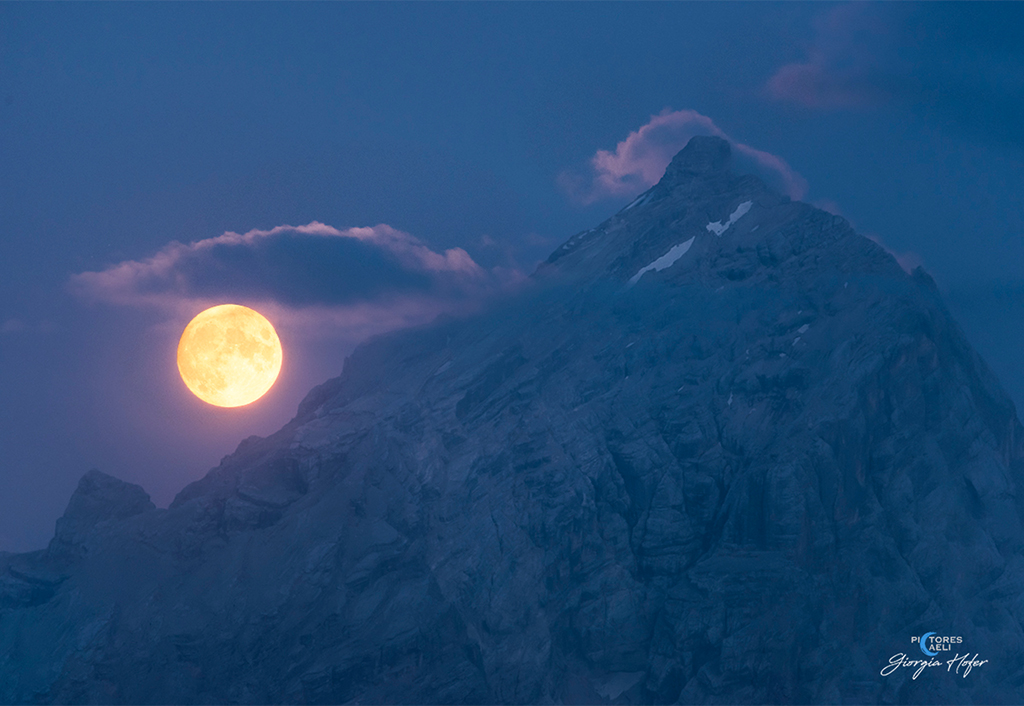
ASTRONOMY - A Blue Hour Full Moon
2021 August 26
Image Credit & Copyright: Giorgia Hofer
Explanation: Nature photographers and other fans of planet Earth always look forward to the blue hour. That's the transition in twilight, just before sunrise or after sunset, when the Sun is below the horizon but land and sky are still suffused with a beautiful blue light. After sunset on August 21, this blue hour snapshot captured the nearly full Moon as it rose opposite the Sun, above the rugged Italian Alps from Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy. Sharing bluish hues with the sky, the rocky pyramid of Monte Antelao, also known as the King of the Dolomites, is the region's prominent alpine peak. The moonlight is yellow, but even so this full Moon was known to some as a seasonal Blue Moon. That's because by one definition the third full Moon of a season with four full moons in it is called a Blue Moon. Recognizing a season as the time between a solstice and an equinox, this season's fourth full Moon will be rising in the blue hour of September 20, just before September's equinox.
28/08/2021
MINERAUX - Le sélénite, une pierre de lune
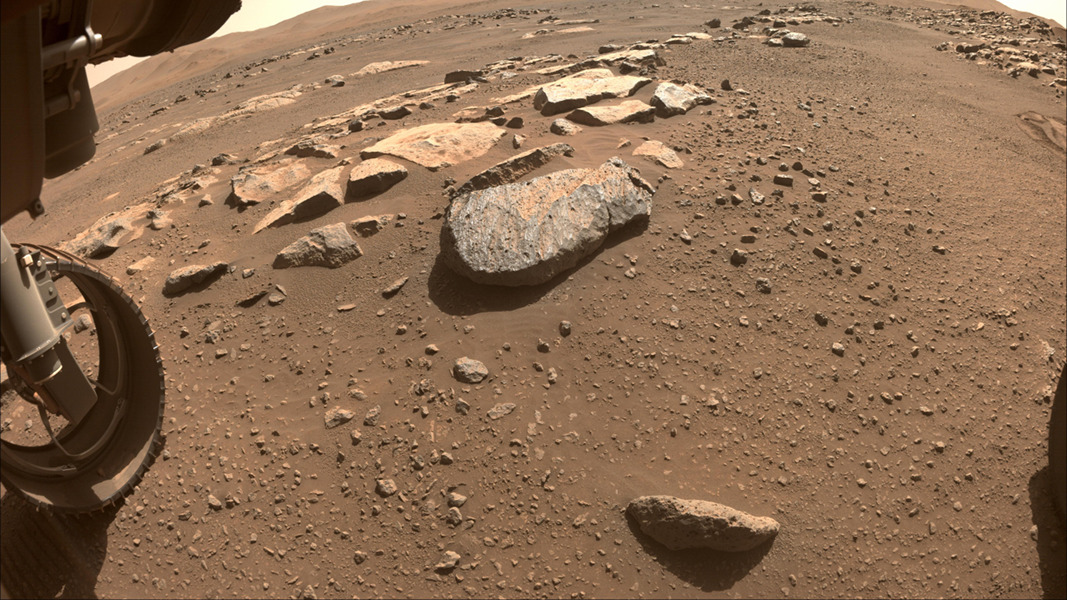
ASTRONOMY - Mars Rock Rochette
2021 August 28
Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech
Explanation: Taken on mission sol 180 (August 22) this sharp image from a Hazard Camera on the Perseverance rover looks out across a rock strewn floor of Jezero crater on Mars. At 52.5 centimeters (21 inches) in diameter, one of the rover's steerable front wheels is at lower left in the frame. Near center is a large rock nicknamed Rochette. Mission planners don't want to avoid Rochette though. Instead Perseverance will be instructed to reach out with its 2 meter long robotic arm and abrade the rock's surface, to determine whether it has a consistency suitable for obtaining a sample, slightly thicker than a pencil, using the rover's coring bit. Samples collected by Perseverance would be returned to Earth by a future Mars mission.
25/08/2021
ASTRONOMY - Solar System Ball Drop
2021 August 25
Video Credit & Copyright: James O'Donoghue (JAXA) & Rami Mandow (Space Australia); Text: James O'Donoghue
Explanation: Does a ball drop faster on Earth, Jupiter, or Uranus? The featured animation shows a ball dropping from one kilometer high toward the surfaces of famous solar system bodies, assuming no air resistance. The force of gravity depends on the mass of the attracting object, with higher masses pulling down with greater forces. But gravitational force also depends on distance from the center of gravity, with shorter distances causing the ball to drop faster. Combining both mass and distance, it might be surprising to see that Uranus pulls the ball down slightly slower than Earth, despite containing over 14 times more mass. This happens because Uranus has a much lower density, which puts its cloud tops further away from its center of mass. Although the falling ball always speeds up, if you were on the ball you would not feel this acceleration because you would be in free-fall. Of the three planets mentioned, the video demonstrates a ball drops even faster on Jupiter than either Earth and Uranus.
24/08/2021
PRATIQUE - Comment Déboucher Un Évier En 3 Étapes Faciles
L'évier de la cuisine est complètement bouché ? Il reflue et en plus, ça pue dans la maison ? Et pour ne rien arranger, ça tombe un dimanche.... Heureusement, mon plombier m'a partagé une astuce super efficace pour déboucher un évier facilement. C'est une méthode rapide et économique en 3 étapes faciles. Elle évite d'appeler un plombier ou d'utiliser des produits toxiques comme le Destop. L'astuce naturelle est de mettre du bicarbonate, du vinaigre blanc et enfin de l'eau bouillante. Regardez :
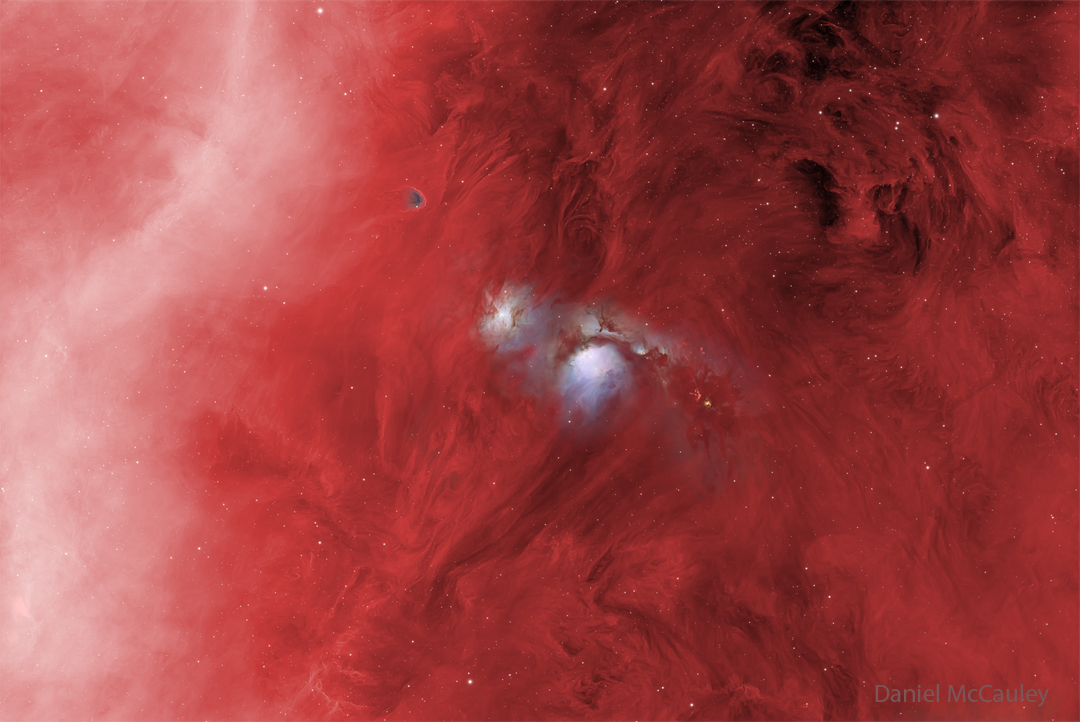
ASTRONOMY - M78: Reflecting Blue in a Sea of Red
2026 January 28 M78: Reflecting Blue in a Sea of Red Image Credit & Copyright: Daniel McCauley Explanation: In the vast Orion Molecu...

-
2022 September 26 All the Water on Planet Earth Illustration Credit: Jack Cook, Adam Nieman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ; Data ...
-
2025 May 11 The Surface of Venus from Venera 14 Image Credit: Soviet Planetary Exploration Program , Venera 14 ; Processing & Copyri...