2021 September 23
Image Credit & Copyright: Mike Cohea
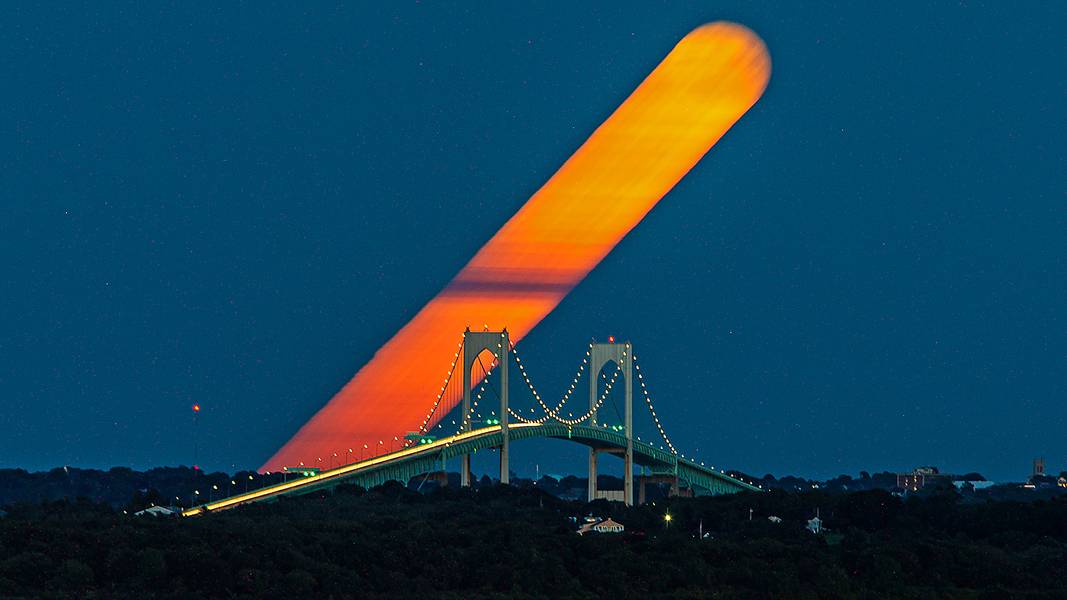
Explanation: Famed in festival, story, and song the best known full moon is the Harvest Moon. For northern hemisphere dwellers that's a traditional name of the full moon nearest the September equinox. Seen from Saunderstown, Rhode Island, planet Earth, this Harvest Moon left a broad streak of warm hues as it rose through a twilight sky over the Newport Bridge. On September 20 its trail was captured in a single 22 minute exposure using a dense filter and a digital camera. Only two days later the September equinox marked a change of season and the beginning of autumn in the north. In fact, recognizing a season as the time between solstice and equinox, this Harvest Moon was the fourth full moon of the season, coming just before the astronomical end of northern summer.