2021 November 1
Image Credit & Copyright: Xie Jie
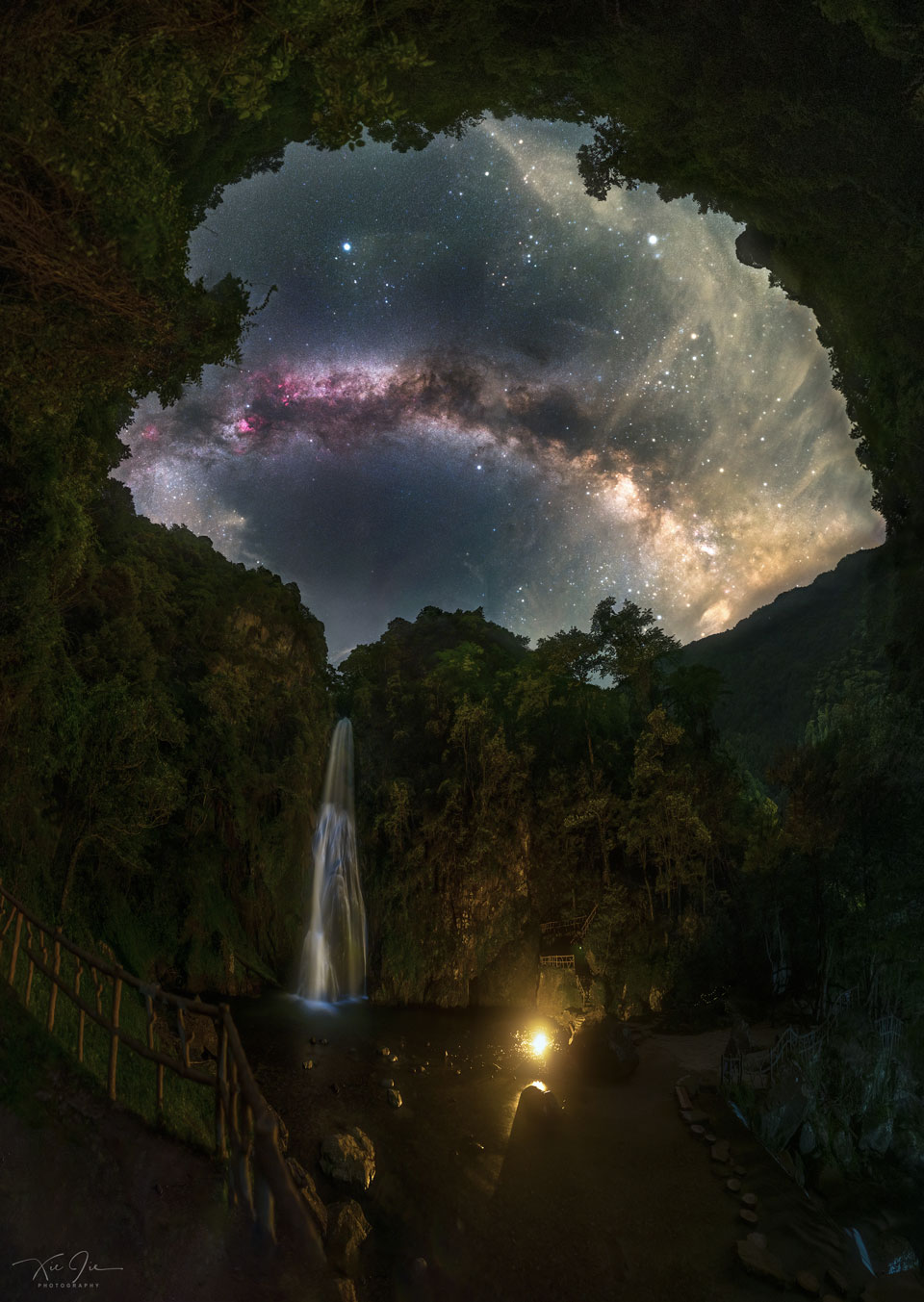
Explanation: The dream was to capture both the waterfall and the Milky Way together. Difficulties included finding a good camera location, artificially illuminating the waterfall and the surrounding valley effectively, capturing the entire scene with numerous foreground and background shots, worrying that fireflies would be too distracting, keeping the camera dry, and avoiding stepping on a poisonous snake. Behold the result -- captured after midnight in mid-July and digitally stitched into a wide-angle panorama. The waterfall is the picturesque Zhulian waterfall in the Luoxiao Mountains in eastern Hunan Province, China. The central band of our Milky Way Galaxy crosses the sky and shows numerous dark dust filaments and colorful nebulas. Bright stars dot the sky -- all residing in the nearby Milky Way -- including the Summer Triangle with bright Vega visible above the Milky Way's arch. After capturing all 78 component exposures for you to enjoy, the photographer and friends enjoyed the view themselves for the rest of the night.