2022 May 13
Image Credit: X-ray - NASA/CXC/SAO, IR - NASA/HST/STScI; Inset: Radio - Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration
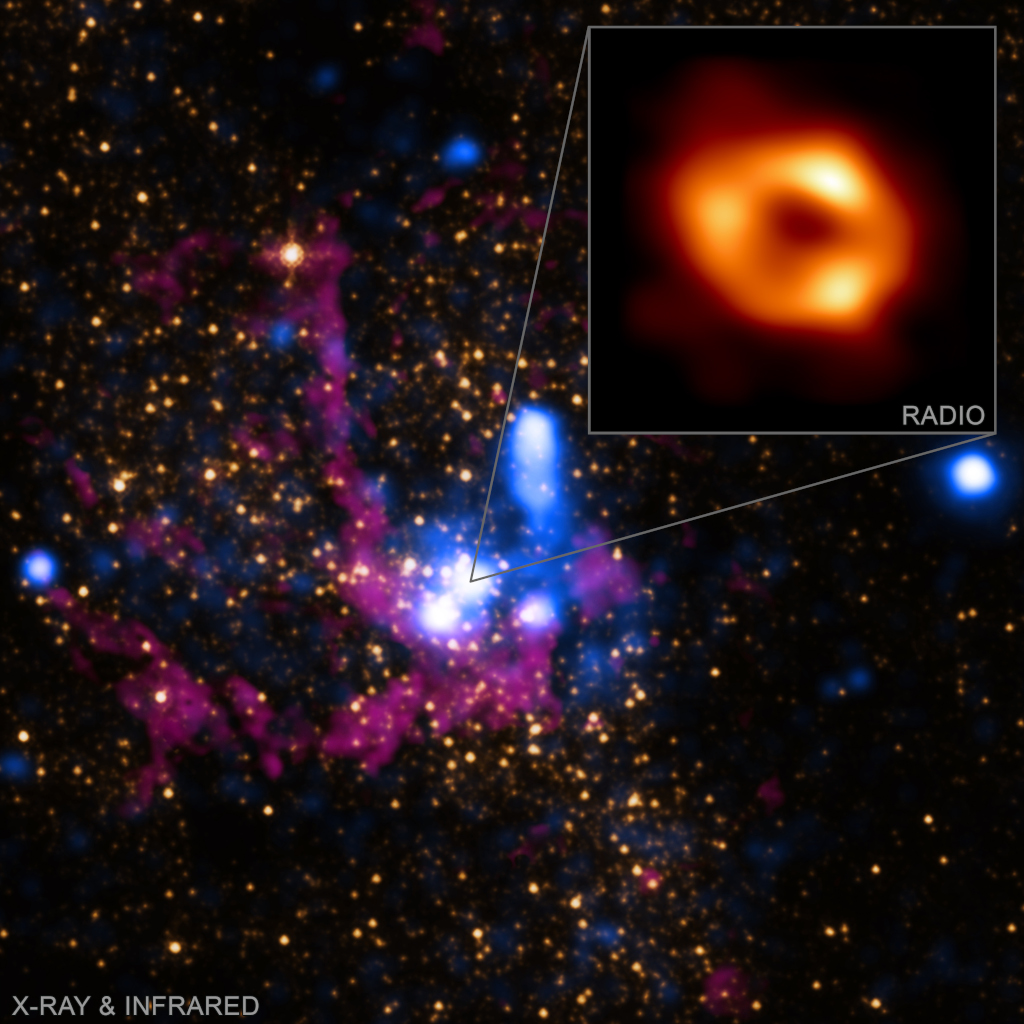
Explanation: There's a black hole at the center of the Milky Way. Stars are observed to orbit a very massive and compact object there known as Sgr A* (say "sadge-ay-star"). But this just released radio image (inset) from planet Earth's Event Horizon Telescope is the first direct evidence of the Milky Way's central black hole. As predicted by Einstein's Theory of General Relativity, the four million solar mass black hole's strong gravity is bending light and creating a shadow-like dark central region surrounded by a bright ring-like structure. Supporting observations made by space-based telescopes and ground-based observatories provide a wider view of the galactic center's dynamic environment and an important context for the Event Horizon Telescope's black hole image. The main panel image shows the X-ray data from Chandra and infrared data from Hubble. While the main panel is about 7 light-years across, the Event Horizon Telescope inset image itself spans a mere 10 light-minutes at the center of our galaxy, some 27,000 light-years away.