Image Credit: Image Credit: NASA, ESA, The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
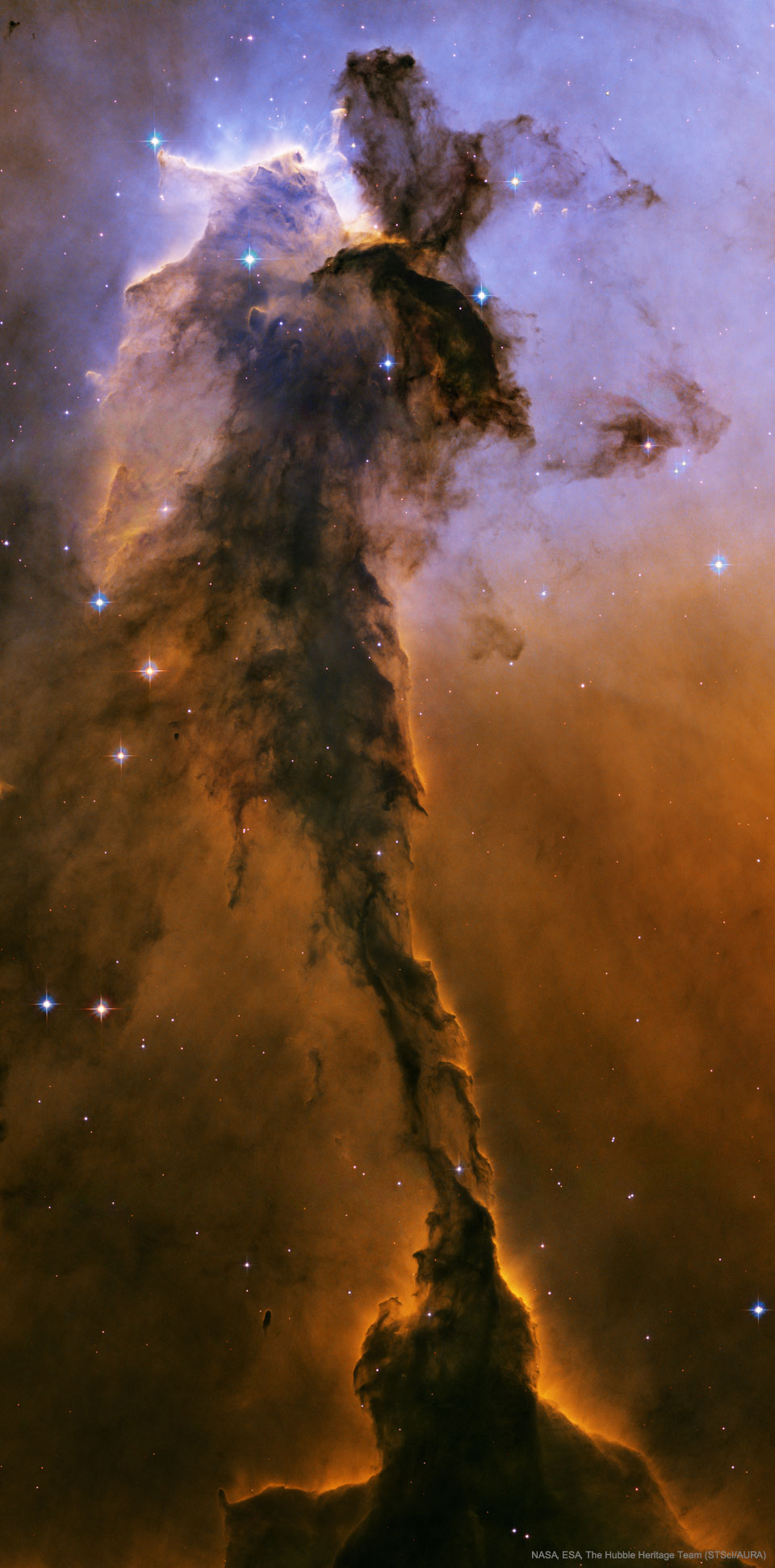
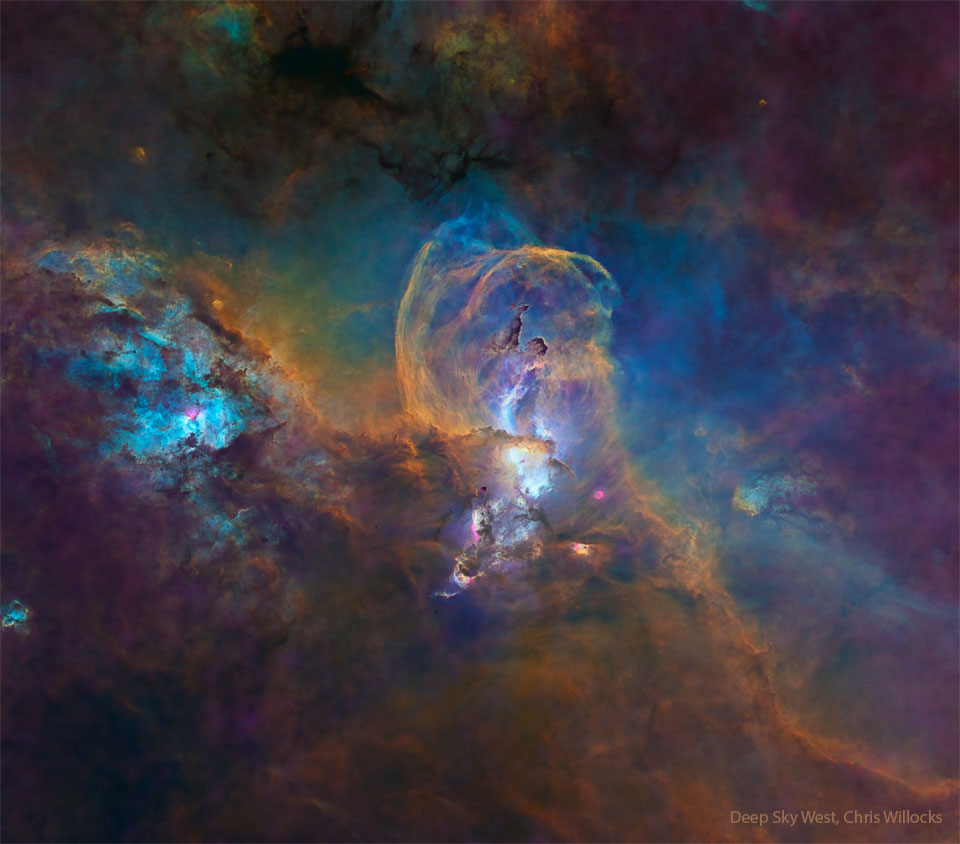
Explanation: The dust sculptures of the Eagle Nebula are evaporating. As powerful starlight whittles away these cool cosmic mountains, the statuesque pillars that remain might be imagined as mythical beasts. Featured here is one of several striking dust pillars of the Eagle Nebula that might be described as a gigantic alien fairy. This fairy, however, is ten light years tall and spews radiation much hotter than common fire. The greater Eagle Nebula, M16, is actually a giant evaporating shell of gas and dust inside of which is a growing cavity filled with a spectacular stellar nursery currently forming an open cluster of stars. This great pillar, which is about 7,000 light years away, will likely evaporate away in about 100,000 years. The featured image is in scientifically re-assigned colors and was taken by the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope.