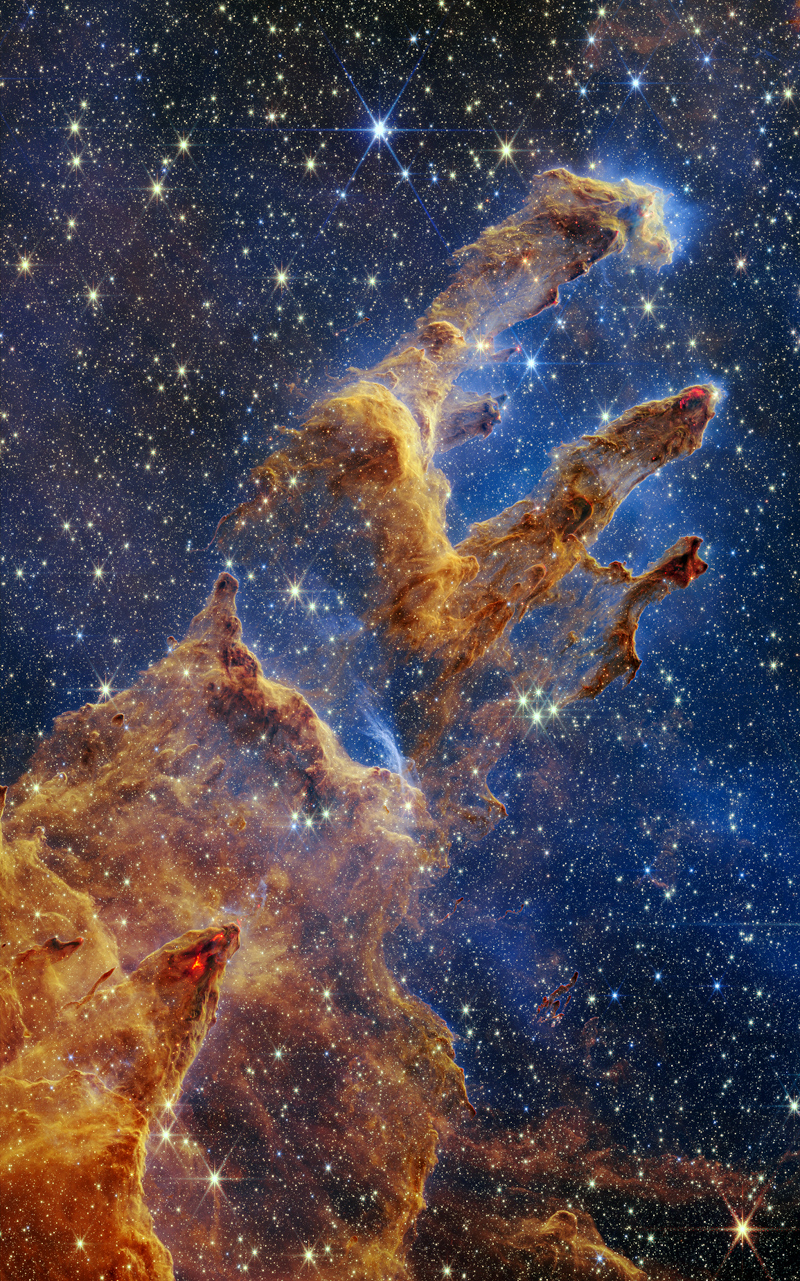
2022 October 31
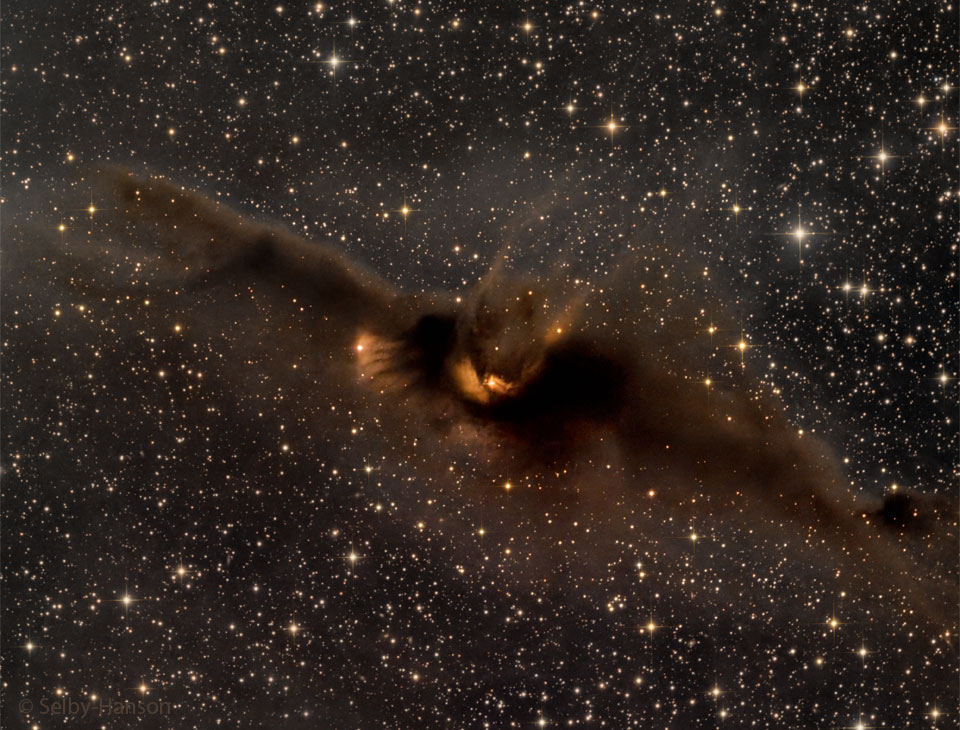
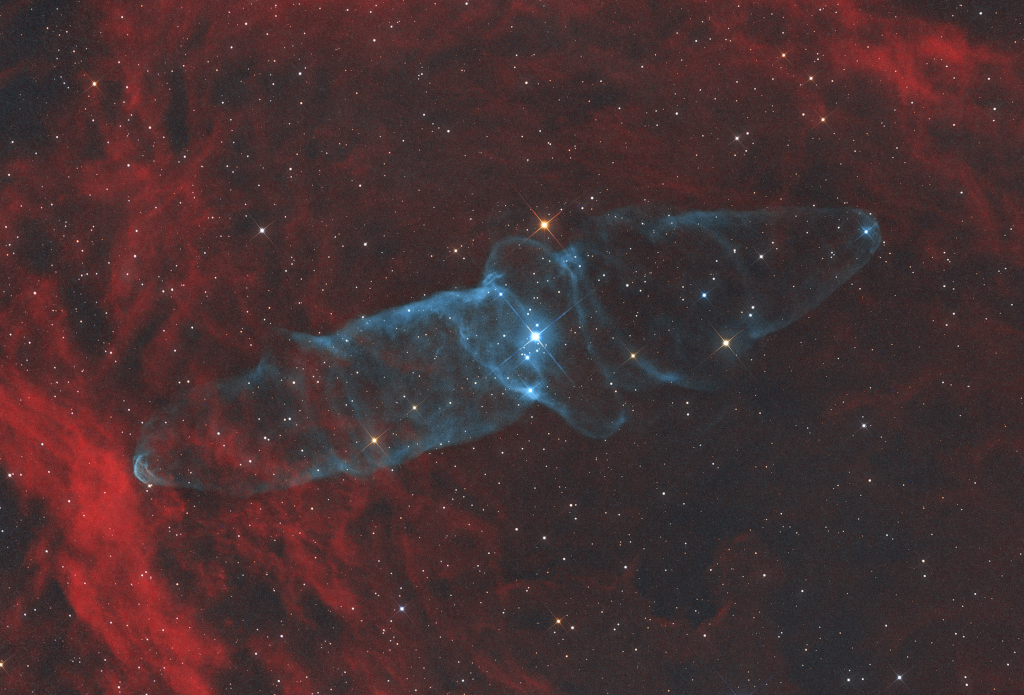
Image Credit & Copyright: Mark Hanson and Mike Selby; Text: Michelle Thaller (NASA's GSFC)
Explanation: What is the most spook-tacular nebula in the galaxy? One contender is LDN 43, which bears an astonishing resemblance to a vast cosmic bat flying amongst the stars on a dark Halloween night. Located about 1400 light years away in the constellation Ophiuchus, this molecular cloud is dense enough to block light not only from background stars, but from wisps of gas lit up by the nearby reflection nebula LBN 7. Far from being a harbinger of death, this 12-light year-long filament of gas and dust is actually a stellar nursery. Glowing with eerie light, the bat is lit up from inside by dense gaseous knots that have just formed young stars.