Nombre total de pages vues
07/09/2020
Simon R. Hudson : The Milky Way over St Michael's Mount - (Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day)
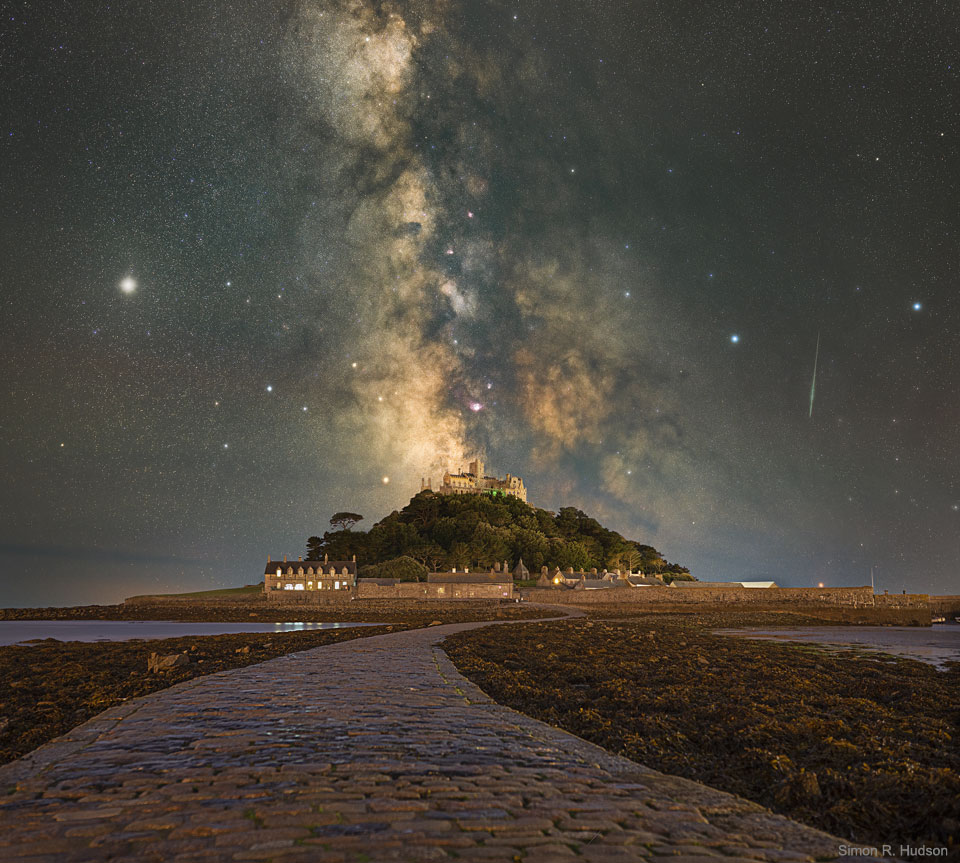

Image Credit: Simon R. Hudson
Explanation: Where do land and sky converge? On every horizon -- but in this case the path on the ground leads to St Michael's Mount (Cornish: Karrek Loos yn Koos), a small historic island in Cornwall, England. The Mount is usually surrounded by shallow water, but at low tide is spanned by a human-constructed causeway. The path on the sky, actually the central band of our Milky Way Galaxy, also appears to lead to St Michael's Mount, but really lies far in the distance. The red nebula in the Milky Way, just above the castle, is theLagoon Nebula, while bright Jupiter shines to the left, and a luminous meteor flashes to the right. The foreground and background images of this featured composite were taken on the same July night and from the same location. Although meteors are fleeting and the Milky Way disk shifts in the night as the Earth turns, Jupiter will remain prominent in the sunset sky into December.
04/09/2020
Nasa : The Wizard Nebula - (Science & Technologie - Astronomy picture of the day)
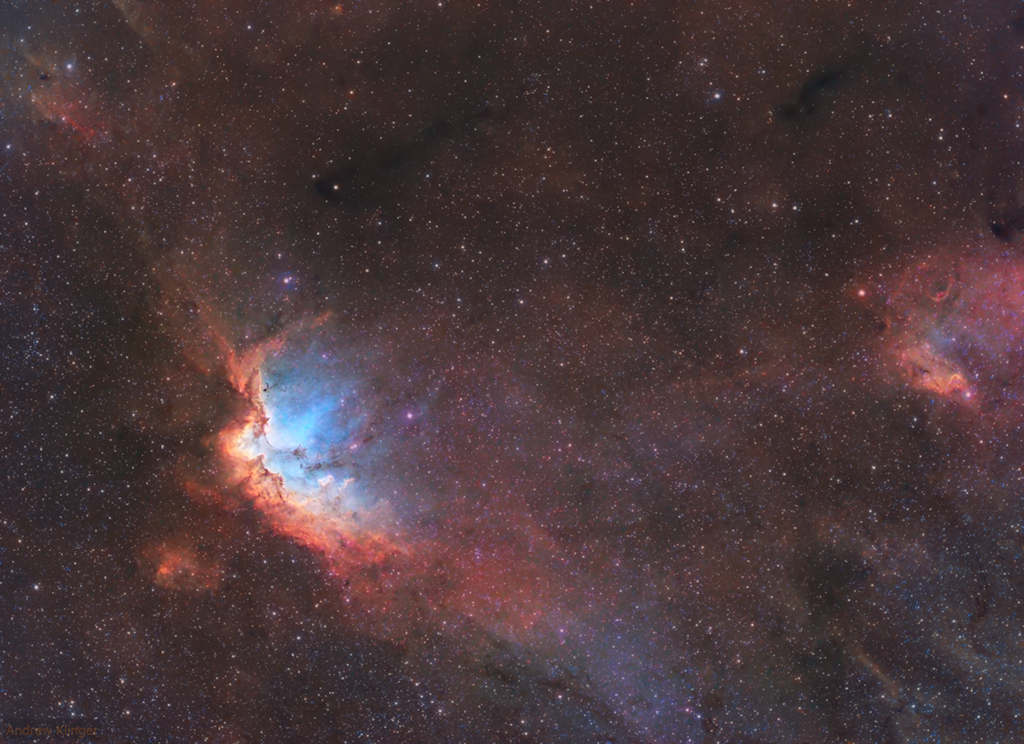

Image Credit & Copyright: Andrew Klinger
Explanation: Open star cluster NGC 7380 is still embedded in its natal cloud of interstellar gas and dust popularly known as the Wizard Nebula. Seen on the left, with foreground and background stars along the plane of our Milky Way galaxy it lies some 8,000 light-years distant, toward the constellation Cepheus. In apparent size on the sky, a full moon would cover the 4 million year young cluster and associated nebula, normally much too faint to be seen by eye. Made with telescope and camera firmly planted on Earth, the image reveals multi light-year sized shapes and structures of cosmic gas and dust within the Wizard though, in a color palette made popular in Hubble Space Telescope images. Recorded with narrowband filters, the visible wavelength light from the nebula's hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur atoms is transformed into green, blue, and red colors in the final digital composite.
03/09/2020
Nasa : A Halo for Andromeda - (Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day)
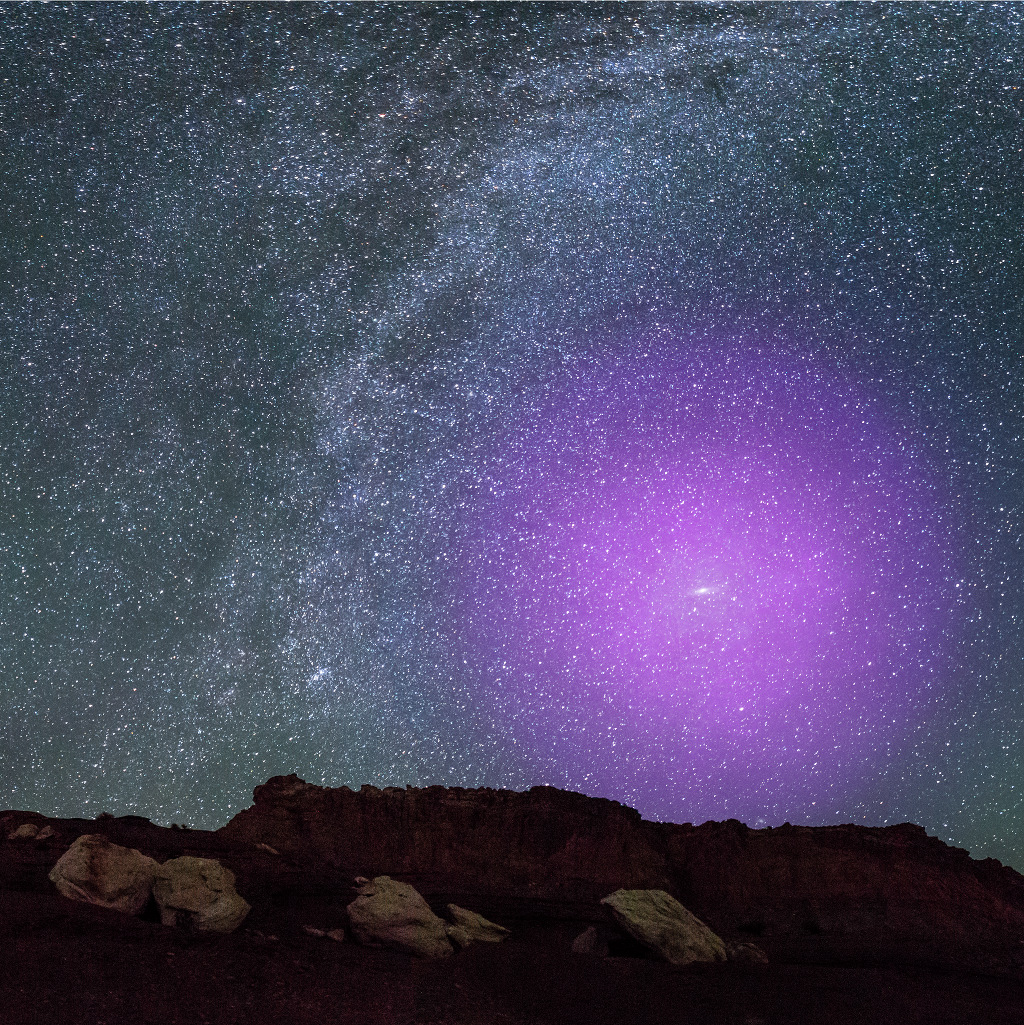

Digital Illustration Credit: NASA, ESA, J. DePasquale and E. Wheatley (STScI) and Z. Levay
Explanation: M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, is the closest large spiral galaxy to our Milky Way. Some 2.5 million light-years distant it shines in Earth's night sky as a small, faint, elongated cloud just visible to the unaided eye. Invisible to the eye though, its enormous halo of hot ionized gas is represented in purplish hues for this digital illustration of our neighboring galaxy above rocky terrain. Mapped by Hubble Space Telescope observations of the absorption of ultraviolet light against distant quasars, the extent and make-up of Andromeda's gaseous halo has been recently determined by the AMIGA project. A reservoir of material for future star formation, Andromeda's halo of diffuse plasma was measured to extend around 1.3 million light-years or more from the galaxy. That's about half way to the Milky Way, likely putting it in contact with the diffuse gaseous halo of our own galaxy.
01/09/2020
Nasa : Salt Water Remnants on Ceres - (Science & Technologie - Astronomy picture of the day)
Video Credit: Dawn Mission, NASA, JPL-Caltech, UCLA, MPS/DLR/IDA
Explanation: Does Ceres have underground pockets of water? Ceres, the largest asteroid in the asteroid belt, was thought to be composed of rock and ice. At the same time, Ceres was known to have unusual bright spots on its surface. These bright spots were clearly imaged during Dawn's exciting approach in 2015. Analyses of Dawn images and spectra indicated that the bright spots arise from the residue of highly-reflective salt water that used to exist on Ceres' surface but evaporated. Recent analysis indicates that some of this water may have originated from deep inside the dwarf planet, indicating Ceres to be a kindred spirit with several Solar System moons, also thought to harbor deep water pockets. The featured video shows in false-color pink the bright evaporated brine named Cerealia Facula inOccator Crater. In 2018, the mission-successful but fuel-depleted Dawn spacecraft was placed in a distant parking orbit, keeping it away from the Ceres' surface for at least 20 years to avoid interfering with any life that might there exist.
30/08/2020
Nasa : NGC 6357: Cathedral to Massive Stars - (Science & Technologie - Astyronomy picture of the day)
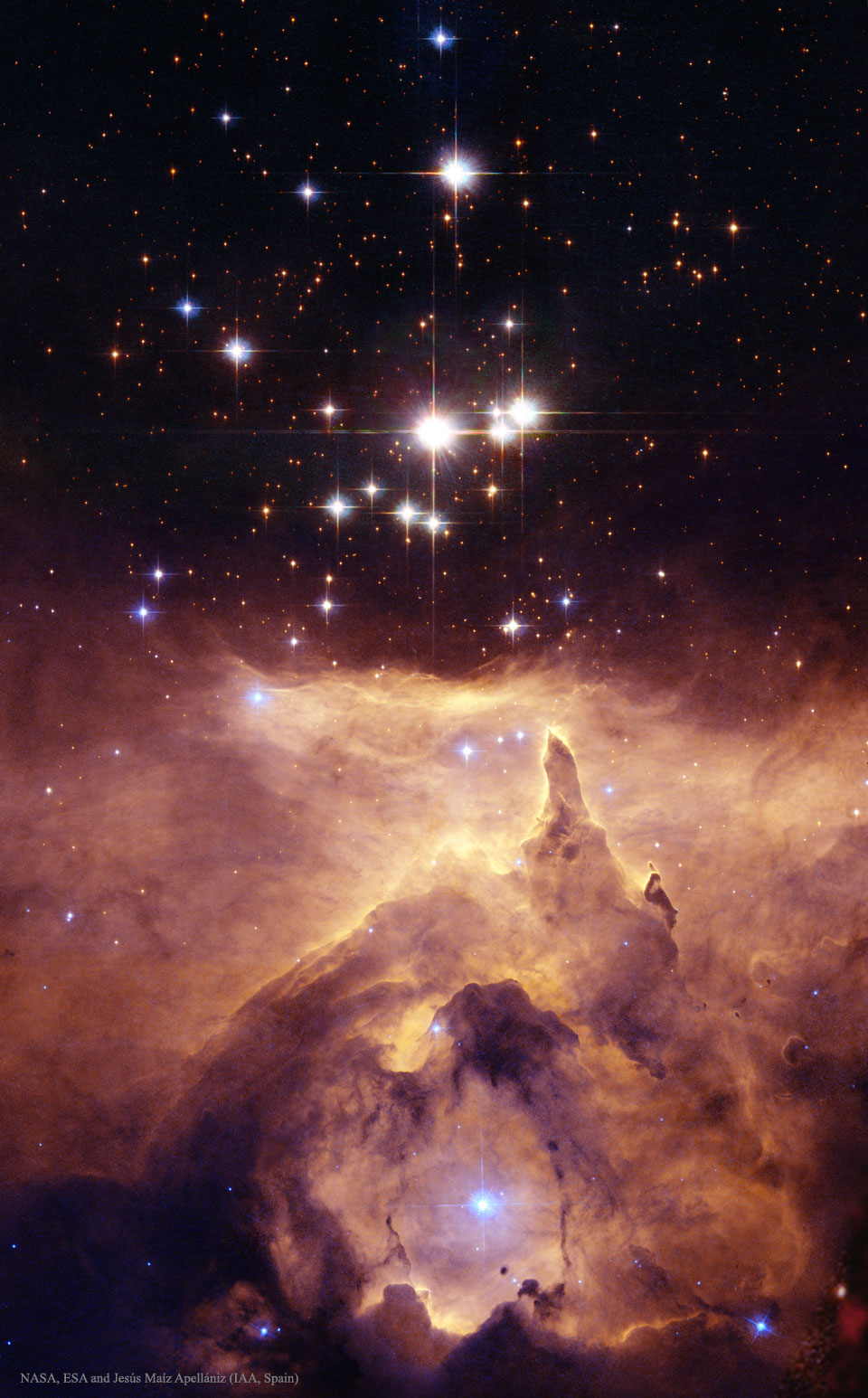

Image Credit: NASA, ESA and Jesús Maíz Apellániz (IAA, Spain); Acknowledgement: Davide De Martin (ESA/Hubble)
Explanation: How massive can a normal star be? Estimates made from distance, brightness and standard solar models had given one star in the open cluster Pismis 24 over 200 times the mass of our Sun, making it one of the most massive stars known. This star is the brightest object located just above the gas front in the featured image. Close inspection of images taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, however, have shown that Pismis 24-1 derives its brilliant luminosity not from a single star but from three at least. Component starswould still remain near 100 solar masses, making them among the more massive stars currently on record. Toward the bottom of the image, stars are still forming in the associated emission nebula NGC 6357. Appearing perhaps like a Gothic cathedral, energetic stars near the center appear to be breaking out and illuminating a spectacular cocoon.
29/08/2020
Nasa : Martian Chiaroscuro - (Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day)
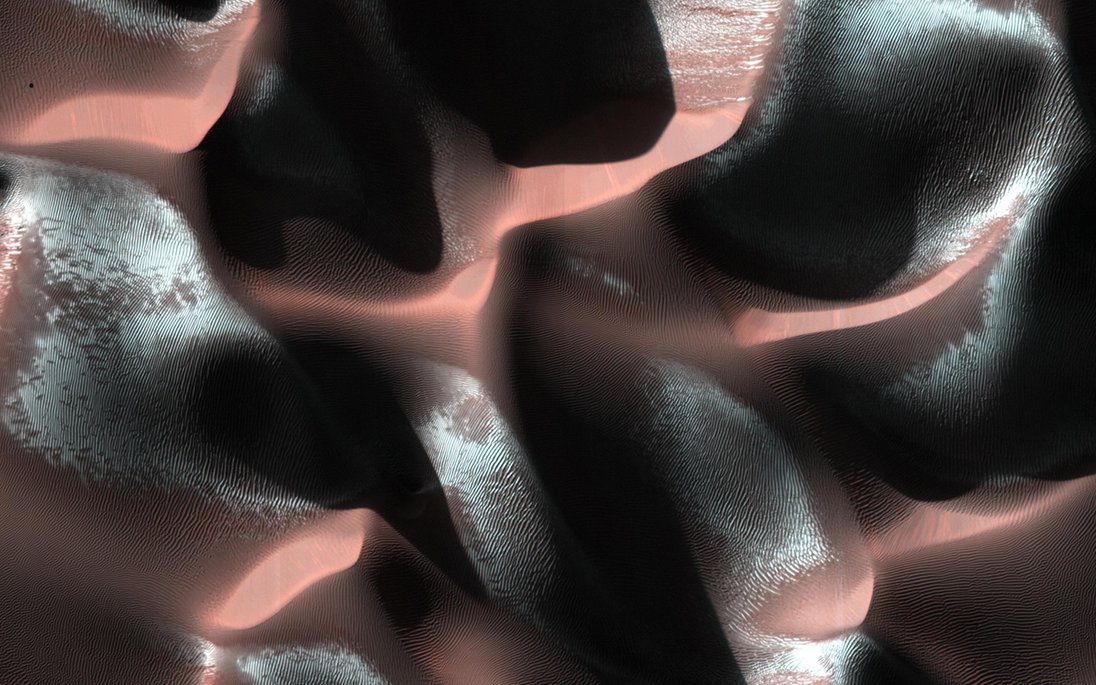
Image Credit: HiRISE, MRO, LPL (U. Arizona), NASA
Explanation: Deep shadows create dramatic contrasts between light and dark in this high-resolution close-up of the martian surface. Recorded on January 24, 2014 by the HiRISE camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, the scene spans about 1.5 kilometers. From 250 kilometers above the Red Planet the camera is looking down at a sand dune field in a southern highlands crater. Captured when the Sun was about 5 degrees above the local horizon, only the dune crests were caught in full sunlight. A long, cold winter was coming to the southern hemisphere and bright ridges of seasonal frost line the martian dunes. The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, one of the oldest operating spacecraft at the Red Planet, celebrated the 15th anniversary of its launch from planet Earth on August 12.
28/08/2020
Nasa : The Valley of Orion - (Science & Technology - Astronomy picture of the day)
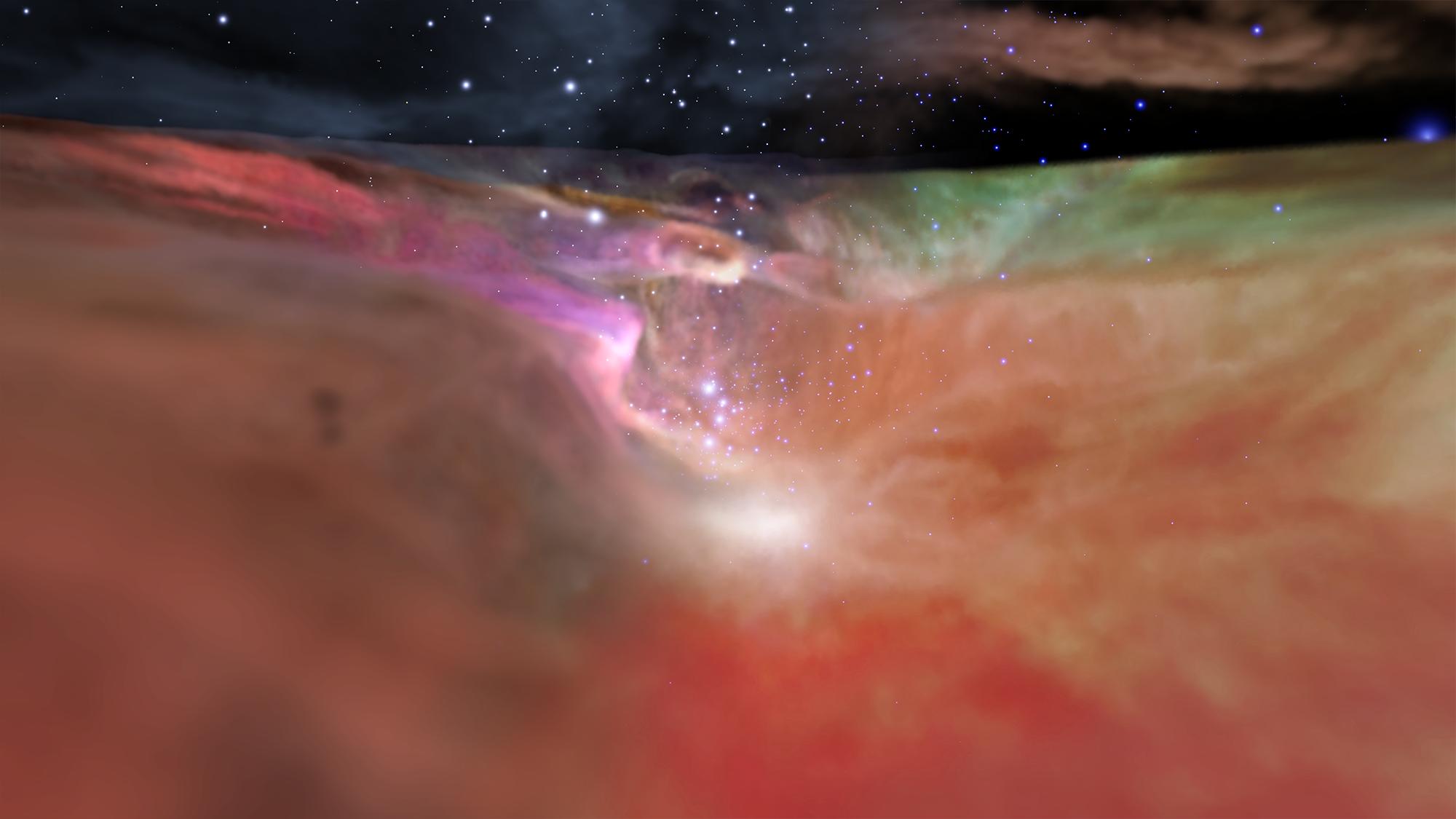

Visualization Credit: NASA, ESA, F. Summers, G. Bacon,
Explanation: This exciting and unfamiliar view of the Orion Nebula is a visualization based on astronomical data and movie rendering techniques. Up close and personal with a famous stellar nursery normally seen from 1,500 light-years away, the digitally modeled frame transitions from a visible light representation based on Hubble data on the left to infrared data from the Spitzer Space Telescope on the right. The perspective at the center looks along a valley over a light-year wide, in the wall of the region's giant molecular cloud. Orion's valley ends in a cavity carved by the energetic winds and radiation of the massive central stars of the Trapezium star cluster. The single frame is part of a multiwavelength, three-dimensional video that lets the viewer experience an immersive, three minute flight through the Great Nebula of Orion.
27/08/2020
Nasa : Shell Galaxies in Pisces - (Science & Technologie - Astronomy picture of the day)
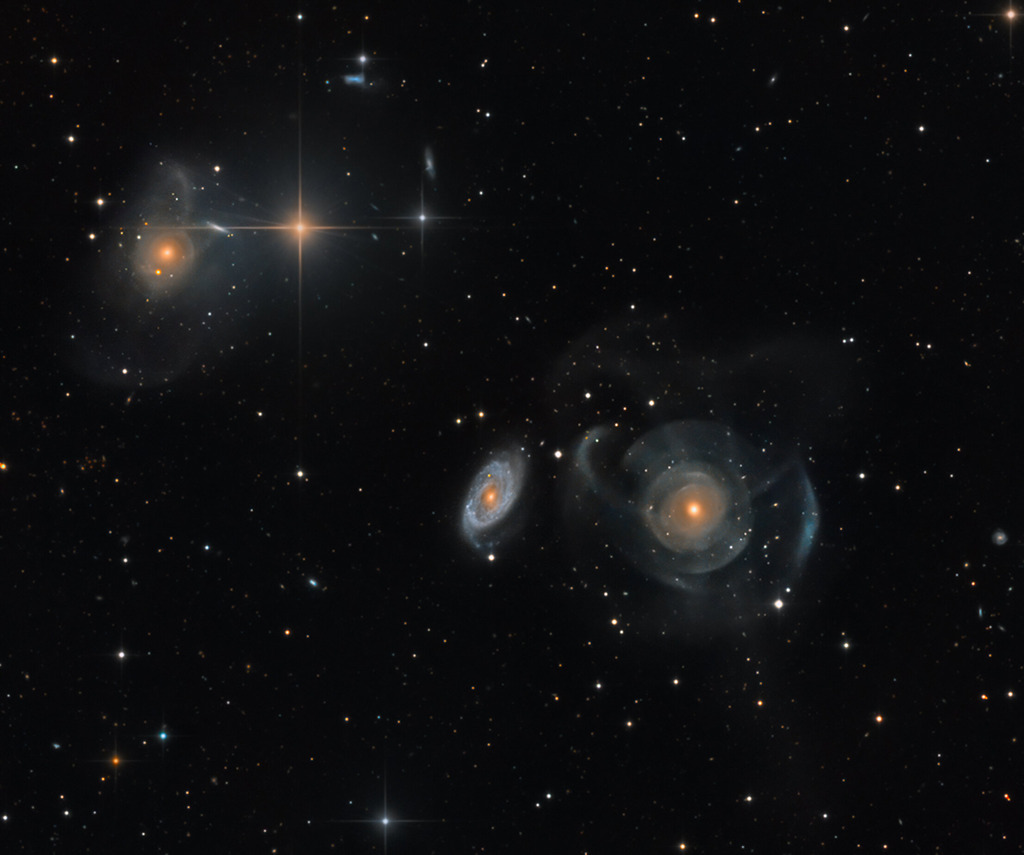

Image Credit & Copyright: Martin Pugh
Explanation: This intergalactic skyscape features a peculiar system of galaxies cataloged as Arp 227 some 100 million light-years distant. Swimming within the boundaries of the constellation Pisces, Arp 227 consists of the two galaxies prominent right of center, the curious shell galaxy NGC 474 and its blue, spiral-armed neighbor NGC 470. The faint, wide arcs or shells of NGC 474 could have been formed by a gravitational encounter with neighbor NGC 470. Alternately the shells could be caused by a merger with a smaller galaxy producing an effect analogous to ripples across the surface of a pond. The large galaxy on the top lefthand side of the deep image, NGC 467, appears to be surrounded by faint shells too, evidence of another interacting galaxy system. Intriguing background galaxies are scattered around the field that also includes spiky foreground stars. Of course, those stars lie well within our own Milky Way Galaxy. The field of view spans 25 arc minutes or about 1/2 degree on the sky.
26/08/2020
Courrier International : Notre ciel, deux soleils ? (Science & Technologie - Astronomie)

“Il y a des milliards d’années, il y avait peut-être deux soleils dans notre Système solaire, rapporte le New Scientist. Si tel est le cas, cela pourrait expliquer comment le système solaire a embarqué ses objets les plus extérieurs, y compris l’hypothétique planète 9.” L’hebdomadaire britannique résume ainsi les travaux d’Amir Siraj et Avi Loeb publiés dans The Astrophysical Journal Letters, le 18 août.
Ces chercheurs de l’université d’Harvard ont calculé que si, durant sa jeunesse, notre Soleil a fait partie d’un système binaire (à deux étoiles), une attraction gravitationnelle plus grande a été exercée sur une plus grande zone, augmentant d’un facteur 5 la probabilité que notre système solaire dispose d’un ensemble de corps célestes à ses confins, comme le nuage d’Oort – dont l’origine demeure un mystère – par rapport à un système à une seule étoile.
En outre, dans leur hypothèse à deux soleils, la probabilité que notre système capture une neuvième planète est augmentée d’un facteur 20 environ.
L’idée que notre système ait pu avoir deux étoiles n’est pas spécialement farfelue : dans l’univers, “plus de la moitié des étoiles qui ressemblent à notre Soleil ont un compagnon”, assure Avi Loeb. Et surtout, si elle permet d’expliquer à la fois la formation du nuage d’Oort et l’existence de l’hypothétique planète 9, elle a de quoi séduire la communauté scientifique.
Inscription à :
Articles (Atom)
SANTé/MEDECINE - Procédé révolutionnaire dans la lutte contre le cancer - 2/6 : Une découverte qui change tout
Jusqu’à présent, la lutte contre le cancer reposait principalement sur la chimiothérapie, la radiothérapie ou la chirurgie. Ces traitements,...

-
2022 September 26 All the Water on Planet Earth Illustration Credit: Jack Cook, Adam Nieman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ; Data ...
-
La majorité des grêlons qui tombent sous les orages et les averses ne pèsent que quelques grammes. Mais il y a quelques années, c'est un...
