2022 March 16
Illustration Credit & Licence: Wikipedia, Pablo Carlos Budassi
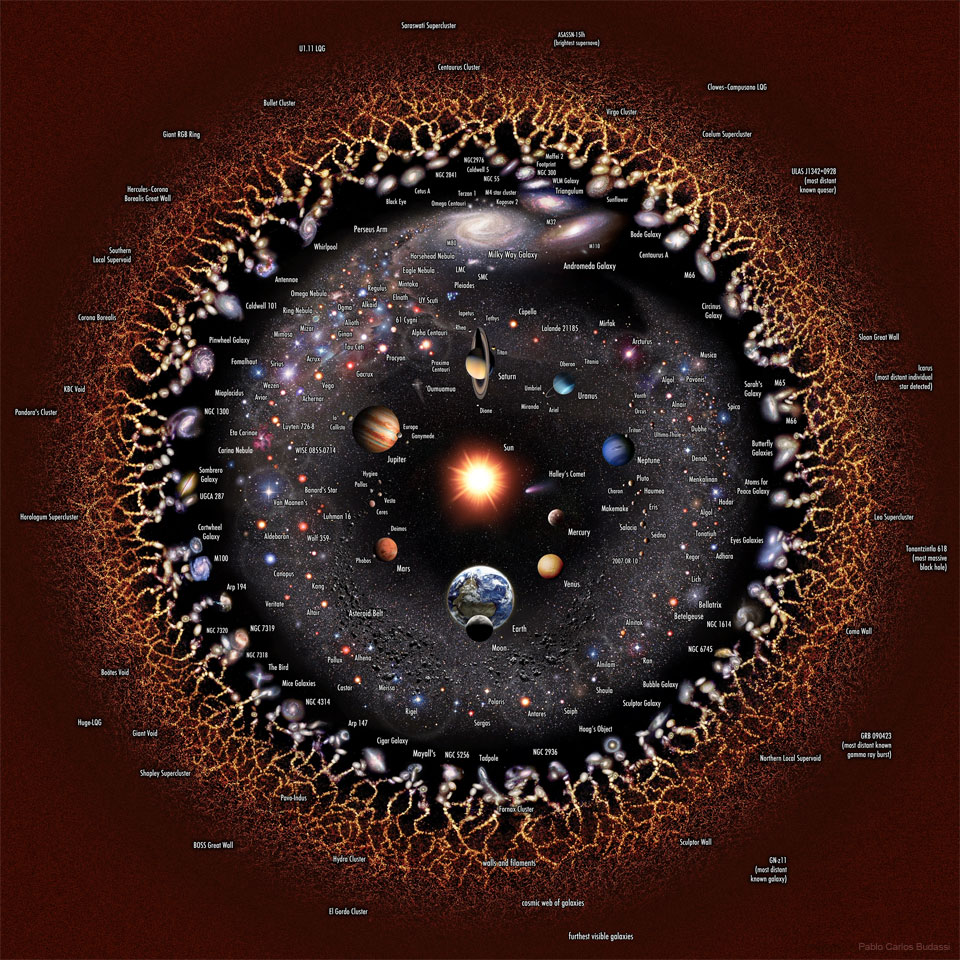
Explanation: How far can you see? Everything you can see, and everything you could possibly see, right now, assuming your eyes could detect all types of radiations around you -- is the observable universe. In light, the farthest we can see comes from the cosmic microwave background, a time 13.8 billion years ago when the universe was opaque like thick fog. Some neutrinos and gravitational waves that surround us come from even farther out, but humanity does not yet have the technology to detect them. The featured image illustrates the observable universe on an increasingly compact scale, with the Earth and Sun at the center surrounded by our Solar System, nearby stars, nearby galaxies, distant galaxies, filaments of early matter, and the cosmic microwave background. Cosmologists typically assume that our observable universe is just the nearby part of a greater entity known as "the universe" where the same physics applies. However, there are several lines of popular but speculative reasoning that assert that even our universe is part of a greater multiverse where either different physical constants occur, different physical laws apply, higher dimensions operate, or slightly different-by-chance versions of our standard universe exist.