Nombre total de pages vues
04/07/2023
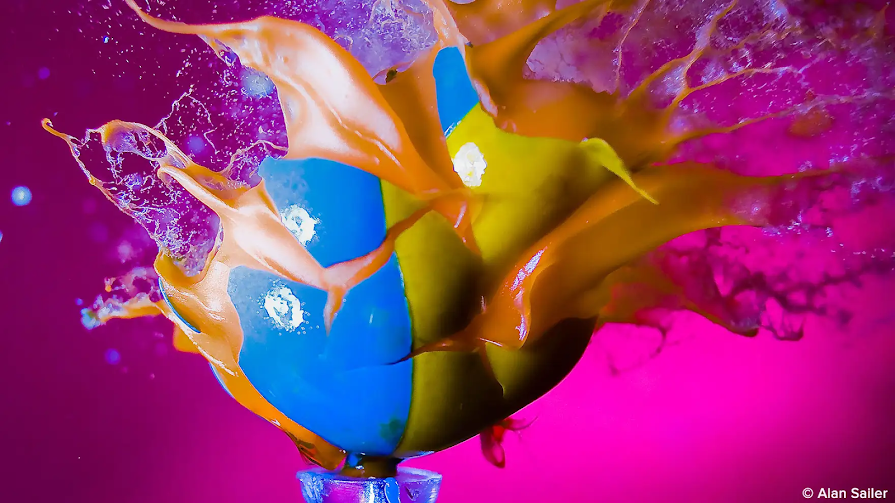
PHOTOGRAPHIE - Le monde explosif d'Alain Sailer - Explosion d'une crème glacée au ralenti
03/07/2023
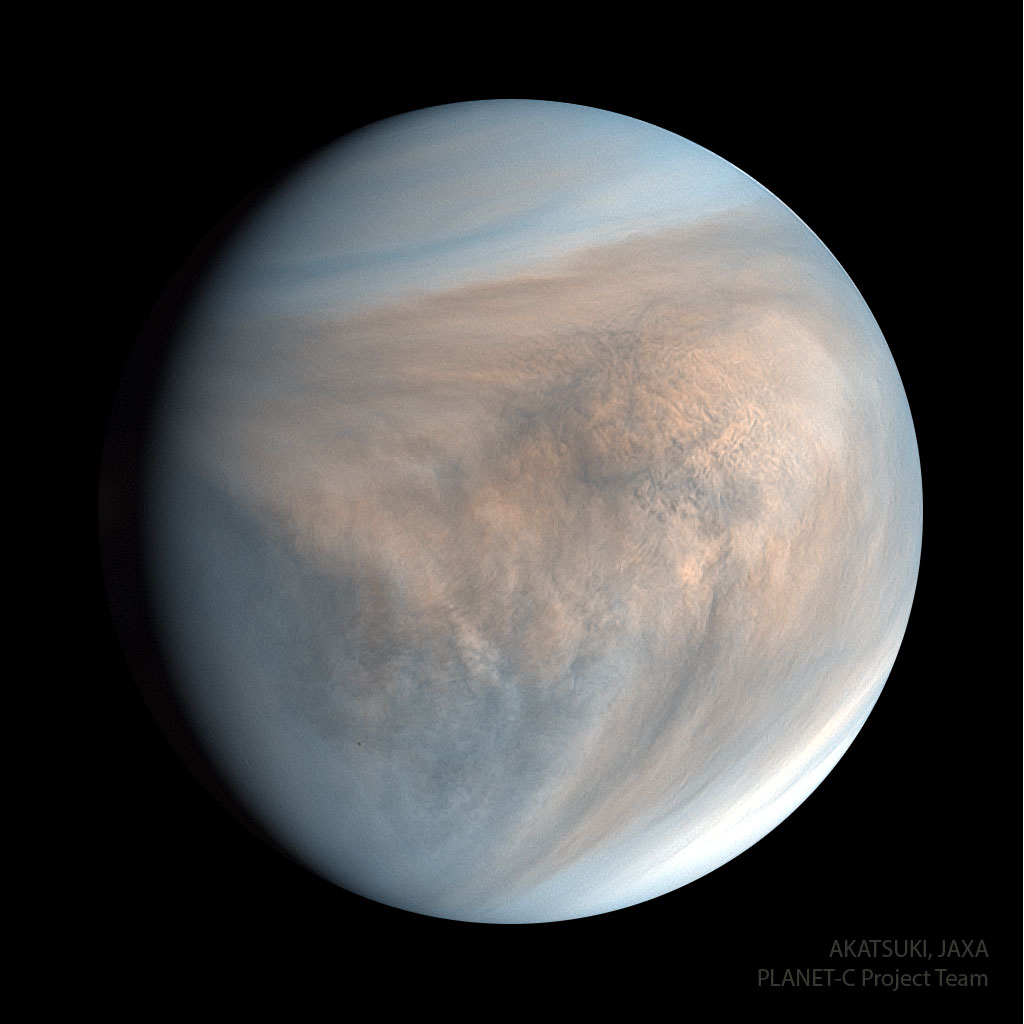
ASTRONOMY - Venus in Ultraviolet from Akatsuki
2023 July 3
Image Credit & Copyright: JAXA, Planet-C Project Team; h/t: Mehmet Hakan Özsaraç
Explanation: Why is Venus so different from Earth? To help find out, Japan launched the robotic Akatsuki spacecraft which entered orbit around Venus late in 2015 after an unplanned five-year adventure around the inner Solar System. Even though Akatsuki was past its original planned lifetime, the spacecraft and instruments were operating so well that much of its original mission was reinstated. Also known as the Venus Climate Orbiter, Akatsuki's instruments investigated unknowns about Earth's sister planet, including whether volcanoes are still active, whether lightning occurs in the dense atmosphere, and why wind speeds greatly exceed the planet's rotation speed. In the featured image taken by Akatsuki's UVI camera, the day-side of Venus is seen shown with planet-scale V-shaped cloud pattern. The image displays three ultraviolet colors and indicates a dip in the relative abundance of sulfur dioxide shown in faint blue. Analyses of Akatsuki images and data has shown, among other discoveries, that Venus has equatorial jet similar to Earth's jet stream.
01/07/2023
PHOTOGRAPHIE - Le monde explosif d'Alan Sailer - Au ralenti : de la pâte à modeler qui explose
30/06/2023
ASTRONOMY - The Belt of Venus over Mount Everest
2023 June 26
Image Credit & Copyright: Soumyadeep Mukherjee
Explanation: You've surely seen it, but you might not have noticed it. During a cloudless twilight, just before sunrise or after sunset, part of the atmosphere above the horizon appears slightly dark and off-color. Called the Belt of Venus, this transitional band between the dark eclipsed sky and the bright day sky can be seen most prominently in the direction opposite the Sun. Straight above, blue sky is normal sunlight reflecting off the atmosphere, while near the horizon the clear sky can appear more orange or red. In the Belt of Venus, the atmosphere reflects more light from the setting (or rising) Sun and so appears more red. Featured here, the Belt of Venus was photographed over several Himalayan mountains including, second from the right, Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on Earth. Although usually not mentioned, the belt is frequently caught by accident in other photographs.
28/06/2023
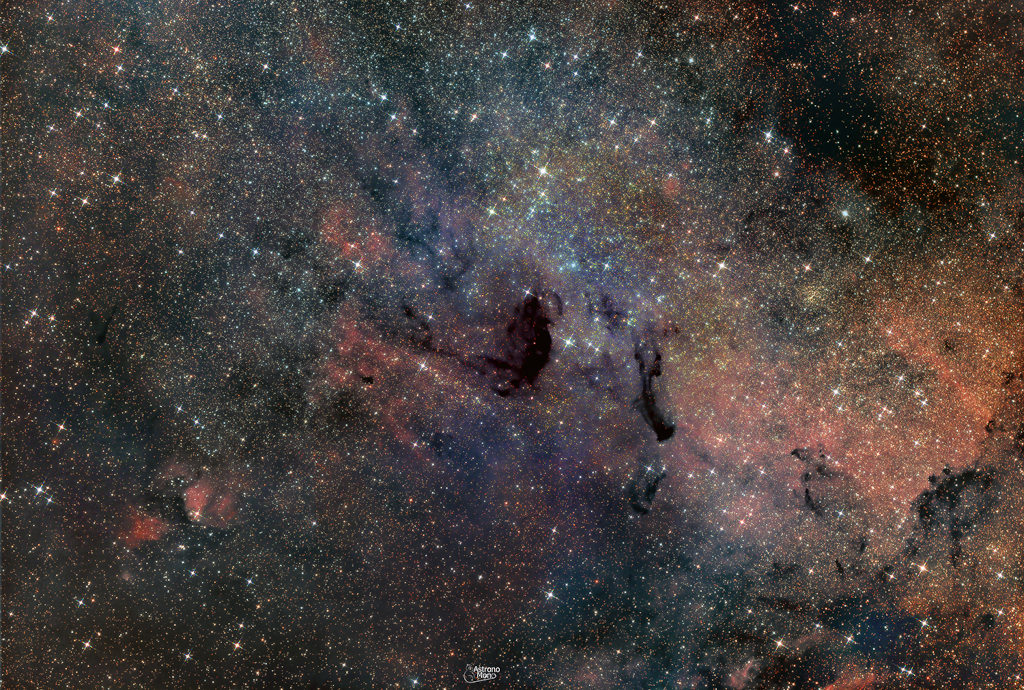
ASTRONOMY - Messier 24: Sagittarius Star Cloud
2023 June 28
Image Credit & Copyright: Emmanuel Astronomono
Explanation: Unlike most entries in Charles Messier's famous catalog of deep sky objects, M24 is not a bright galaxy, star cluster, or nebula. It's a gap in nearby, obscuring interstellar dust clouds that allows a view of the distant stars in the Sagittarius spiral arm of our Milky Way galaxy. Direct your gaze through this gap with binoculars or small telescope and you are looking through a window over 300 light-years wide at stars some 10,000 light-years or more from Earth. Sometimes called the Small Sagittarius Star Cloud, M24's luminous stars fill this gorgeous starscape. Covering over 3 degrees or the width of 6 full moons in the constellation Sagittarius, the telescopic field of view includes dark markings B92 and B93 near center, along with other clouds of dust and glowing nebulae toward the center of the Milky Way.
26/06/2023
PHOTOGRAPHIE - le monde explosif d'Alan Sailer
25/06/2023
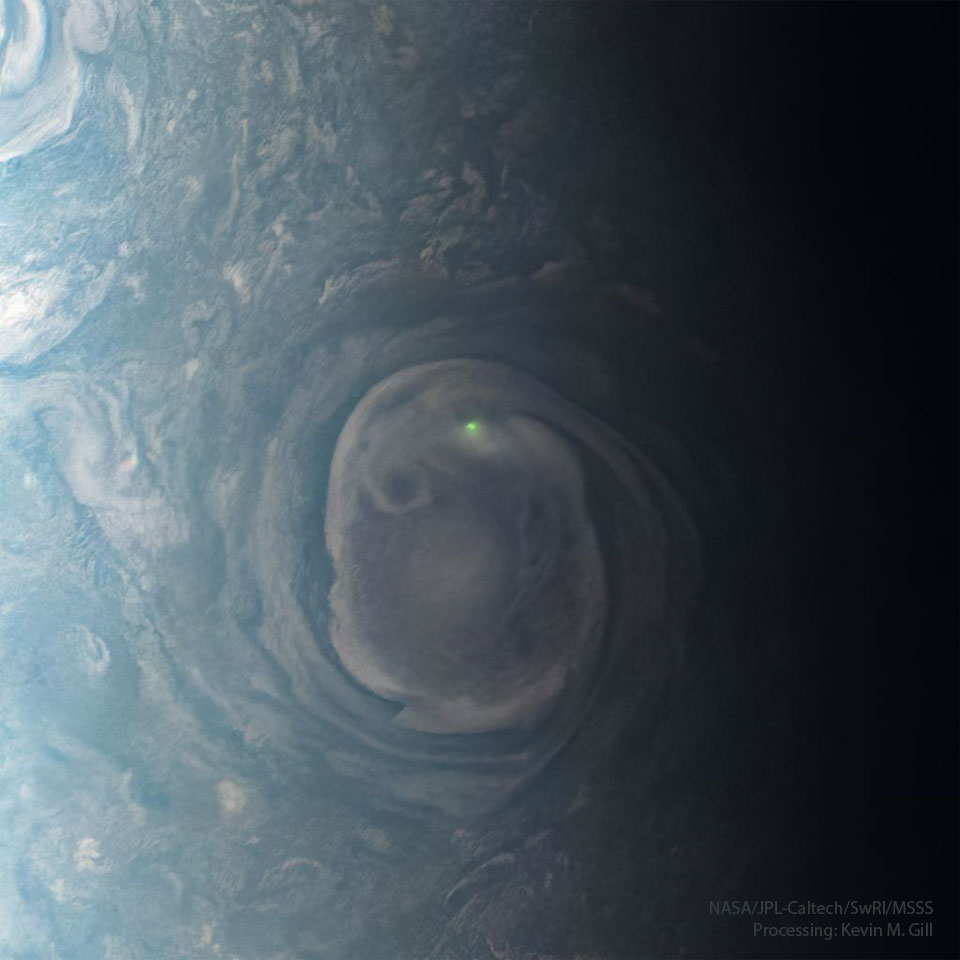
ASTRONOMY - Lightning on Jupiter
2023 June 25
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS; Processing & License: Kevin M. Gill
Explanation: Does lightning occur only on Earth? No. Spacecraft in our Solar System have detected lightning on other planets, including Mars, Jupiter and Saturn, and lightning is likely on Venus, Uranus, and Neptune. Lightning is a sudden rush of electrically charged particles from one location to another. On Earth, drafts of colliding ice and water droplets usually create lightning-generating charge separation, but what happens on Jupiter? Images and data from NASA's Jupiter-orbiting Juno spacecraft bolster previous speculation that Jovian lightning is also created in clouds containing water and ice. In the featured Juno photograph, an optical flash was captured in a large cloud vortex near Jupiter's north pole. During the next few months, Juno will perform several close sweeps over Jupiter's night side, likely allowing the robotic probe to capture more data and images of Jovian lightning.
ASTRONOMY - Sublime carte postale de Mars
24/06/2023
GEMMOLOGIE - La topaze, un silicate
MICROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Zoom sur une abeille mellifère
Le monde de l’infiniment petit est fascinant de beauté. Une beauté qui pourrait bien servir à sensibiliser le grand public à l’importance de...

-
2022 September 26 All the Water on Planet Earth Illustration Credit: Jack Cook, Adam Nieman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ; Data ...
-
2025 May 11 The Surface of Venus from Venera 14 Image Credit: Soviet Planetary Exploration Program , Venera 14 ; Processing & Copyri...