Nombre total de pages vues
24/11/2022
MACROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Un scarabée tigre aux couleurs chatoyantes
MICROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Marek Miś - Un mélange à base d'hématoxyline qui fait des étincelles
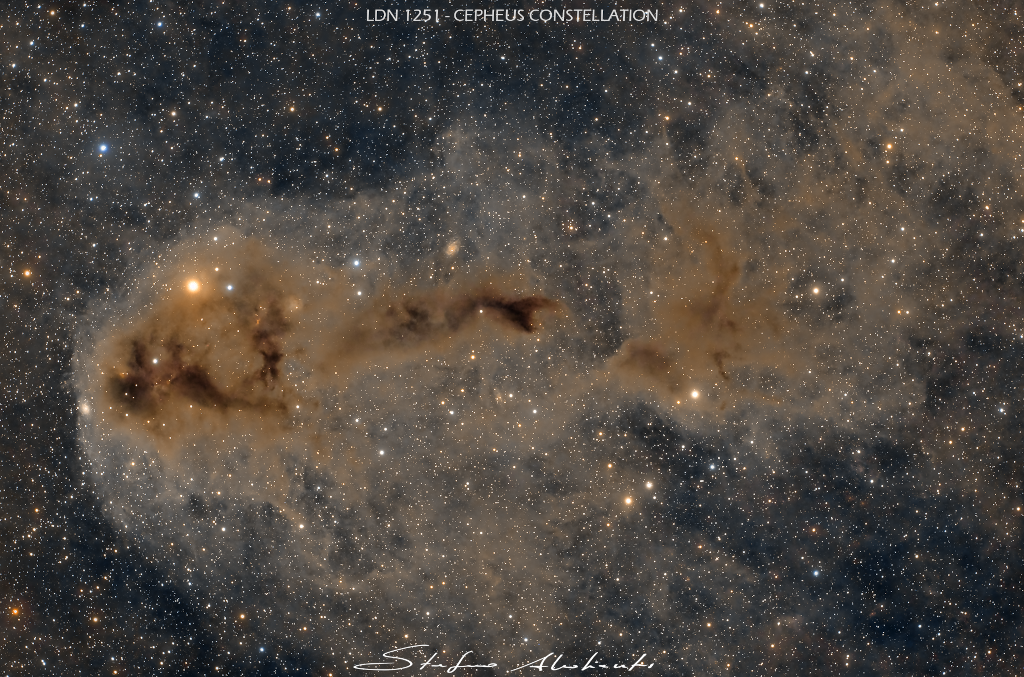
ASTRONOMY - Lynds Dark Nebula 1251
2022 November 24
Image Credit & Copyright: Stefano Attalienti
Explanation: Stars are forming in Lynds Dark Nebula (LDN) 1251. About 1,000 light-years away and drifting above the plane of our Milky Way galaxy, the dusty molecular cloud is part of a complex of dark nebulae mapped toward the Cepheus flare region. Across the spectrum, astronomical explorations of the obscuring interstellar clouds reveal energetic shocks and outflows associated with newborn stars, including the telltale reddish glow from scattered Herbig-Haro objects hiding in the image. Distant background galaxies also lurk on the scene, almost buried behind the dusty expanse. This alluring view spans over four full moons on the sky, or 35 light-years at the estimated distance of LDN 1251.
AVIATION IMAGINEE - L'arrivée du courrier en avion
© Couverture de Literary Digest, le 31 mai 1919
23/11/2022
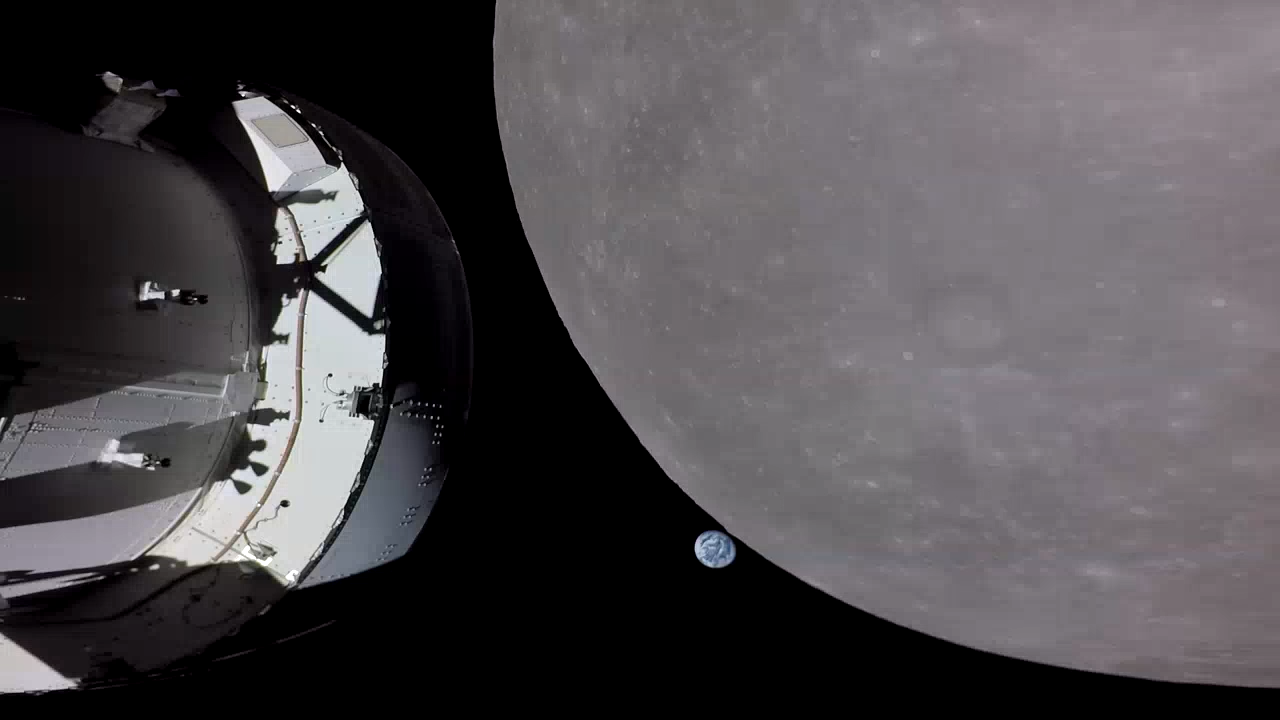
ASTRONOMY - Earthset from Orion
2022 November 23
Image Credit: NASA, Artemis 1
Explanation: Eight billion people are about to disappear in this snapshot from space. Taken on November 21, the sixth day of the Artemis 1 mission, their home world is setting behind the Moon's bright edge as viewed by an external camera on the outbound Orion spacecraft. The Orion was headed for a powered flyby that took it to within 130 kilometers of the lunar surface. Velocity gained in the flyby maneuver will be used to reach a distant retrograde orbit around the Moon. That orbit is considered distant because it's another 92,000 kilometers beyond the Moon, and retrograde because the spacecraft will orbit in the opposite direction of the Moon's orbit around planet Earth. Orion will enter its distant retrograde orbit on Friday, November 25. Swinging around the Moon, Orion will reach a maximum distance (just over 400,000 kilometers) from Earth on Monday November 28 exceeding a record set by Apollo 13 for most distant spacecraft designed for human space exploration.
22/11/2022
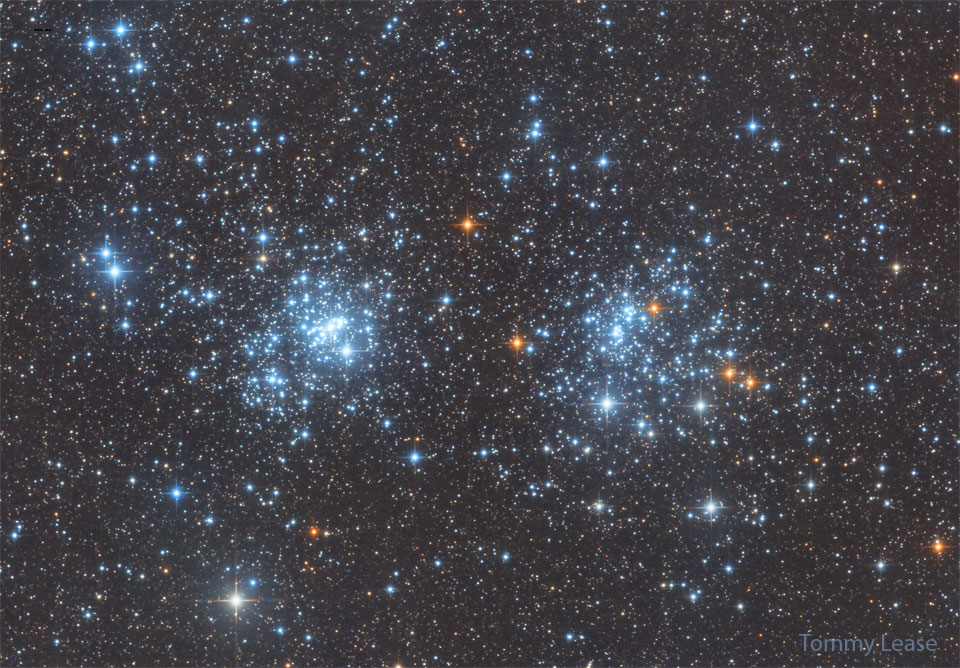
ASTRONOMY - A Double Star Cluster in Perseus
2022 November 22
Image Credit & Copyright: Tommy Lease
Explanation: Few star clusters this close to each other. Visible to the unaided eye from dark sky areas, it was cataloged in 130 BC by Greek astronomer Hipparchus. Some 7,000 light-years away, this pair of open star clusters is also an easy binocular target, a striking starfield in the northern constellation of the mythical Greek hero Perseus. Now known as h and chi Persei, or NGC 869 (above right) and NGC 884, the clusters themselves are separated by only a few hundred light-years and contain stars much younger and hotter than the Sun. In addition to being physically close together, the clusters' ages based on their individual stars are similar - evidence that both clusters were likely a product of the same star-forming region.
21/11/2022
BIOMIMETISME - LA NATURE INSPIRE LA SCIENCE - Les feuilles autonettoyantes du lotus
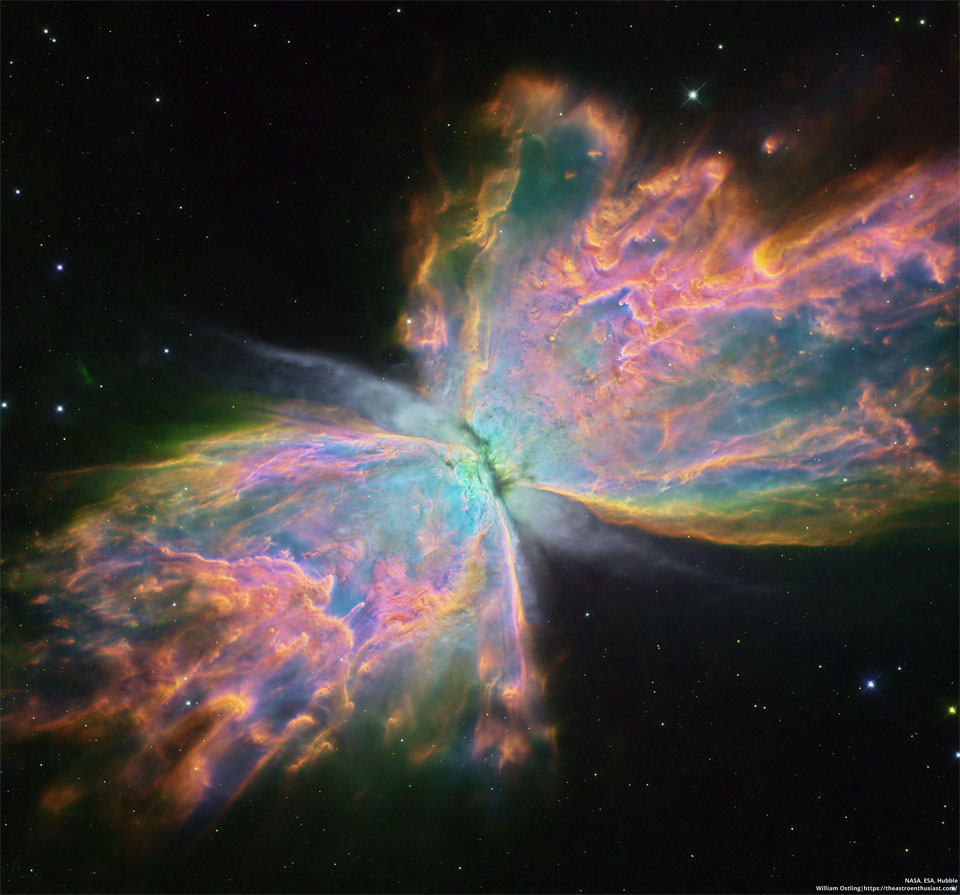
ASTRONOMY - The Butterfly Nebula from Hubble
2022 November 21
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble; Processing: William Ostling
Explanation: Stars can make beautiful patterns as they age -- sometimes similar to flowers or insects. NGC 6302, the Butterfly Nebula, is a notable example. Though its gaseous wingspan covers over 3 light-years and its estimated surface temperature exceeds 200,000 degrees C, the aging central star of NGC 6302, the featured planetary nebula, has become exceptionally hot, shining brightly in visible and ultraviolet light but hidden from direct view by a dense torus of dust. This sharp close-up was recorded by the Hubble Space Telescope and is processed here to show off remarkable details of the complex planetary nebula, highlighting in particular light emitted by oxygen (shown as blue), hydrogen (green), and nitrogen (red). NGC 6302 lies about 3,500 light-years away in the arachnologically correct constellation of the Scorpion (Scorpius). Planetary nebulas evolve from outer atmospheres of stars like our Sun, but usually fade in about 20,000 years.
20/11/2022
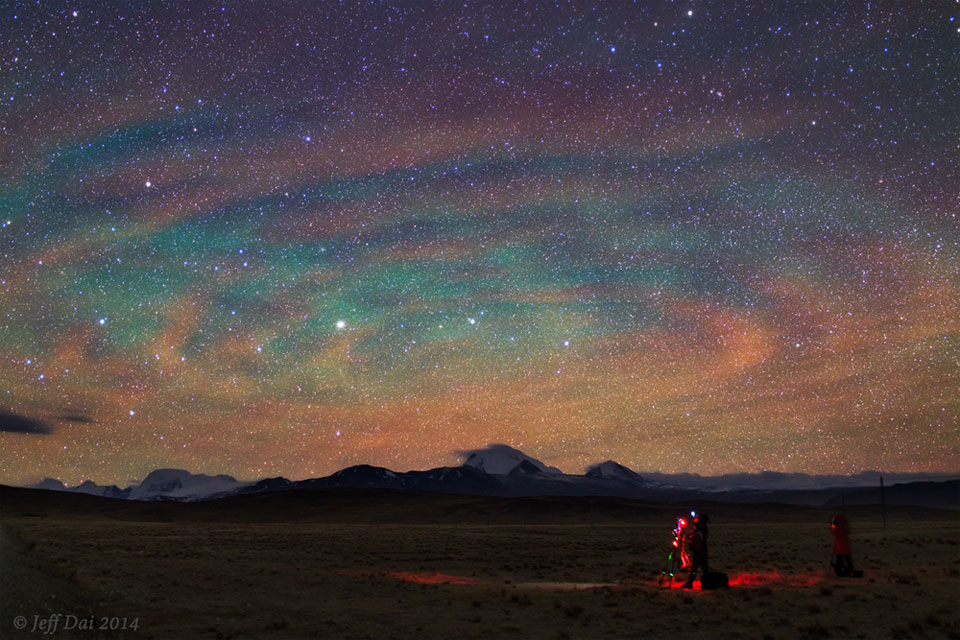
ASTRONOMY - Airglow Ripples over Tibet
2022 November 20
Image Credit & Copyright: Jeff Dai
Explanation: Why would the sky look like a giant target? Airglow. Following a giant thunderstorm over Bangladesh in late April, giant circular ripples of glowing air appeared over Tibet, China, as pictured here. The unusual pattern is created by atmospheric gravity waves, waves of alternating air pressure that can grow with height as the air thins, in this case about 90-kilometers up. Unlike auroras powered by collisions with energetic charged particles and seen at high latitudes, airglow is due to chemiluminescence, the production of light in a chemical reaction. More typically seen near the horizon, airglow keeps the night sky from ever being completely dark.
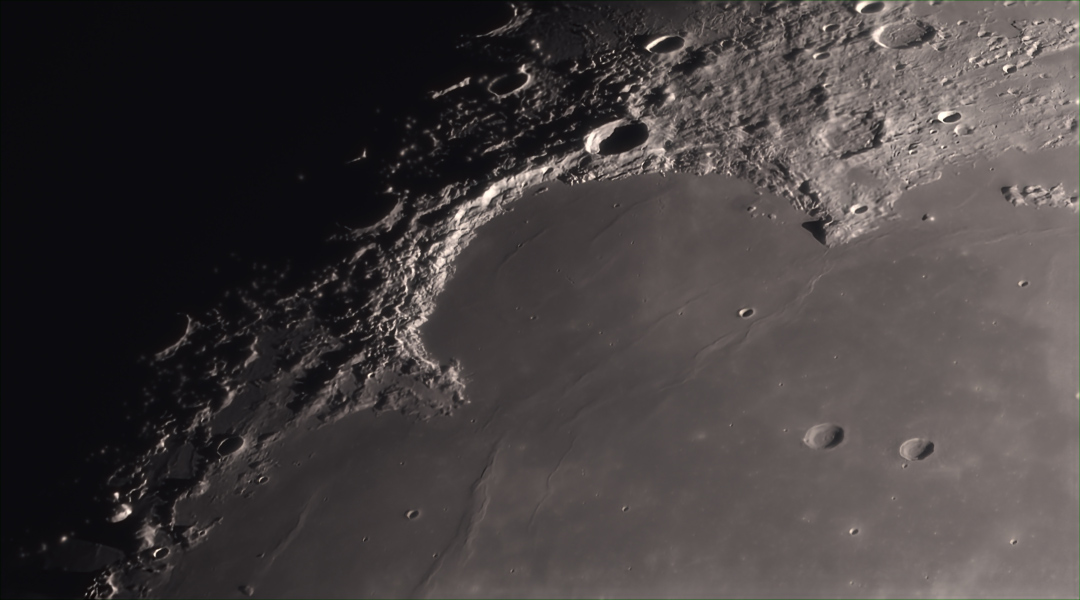
ASTRONOMY -The Bay of Rainbows
2026 February 12 The Bay of Rainbows Image Credit & Copyright : Olaf Filzinger Explanation: Dark, smooth regions that cover the Moon...

-
2022 September 26 All the Water on Planet Earth Illustration Credit: Jack Cook, Adam Nieman, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ; Data ...
-
2025 May 11 The Surface of Venus from Venera 14 Image Credit: Soviet Planetary Exploration Program , Venera 14 ; Processing & Copyri...