Nombre total de pages vues
31/01/2026
SANTé/MEDECINE - Tout savoir sur le coeur humain - 5 - Vue gauche du cœur : les structures internes
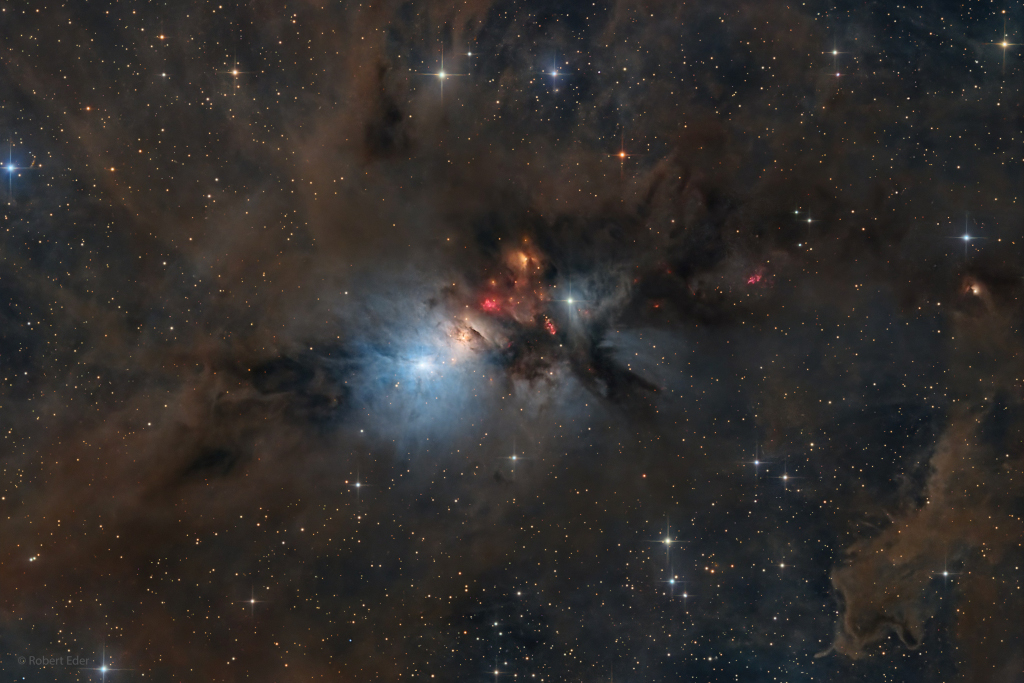
ASTRONOMY - NGC 1333: Stellar Nursery in Perseus
2026 January 30
Image Credit & Copyright: Robert Eder
Explanation: NGC 1333 is seen in visible light as a reflection nebula, dominated by bluish hues characteristic of starlight reflected by interstellar dust. A mere 1,000 light-years distant toward the heroic constellation Perseus, it lies at the edge of a large, star-forming molecular cloud. This telescopic close-up spans over two full moons on the sky or just over 15 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 1333. It shows details of the dusty region along with telltale hints of contrasty red emission from Herbig-Haro objects, jets and shocked glowing gas emanating from recently formed stars. In fact, NGC 1333 contains hundreds of stars less than a million years old, most still hidden from optical telescopes by the pervasive stardust. The chaotic environment may be similar to one in which our own Sun formed over 4.5 billion years ago.
29/01/2026
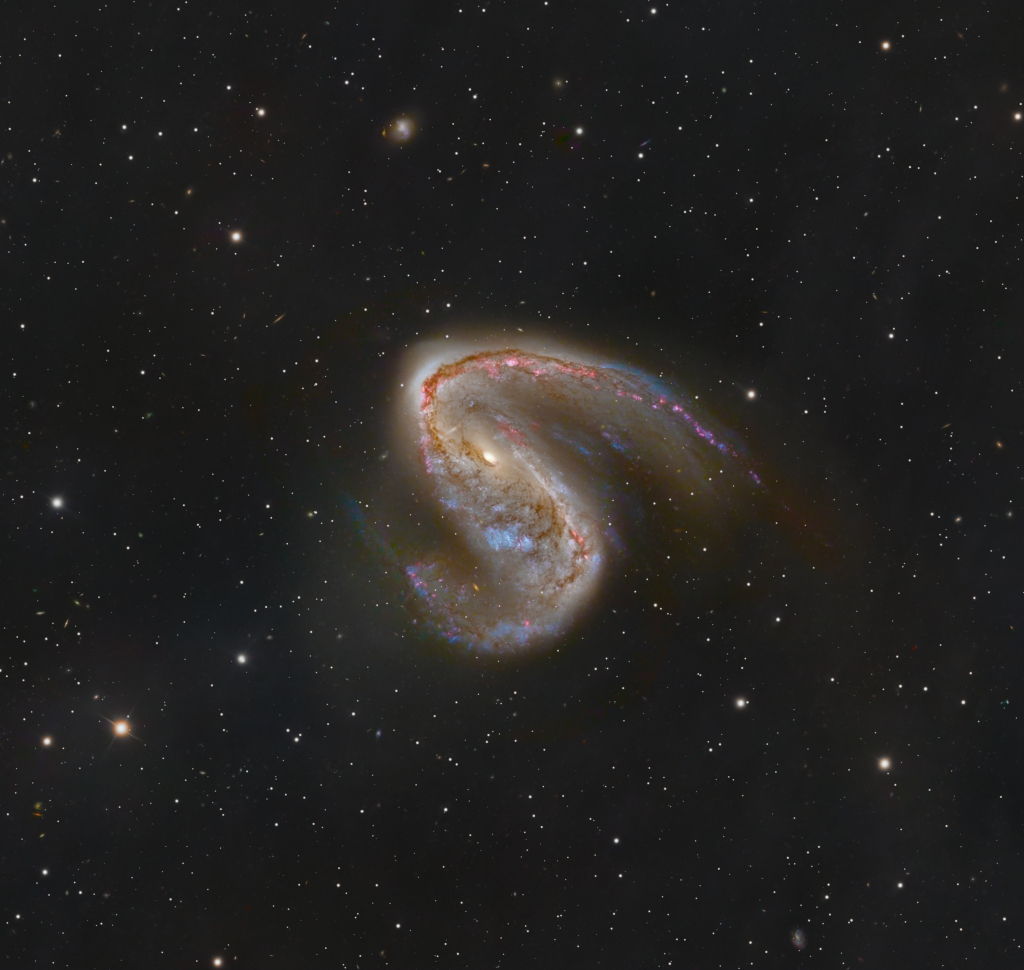
ASTRONOMY - NGC 2442: Galaxy in Volans
Image Credit & Copyright: Mike Selby
Explanation: Distorted galaxy NGC 2442 can be found in the southern constellation of the flying fish, (Piscis) Volans. Located about 50 million light-years away, the galaxy's two spiral arms extending from a pronounced central bar give it a hook-shaped appearance in this deep and colorful image, with foreground stars scattered across the telescopic field of view. The image also reveals the distant galaxy's obscuring dust lanes, young blue star clusters and reddish star forming regions surrounding a core of yellowish light from an older population of stars. But the star forming regions seem more concentrated along the drawn-out (upper right) spiral arm. The distorted structure is likely the result of an ancient close encounter with a smaller galaxy that lies off top left of the frame. This telescopic field of view spans over 200,000 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 2442.
28/01/2026
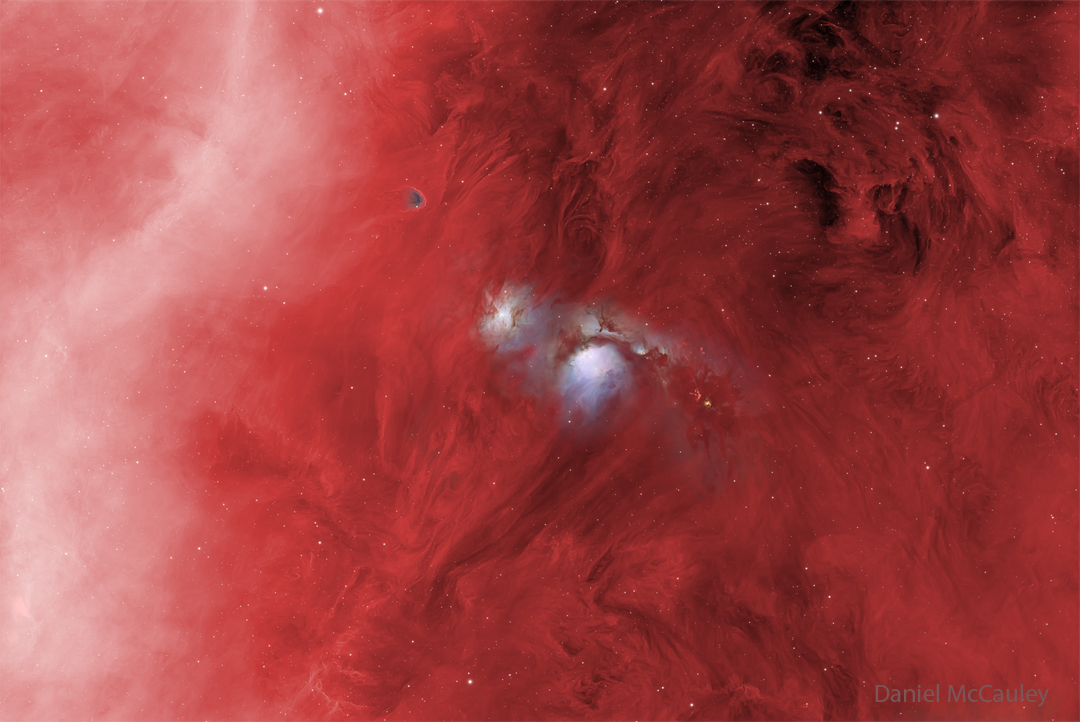
ASTRONOMY - M78: Reflecting Blue in a Sea of Red
2026 January 28
Image Credit & Copyright: Daniel McCauley
Explanation: In the vast Orion Molecular Cloud complex, several bright blue nebulas are particularly apparent. Pictured here in the center are two of the most prominent reflection nebulas - dust clouds lit by the reflecting light of bright embedded stars. The more famous nebula is M78, in the image center, cataloged over 200 years ago. To its upper left is the lesser known NGC 2071. Astronomers continue to study these reflection nebulas to better understand how interior stars form. The overall red glow is from diffuse hydrogen gas that covers much of the Orion complex that spans much of the constellation of Orion. Nearby in the greater complex, which lies about 1,500 light years away, are the Orion Nebula, the Horsehead Nebula, and Barnard's Loop -- partially seen here as the white band on the upper left.
27/01/2026
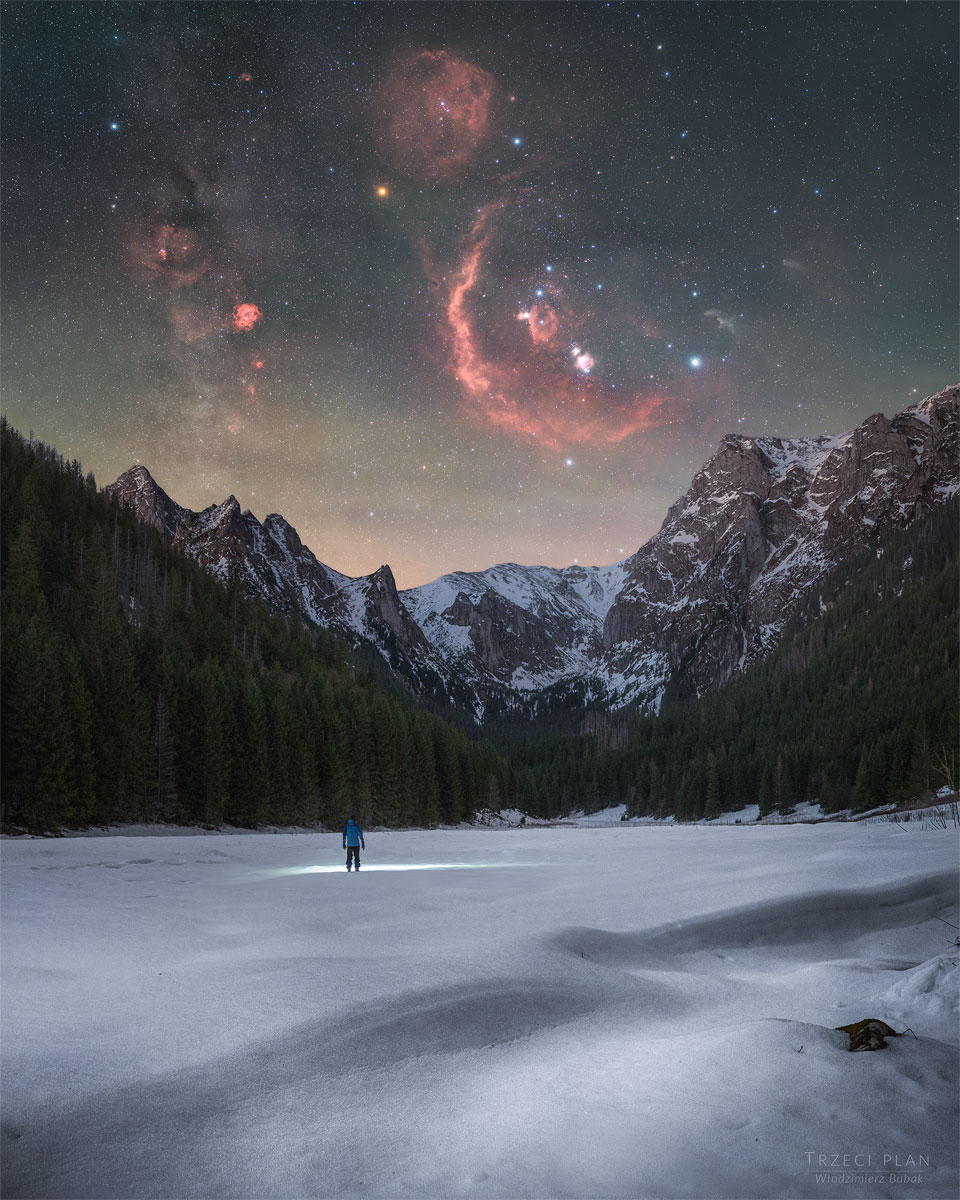
ASTRONOMY - Orion's Treasures over Snowy Mountains
2026 January 27
Image Credit & Copyright: Włodzimierz Bubak; Text: Ogetay Kayali (MTU)
Explanation: Rising over a frozen valley in the Tatra Mountains, the familiar stars and nebulas of Orion dominate this wide-field nightscape. The featured deep photo was taken in southern Poland's highest mountain range last month, where dark skies and alpine terrain combined to reveal both Earth's rugged beauty and the structure of our galaxy. Above the snowy mountains, Orion's bright belt stars anchor a region of glowing interstellar clouds. The Great Orion Nebula, a vast stellar nursery visible even to the unaided eye, shines near the center of the scene. Surrounding it is the enormous arc of Barnard's Loop, a faint shell of ionized hydrogen gas spanning much of the constellation. To the left, the round Rosette Nebula glows softly, while the grayish Witch Head Nebula hovers to the right, illuminated by nearby starlight. Near the top, the orange supergiant Betelgeuse marks the hunter's shoulder.
SANTé/MEDECINE - Tout savoir sur le coeur humain - 4 - Les valves
26/01/2026
LANGAGE - Quelle langue vivante ressemble le plus au latin ? 1/4
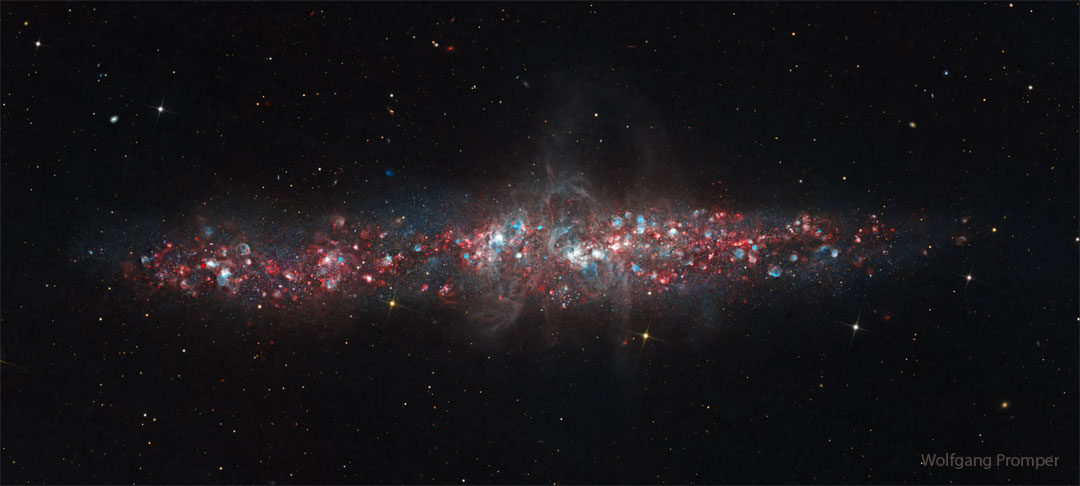
ASTRONOMY - NGC 55: A Galaxy of Nebulas
2026 January 26
Image Credit & Copyright: Wolfgang Promper; Text: Ogetay Kayali (MTU)
Explanation: Can you see nebulas in other galaxies? Yes, some nebulas shine brightly enough -- if you know how to look. Clouds of hydrogen and oxygen emit light at very specific colors, and by isolating them, astronomers and astrophotographers can reveal structures that would otherwise be too faint to notice. This deep, 50-hour exposure highlights glowing hydrogen (red) and oxygen (blue) across galaxy NGC 55, viewed nearly edge-on. Also known as the String of Pearls Galaxy, NGC 55 is often compared to our Milky Way's satellite galaxy the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), although NGC 55 lies much farther away at about 6.5 million light-years. The resulting image uncovers a sprinkling of emission nebulas within and sometimes above the galaxy's dusty disk, offering a detailed look at distant star-forming regions.
25/01/2026
SANTé/MEDECINE - Tout savoir sur le coeur humain - 3 - Coupe dans le ventricule gauche
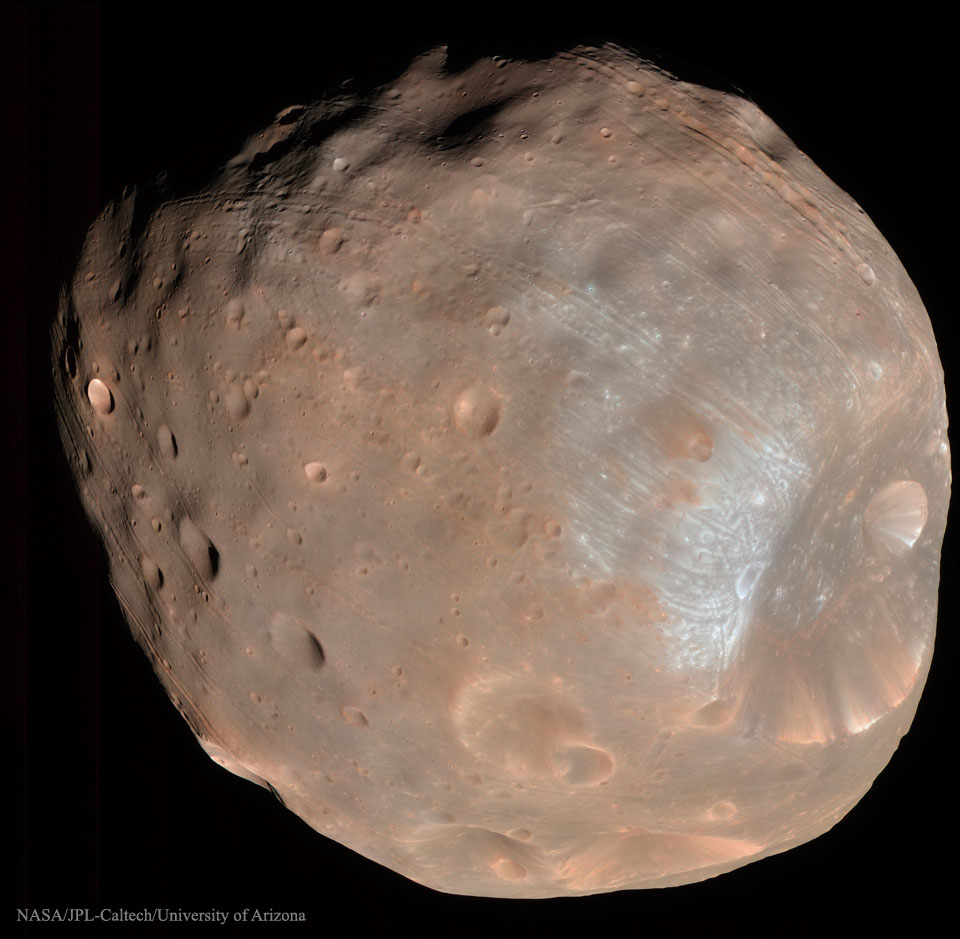
ASTRONOMY - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
2026 January 25
Image Credit: NASA, LPL (U. Arizona), MRO, HiRISE
Explanation: This moon is doomed. Mars, the red planet named for the Roman god of war, has two tiny moons, Phobos and Deimos, whose names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic. These Martian moons may well be captured asteroids originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter or perhaps from even more distant reaches of our Solar System. The larger moon, Phobos, is indeed seen to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this stunning color image from the robotic Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, which can image objects as small as 10 meters. But Phobos orbits so close to Mars - about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers for our Moon - that gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down. In perhaps 50 million years, Phobos is expected to disintegrate into a ring of debris.
Explication : Cette lune est condamnée. Mars , la planète rouge nommée d'après le dieu romain de la guerre , possède deux petites lunes, Phobos et Deimos , dont les noms dérivent du grec et signifient respectivement « peur » et « panique » . Ces lunes martiennes pourraient bien être des astéroïdes capturés , provenant de la ceinture d'astéroïdes principale située entre Mars et Jupiter , voire de régions encore plus éloignées de notre système solaire . Phobos , la plus grande lune , apparaît effectivement comme un objet cratérisé, semblable à un astéroïde, sur cette magnifique image en couleur prise par la sonde Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter , capable d'imager des objets aussi petits que 10 mètres. Mais Phobos orbite si près de Mars – à environ 5 800 kilomètres au-dessus de sa surface, contre 400 000 kilomètres pour notre Lune – que les forces de marée gravitationnelles l'attirent vers le bas. Dans environ 50 millions d'années, Phobos devrait se désintégrer en un anneau de débris.
24/01/2026
ASTRONOMY - Earthset from Orion
2026 January 24
Image Credit: NASA, Artemis 1
Explanation: Eight billion people are about to disappear in this snapshot from space taken on 2022 November 21. On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, their home world is setting behind the Moon's bright edge as viewed by an external camera on the outbound Orion spacecraft. Orion was headed for a powered flyby that took it to within 130 kilometers of the lunar surface. Velocity gained in the flyby maneuver was used to reach a distant retrograde orbit around the Moon. That orbit is considered distant because it's another 92,000 kilometers beyond the Moon, and retrograde because the spacecraft orbited in the opposite direction of the Moon's orbit around planet Earth. Swinging around the Moon, Orion reached a maximum distance (just over 400,000 kilometers) from Earth on 2022 November 28, exceeding a record set by Apollo 13 for most distant spacecraft designed for human space exploration. The Artemis II mission, carrying 4 astronauts around the moon and back again, is due to launch as early as February 6.
23/01/2026
SANTé/MEDECINE - Tout savoir sur le coeur humain - 2 - Anatomie du cœur humain
ASTRONOMY - Planetary Nebula Abell 7
2026 January 23
Image Credit & Copyright: Martin Pugh
Explanation: Very faint planetary nebula Abell 7 is about 1,800 light-years distant. It lies just south of Orion in planet Earth's skies toward the constellation Lepus, The Hare. Posing with scattered Milky Way stars, its generally simple spherical shape about 8 light-years in diameter is revealed in this deep telescopic image. The beautiful and complex shapes seen within the cosmic cloud are visually enhanced by the use of long exposures and narrowband filters that capture emission from hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Otherwise Abell 7 would be much too faint to be appreciated by eye. A planetary nebula represents a very brief final phase in stellar evolution that our own Sun will experience 5 billion years hence, as the nebula's central, once sun-like star shrugs off its outer layers. Abell 7 itself is estimated to be 20,000 years old. But its central star, seen here as a fading white dwarf, is some 10 billion years old.
22/01/2026
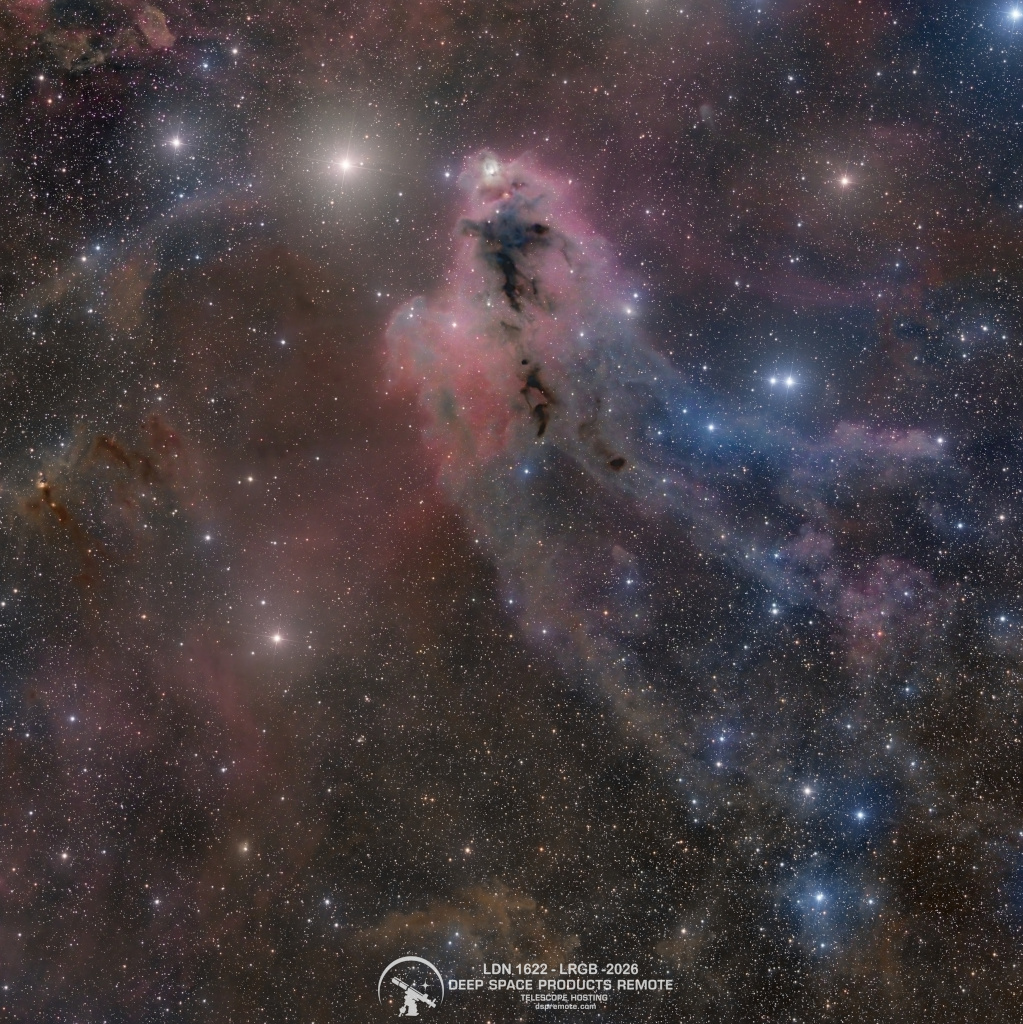
ASTRONOMY - LDN 1622: Dark Nebula in Orion
2026 January 22
Image Credit & Copyright: Chris Fellows
Explanation: The silhouette of an intriguing dark nebula inhabits this cosmic scene. Lynds' Dark Nebula (LDN) 1622 appears against a faint background of glowing hydrogen gas only visible in long telescopic exposures of the region. In contrast, a brighter reflection nebula, vdB 62, is more easily seen just above the dusty dark nebula. LDN 1622 lies near the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy, close on the sky to Barnard's Loop, a large cloud surrounding the rich complex of emission nebulae found in the Belt and Sword of Orion. With swept-back outlines, the obscuring dust of LDN 1622 is thought to lie at a similar distance, perhaps 1,500 light-years away. At that distance, this 3 degree wide field of view would span about 100 light-years. Young stars do lie hidden within the dark expanse and have been revealed in Spitzer Space telescope infrared images. Still, the foreboding visual appearance of LDN 1622 inspires its popular name, the Boogeyman Nebula.
21/01/2026
SANTé/MEDECINE - Tout savoir sur le coeur humain - 1
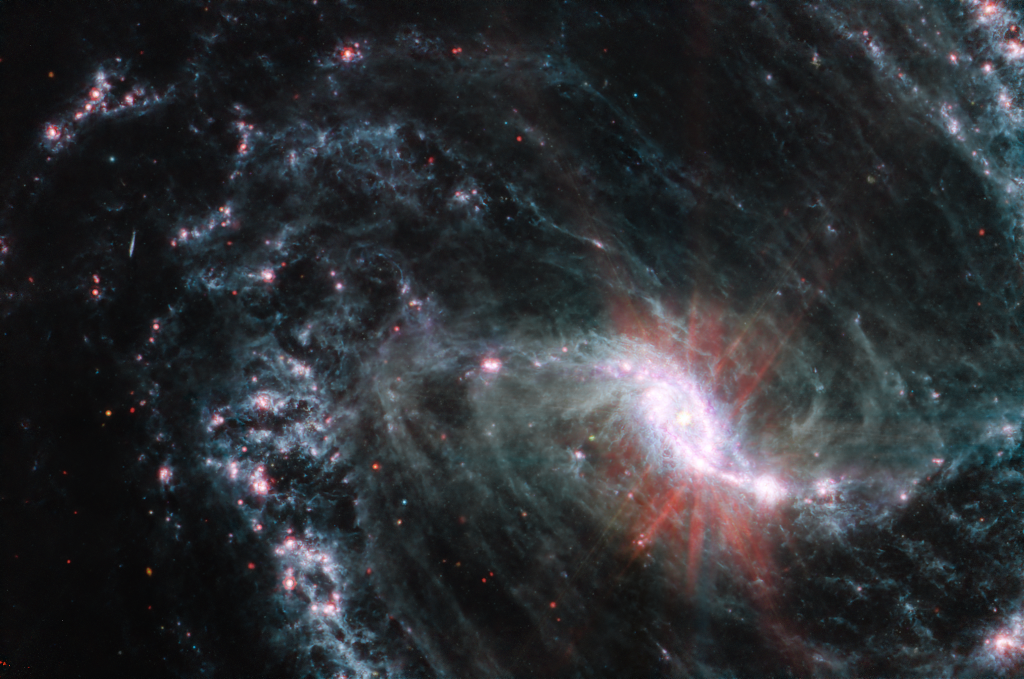
ASTRONOMY - Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1365 from Webb
2026 January 21
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Janice Lee (NOIRLab) - Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
Explanation: A mere 56 million light-years distant toward the southern constellation Fornax, NGC 1365 is an enormous barred spiral galaxy about 200,000 light-years in diameter. That's twice the size of our own barred spiral Milky Way. This sharp image from the James Webb Space Telescope's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) reveals stunning details of this magnificent spiral in infrared light. Webb's field of view stretches about 60,000 light-years across NGC 1365, exploring the galaxy's core and bright newborn star clusters. The intricate network of dusty filaments and bubbles is created by young stars along spiral arms winding from the galaxy's central bar. Astronomers suspect the gravitational field of NGC 1365's bar plays a crucial role in the galaxy's evolution, funneling gas and dust into a star-forming maelstrom and ultimately feeding material into the active galaxy's central, supermassive black hole.
20/01/2026
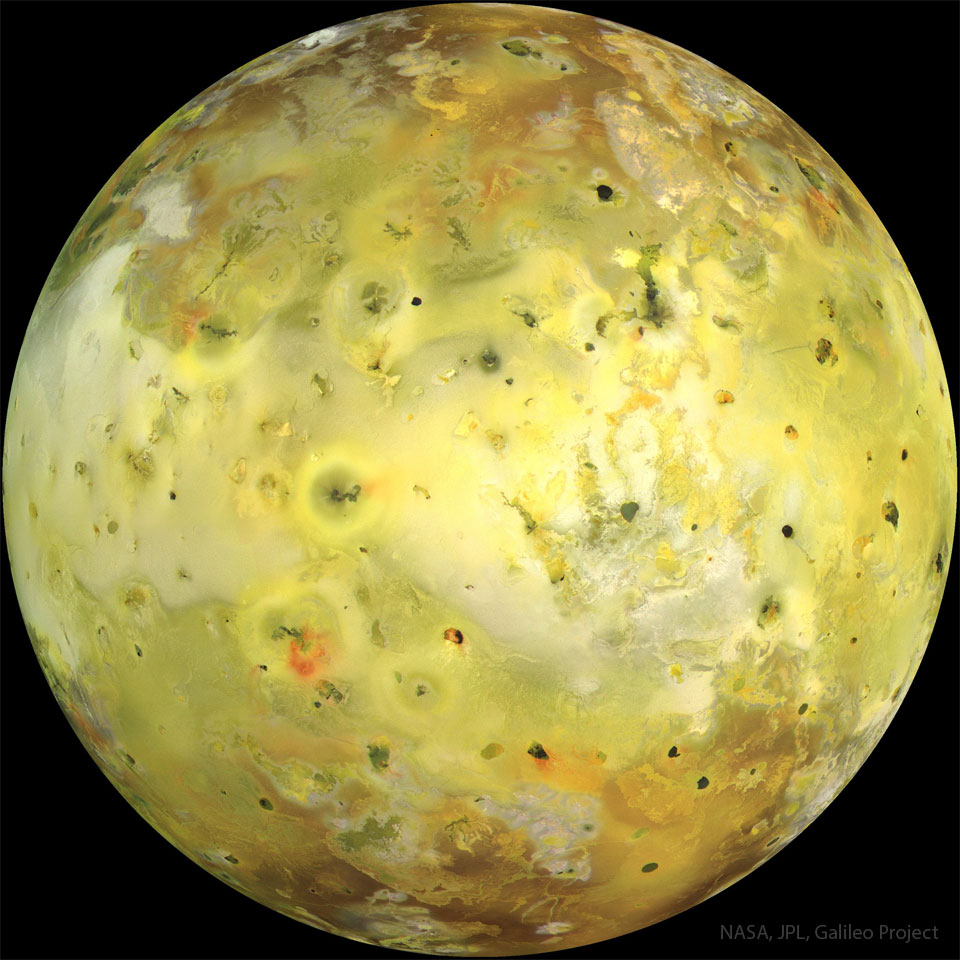
ASTRONOMY - Io in True Color
2026 January 20
Image Credit: NASA, JPL, Galileo Project
Explanation: The strangest moon in the Solar System is bright yellow. The featured picture, an attempt to show how Io would appear in the "true colors" perceptible to the average human eye, was taken in 1999 July by the Galileo spacecraft that orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003. Io's colors derive from sulfur and molten silicate rock. The unusual surface of Io is kept very young by its system of active volcanoes. The intense tidal gravity of Jupiter stretches Io and damps wobbles caused by Jupiter's other Galilean moons. The resulting friction greatly heats Io's interior, causing molten rock to explode through the surface. Io's volcanoes are so active that they are effectively turning the whole moon inside out. Some of Io's volcanic lava is so hot it glows in the dark.
19/01/2026
LES BELLES INVENTIONS DE LEONARD DE VINCI - La scie hydraulique et sa roue à godets
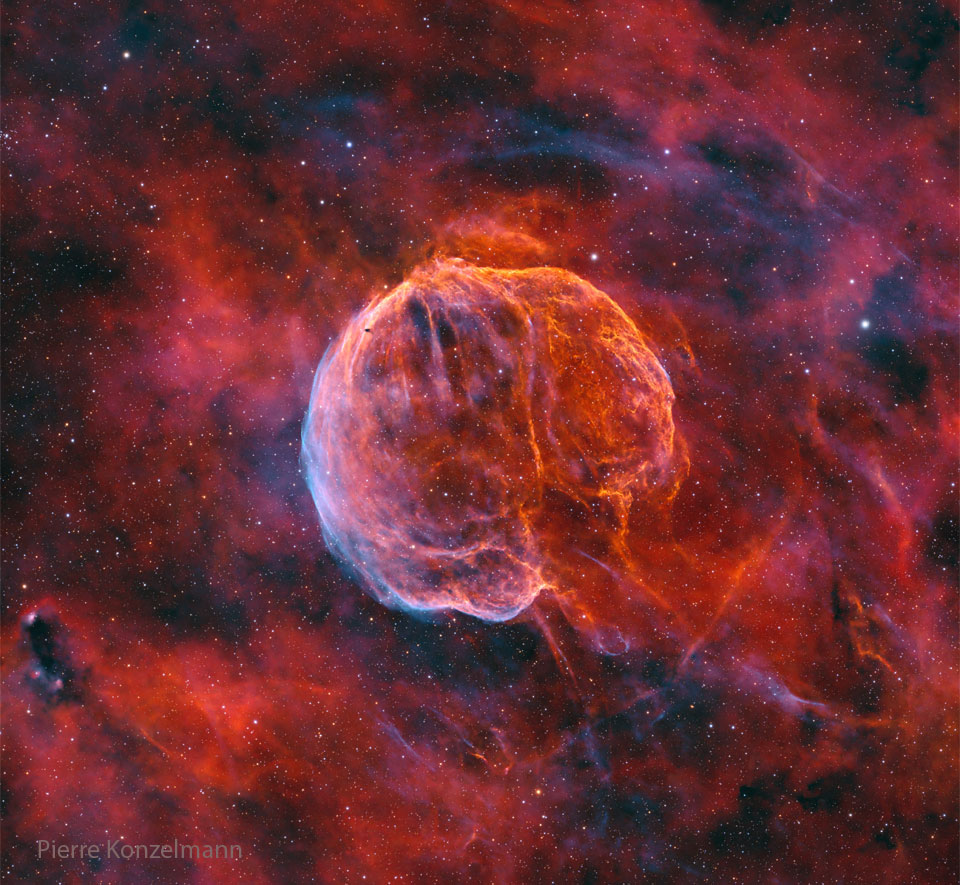
ASTRONOMY - CTB 1: The Medulla Nebula
2026 January 19
Image Credit: Pierre Konzelmann
Explanation: What powers this unusual nebula? CTB 1 is the expanding gas shell that was left when a massive star toward the constellation of Cassiopeia exploded about 10,000 years ago. The star likely detonated when it ran out of elements, near its core, that could create stabilizing pressure with nuclear fusion. The resulting supernova remnant, nicknamed the Medulla Nebula for its brain-like shape, still glows in visible light because of the heat generated by its collision with confining interstellar gas. Why the nebula also glows in X-ray light, though, remains a topic of research. One hypothesis holds that an energetic pulsar was created and powers the nebula with a fast outwardly moving wind. Following this lead, a pulsar was found in radio waves that appears to have been expelled by the supernova explosion at over 1000 kilometers per second. Although the Medulla Nebula appears as large as a full moon, it is so faint that it took 84-hours of exposure with a small telescope in Texas, USA, to create the featured image.
18/01/2026
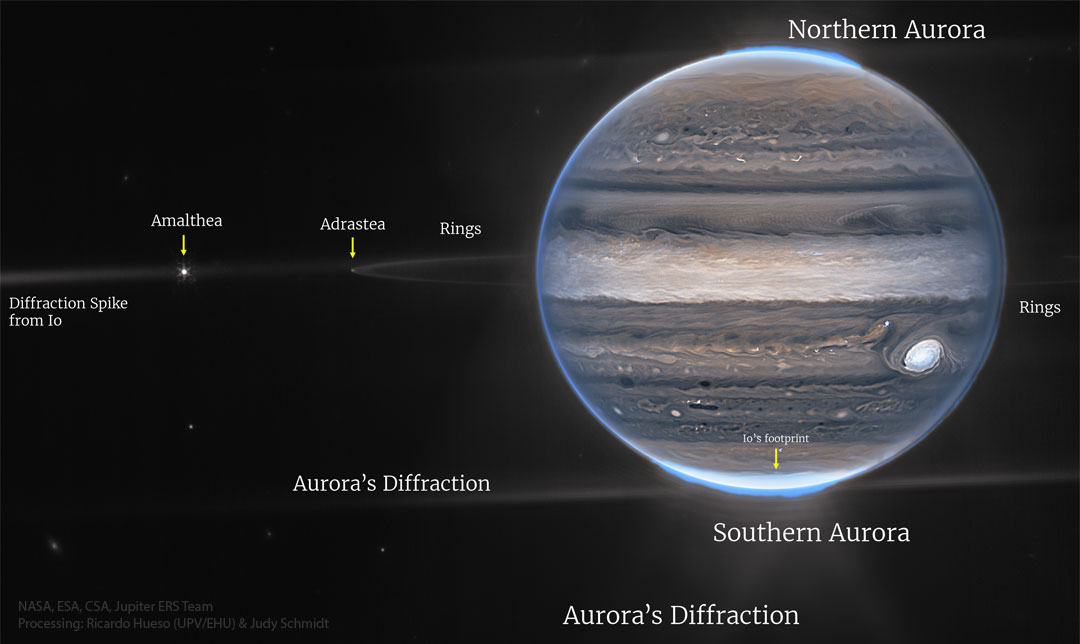
ASTRONOMY - Jupiter from the Webb Space Telescope
2026 January 18
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Jupiter ERS Team; Processing: Ricardo Hueso (UPV/EHU) & Judy Schmidt
Explanation: This infrared view of Jupiter by Webb is illuminating. High-resolution infrared images of Jupiter from the James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) reveal, for example, differences between high-floating bright clouds -- including the Great Red Spot -- and low-lying dark clouds. Also clearly visible in the featured Webb image are Jupiter's dust ring, bright auroras at the poles, and Jupiter's moons Amalthea and Adrastea. The footprint of large volcanic moon Io's magnetic funneling of charged particles onto Jupiter is also visible in the southern aurora. Some objects are so bright that light noticeably diffracts around Webb's optics creating streaks. Webb, which orbits the Sun near the Earth, has a mirror over six meters across making it the largest astronomical telescope ever launched -- with over six times more light-collecting area than Hubble.
17/01/2026
MICROPHOTOGRAPHIE - La clé de voûte de la propreté des abeilles
ASTRONOMY - Apollo 14: A View from Antares
2026 January 17
Image Credit: Edgar Mitchell, Apollo 14, NASA; Mosaic - Eric M. Jones
Explanation: Apollo 14's Lunar Module Antares landed on the Moon on February 5, 1971. Toward the end of the stay astronaut Ed Mitchell snapped a series of photos of the lunar surface while looking out a window, assembled into this detailed mosaic by Apollo Lunar Surface Journal editor Eric Jones. The view looks across the Fra Mauro highlands to the northwest of the landing site after the Apollo 14 astronauts had completed their second and final walk on the Moon. Prominent in the foreground is their Modular Equipment Transporter, a two-wheeled, rickshaw-like device used to carry tools and samples. Near the horizon at top center is a 1.5 meter wide boulder dubbed Turtle rock. In the shallow crater below Turtle rock is the long white handle of a sampling instrument, thrown there javelin-style by Mitchell. Mitchell's fellow moonwalker and first American in space, Alan Shepard, also used a makeshift six iron to hit two golf balls. One of Shepard's golf balls is just visible as a white spot below Mitchell's javelin.
16/01/2026
ASTRONOMY - NGC 7023: The Iris Nebula
2026 January 16
Image Credit & Copyright: Justus Falk
Explanation: These cosmic clouds have blossomed 1,300 light-years away in the fertile starfields of the constellation Cepheus. Called the Iris Nebula, NGC 7023 is not the only nebula to evoke the imagery of flowers. Still, this deep telescopic image shows off the Iris Nebula's range of colors and symmetries embedded in surrounding fields of interstellar dust. Within the Iris itself, dusty nebular material surrounds a hot, young star. The dominant color of the brighter reflection nebula is blue, characteristic of dust grains reflecting starlight. Central filaments of the reflection nebula glow with a faint reddish photoluminescence as some dust grains effectively convert the star's invisible ultraviolet radiation to visible red light. Infrared observations indicate that this nebula contains complex carbon molecules known as PAHs. The dusty blue petals of the Iris Nebula span about six light-years.
15/01/2026
ASTRONOMY - Plato and the Lunar Alps
2026 January 15
Image Credit & Copyright: Luigi Morrone
Explanation: The dark-floored, 95 kilometer wide crater Plato and sunlit peaks of the lunar Alps (Montes Alpes) are highlighted in this this sharp telescopic snapshot of the Moon's surface. While the Alps of planet Earth were uplifted over millions of years as continental plates slowly collided, the lunar Alps were likely formed by a sudden collision that created the giant impact basin known as the Mare Imbrium or Sea of Rains. The mare's generally smooth, lava-flooded floor is seen below the bordering mountain range. The prominent straight feature cutting through the mountains is the lunar Alpine Valley (Vallis Alpes). Joining the Mare Imbrium and northern Mare Frigoris (Sea of Cold) the valley extends toward the upper right, about 160 kilometers long and up to 10 kilometers wide. Of course, the large, bright lunar alpine mountain below and right of Plato crater is named Mont Blanc. Lacking an atmosphere, not to mention snow, the lunar Alps are probably not an ideal location for a winter vacation. Still, a 150 pound skier would weigh a mere 25 pounds on the Moon.
14/01/2026
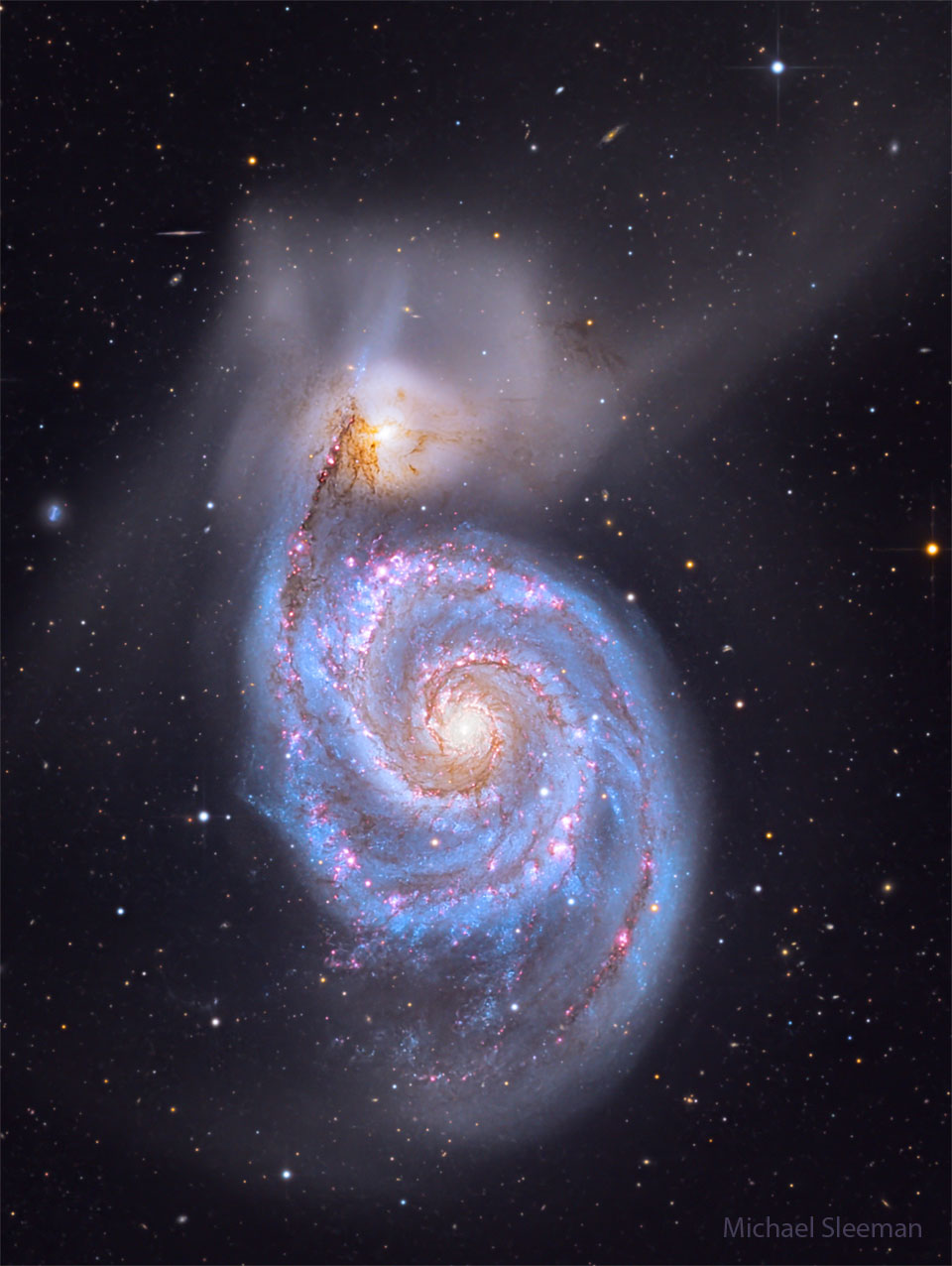
ASTRONOMY - M51: The Whirlpool Galaxy
2026 January 14
Image Credit & Copyright: Michael Sleeman
Explanation: The Whirlpool Galaxy is a classic spiral galaxy. At only 30 million light years distant and fully 60 thousand light years across, M51, also known as NGC 5194, is one of the brightest and most picturesque galaxies on the sky. The featured deep image is a digital combination of images taken in different colors over 58 hours with a telescope from Lijiang, China. Anyone with a good pair of binoculars, however, can see this Whirlpool toward the constellation of the Hunting Dogs (Canes Venatici). M51 is a spiral galaxy of type Sc and is the dominant member of a whole group of galaxies. Astronomers speculate that M51's spiral structure is primarily due to its gravitational interaction with the smaller galaxy just above it.
13/01/2026
LES BELLES INVENTIONS DE LEONARD DE VINCI - L'Homme de Vitruve - le compas et les proportions
ASTRONOMY - A Solar Eruption from SDO
2026 January 13
Video Credit: NASA, SDO, AIA, Helioviewer; Processing & Text: Ogetay Kayali (MTU)
Explanation: What just leapt from the Sun? A towering structure of solar plasma suddenly rose from the Sun's surface and unfurled into space -- a structure so large that many Earths would easily fit within it-- marking the onset of a dramatic Coronal Mass Ejection (CME). The event was captured in striking detail in late 2024 by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), whose continuous monitoring improves space weather forecasts and helps humanity better understand how solar activity affects satellites, GPS, radio communications, and power grids on Earth. The featured video blends three extreme-ultraviolet views from SDO’s Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA), revealing how plasma at different temperatures surged upward as the eruption unfolded. Here, red highlights cooler, denser material lifted from the Sun’s lower atmosphere, while yellow traces hotter, million-degree coronal loops stretching outward as magnetic fields open. After the main outburst, the Sun’s magnetic fields quickly reorganize.
12/01/2026
ASTRONOMY - Meteor Dust
Image Credit & Copyright: Xu Chen
Explanation: What's happening to this meteor? It is shedding its outer layers as it passes through the Earth's atmosphere and heats up. The sudden high temperatures not only cause the bright glow along the dramatic streak but also melt and vaporize the meteor's component rock and ice, creating dust. Wind in the atmosphere typically blows this dust away over the next few seconds, leaving no visible trace after only a few minutes. Much of this dust will eventually settle down to the Earth. The featured image was captured in mid-December, coincident with the Geminids meteor shower. On the upper left is Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, while in the foreground is fog-engulfed Huangshan, the Yellow Mountains of eastern China.
11/01/2026
MICROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Quand le micromonde s’autoassemble
NUCLEAIRE/RADIOACTIVITé - Le kit de survie anti-nucléaire après un impact de bombe
10/01/2026
MICROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Une amibe dans sa coquille
ASTRONOMY - Jupiter with the Great Red Spot
2026 January 10
Image Credit & Copyright: Christopher Go
Explanation: Jupiter reaches its 2026 opposition today, January 10. That puts our Solar System's most massive planet opposite the Sun and near its closest and brightest for viewing from planet Earth. In fact, captured only 3 days ago this sharp telescopic snapshot reveals excellent details of the ruling gas giant's swirling cloudtops, in light zones and dark belts girdling the rapidly rotating outer planet. Jupiter's famous, persistent anticyclonic vortex, known as the Great Red Spot, is south of the equator at the lower right. But two smaller red spots are also visible, one near the top in the northernmost zone, and one close to Jupiter's south pole. And while Jupiter's Great Red Spot is known to be shrinking, it's still about the size of the Earth itself.
09/01/2026
MICROPHOTOGRAPHIE - Zoom sur une abeille mellifère
ASTRONOMY - Ice Halos by Moonlight and Sunlight
2026 January 9
Image Credit & Copyright: Antonella Cicala
Explanation: Both Moon and Sun create beautiful ice halos in planet Earth's sky. In fact, the two brightest celestial beacons are each surrounded by a complex of ice halos in these photos of the sky above Chamonix-Mont-Blanc in France. The panels were recorded one night (left) and the following day at the end of December 2025. Similar ice halos appear in moonlight and sunlight because they are all formed through the geometry of flat, hexagonal ice crystals. The ice crystals reflect and refract light as they flutter in the cold atmosphere above the mountain resort. In the pictures both Moon and Sun are surrounded by a more commonly seen 22 degree circular halo. Bright and sometimes colorful patches at the intersections of the 22 degree circular halos with the indicated parselenic and parhelic arcs are also known as Moon dogs and Sun dogs.
08/01/2026
ASTRONOMIE - NGC2392 - la nébuleuse de l’Esquimau
|
ASTRONOMY - IC 342: Hidden Galaxy in Camelopardalis
2026 January 8
Image Credit & Copyright: Gaetan Maxant
Explanation: Similar in size to large, bright spiral galaxies in our neighborhood, IC 342 is a mere 10 million light-years distant toward the long-necked, northern constellation Camelopardalis. A sprawling island universe, IC 342 would otherwise be a prominent galaxy in our night sky, but it is hidden from clear view and only glimpsed through the veil of stars, gas and dust clouds along the plane of our own Milky Way galaxy. Even though IC 342's light is dimmed and reddened by intervening cosmic clouds, this sharp telescopic image traces the galaxy's own obscuring dust, young star clusters, and glowing star forming regions along spiral arms that wind far from the galaxy's core. IC 342 has undergone a recent burst of star formation activity and is close enough to have influenced the evolution of the local group of galaxies and the Milky Way.
Les belles inventions de Leonard de Vinci - LE BATEAU A AUBES
Léonard de Vinci n'est pas l'inventeur du concept du bateau à aubes : on le trouve déjà dans les œuvres de l'ingénieur et arch...

-
2025 May 11 The Surface of Venus from Venera 14 Image Credit: Soviet Planetary Exploration Program , Venera 14 ; Processing & Copyri...
-
2025 April 14 The Galactic Center in Radio from MeerKAT Image Credit: NASA , ESA , CSA , STScI , SARAO , S. Crowe ( UVA ), J. Bally ...